- Gorgopotamos
-
Gorgopotamos
Γοργοπόταμος
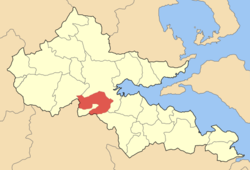
The rail bridge of Gorgopotamos that was blown up by the Greek Resistance during WWII.Location Coordinates 38°50′N 22°24′E / 38.833°N 22.4°ECoordinates: 38°50′N 22°24′E / 38.833°N 22.4°E Government Country: Greece Region: Central Greece Regional unit: Phthiotis Municipality: Lamia Population statistics (as of 2001) Municipal unit - Population: 4,510 - Area: 157.3 km2 (61 sq mi) - Density: 29 /km2 (74 /sq mi) Other Time zone: EET/EEST (UTC+2/3) Postal: 360 00 Auto: ΜΙ Website dimosgorgopotamou.gr Gorgopotamos (Greek: Γοργοπόταμος) is a village and a former municipality in Phthiotis, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lamia, of which it is a municipal unit.[1] It is located 10 km southwest of Lamia. Its 2001 population was 443 for the village and 4,510 for the municipal unit. The seat of the municipality was in Moschochori. It is named after the Gorgopotamos river which flows nearby (its name means in Greek "the rushing river"). The Oiti mountains and the Oiti National Park lie to the southwest. The municipal unit of Gorgopotamos borders Lamia to the north and Phocis to the southwest.
Contents
Subdivisions
- Gorgopotamos
- Damasta (Ano Damasta, Kato Damasta, Chalvantzaiika)
- Delfino
- Dyo Vouna
- Eleftherochori
- Irakleia
- Koumaritsi
- Moschochori
- Neo Krikello
- Oiti (Oiti, Skamnos)
- Vardates (Ano Vardates)
Population
Year Population village Municipal district population Municipality population 1981 332 - - 1991 429 - 4,401 2001 443 472 4,510 Location
Gorgopotamos is located 225 km NNW of Athens, south of Larissa, southwest of Volos, north of Amfissa and east of Karpenissi.
Geography
The geography varies heavily, with marshes and farmlands to the east and more farmlands in the valley areas, hills to the center, forests up to 1,500 m and grasslands higher.
Features
The village of Gorgopotamos has a school, a lyceum (middle school), a gymnasium (secondary school), a church, a post office, a train station and a square (plateia). Gorgopotamos featured a watermill and electricity as well as an acetyl plant between 1907 and 1945.
At the elevation of 800 m, Kangelogefirou features several stone bridges and waterfalls.
At the slope of Kallidromo is the village of Eleftherochori situated at 800 m above sea level, with many pine trees and a view of the Malian Gulf.
The village of Pavliani, built at the slops of mountain Oitis, features the Heraklia castle and is near the highest mountain bridge in Greece.
The village of Damasta features the natural spring known as Psoroneri.
The river of Gorgopotamos is host to the Ellinopygosteos fish (Pungitius hellenicus).
History
The name of Gorgopotamos became famous during World War II, when 150 Greek partisans, following plans drawn by E. C. W. "Eddie" Myers and assisted by a group of British SOE officers, which included C.M. Woodhouse, blew up the railroad bridge over the Gorgopotamos river on November 25, 1942 as part of "Operation Harling" and cut off the enemy-controlled route between Thessaloniki and Athens.[2] The blast ruined two of the six poles of the bridge. In an act of reprisals, the German occupation forces executed 16 Greek locals. The area around the bridge has been designated a national monument.[3]
After World War II and the Greek Civil War, the bridge of Gorgopotamos was partially rebuilt, the poles being replaced with steel girders. Minor improvements in local condition would not inhibit emigration of the population after the war.
Gorgopotamos was eventually connected with the asphalt-paved road network in the 1960s. Electricity, radio and automobiles were introduced in the 1950s, television in the l970s and computer and internet at the turn of the century. The municipality was officially established in the late-1990s. In the 1990s, Pedini increased significantly in population, as it became a place of tourist attraction.
Politics
The mayor of the municipality is currently Panagiotis Spathoulas.[4]
References
- ^ Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (Greek)
- ^ Operation Harling: Destruction of the Gorgopotamos Rail Bridge, 1942
- ^ Village history, in Greek
- ^ Local government data, in Greek
External links
Categories:- Populated places in Phthiotis
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.