- Coma (optics)
-
Optical aberration  Distortion
Distortion
 Spherical aberration
Spherical aberration
 Coma
Coma
 Astigmatism
Astigmatism
 Petzval field curvature
Petzval field curvature
 Chromatic aberration
Chromatic aberration
Defocus
Piston
Tilt Example of coma and chromatic aberration
Example of coma and chromatic aberration
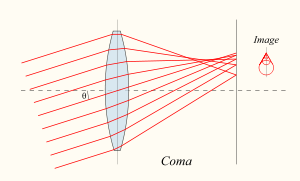
In optics (especially telescopes), the coma (aka comatic aberration) in an optical system refers to aberration inherent to certain optical designs or due to imperfection in the lens or other components which results in off-axis point sources such as stars appearing distorted, appearing to have a tail (coma) like a comet. Specifically, coma is defined as a variation in magnification over the entrance pupil. In refractive or diffractive optical systems, especially those imaging a wide spectral range, coma can be a function of wavelength, in which case it is a form of chromatic aberration.
Coma is an inherent property of telescopes using parabolic mirrors. Light from a point source (such as a star) in the center of the field is perfectly focused at the focal point of the mirror (unlike a spherical mirror, where light from the outer part of the mirror focuses closer to the mirror than light from the center--spherical aberration). However, when the light source is off-center (off-axis), the different parts of the mirror do not reflect the light to the same point. This results in a point of light that is not in the center of the field looking wedge-shaped. The further off-axis, the worse this effect is. This causes stars to appear to have a cometary coma, hence the name.
Schemes to reduce spherical aberration without introducing coma include Schmidt, Maksutov, ACF and Ritchey-Chrétien optical systems. Correction lenses for Newtonian reflectors have been designed which reduce coma in telescopes below f/6. These work by means of a dual lens system of a plano-convex and a plano-concave lens fitted into an eyepiece adaptor which superficially resembles a Barlow lens. [1][2]
Coma of a single lens or a system of lenses can be minimized (and in some cases eliminated) by choosing the curvature of the lens surfaces to match the application. Lenses in which both spherical aberration and coma are minimized at a single wavelength are called bestform or aplanatic or aspheric lenses.
Vertical coma is the most common higher-order aberration in the eyes of patients with keratoconus.[3]
See also
- Aberration in optical systems
References
- ^ US a coma-correcting meniscus lens 4571036, Gebelein, Rolin J. & David Shafer, "Reflecting telescope with correcting lens", published 02/18/1986
- ^ Knisely, David (2004). "Tele Vue Paracor Coma Corrector for Newtonians" (pdf). Cloudy Nights Telescope Review. http://www.cloudynights.com/documents/paracorr.pdf. Retrieved 29 November, 2010.
- ^ Pantanelli S, MacRae S, Jeong TM, Yoon G (November 2007). "Characterizing the wave aberration in eyes with keratoconus or penetrating keratoplasty using a high-dynamic range wavefront sensor". Ophthalmology 114 (11): 2013–21. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.01.008. PMID 17553566. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0161-6420(07)00072-3.
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.