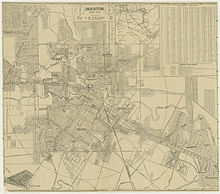
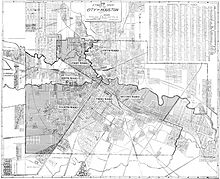
- The six wards of Houston
-
When the city of Houston was founded in 1836 and incorporated in 1837, its founders—John Kirby Allen and Augustus Chapman Allen—divided it into political geographic districts called "wards." The ward system, a precursor to today's City Council districts, was a common political tool of the early 19th century, and is still used in some American cities. When the system was at its peak, the city had six wards, from the first to the sixth.[1]
Contents
History of wards
In 1840, the Republic of Texas altered the city charter for Houston, dividing it into four wards. Historically the wards reflected geographic boundaries, without consideration of the population density within the wards.[2] The voting population of the wards was lower than the population, since women and African-Americans had been forbidden from voting. Instead, wards followed boundaries of features such as the Buffalo Bayou, Congress Street, and Main Street. Each ward elected two aldermen to the Houston City Council. The election of the Mayor of Houston was citywide.[3] Betty Chapman, a historian, said "They really were mixed societies in the early days. Where you worked dictated where you lived, not who you wanted to live around."[2]
The ward boundaries touched each other at the intersection of Congress Street and Main Street. The first ward was northwest of that intersection. The ward housed the city's market house and produce industry facilities. The second ward was located to the northeast. The courthouse and the heavy warehouses were located there. Therefore many lawyers and merchants resided there. The third was situated to the southeast. Businesspeople, craftsmen, and professionals lived there. The Third Ward had fancier houses than other wards. The fourth ward was southwest of the intersection. That ward included what was then the central portion of the city. Freed slaves developed Freedmen's Town in a 5 square miles (13 km2) area in the Fourth Ward.[2]
By December 1866 the Fifth Ward had been created, with two aldermen elected from that area during that month. The Fifth Ward was added in 1866 to accommodate the city's growth, and by the Sixth Ward in the following decade. Buffalo Bayou served as the ward's southern border, while the White Oak Bayou served as the ward's western border.[2] The idea was not to have an equal number of residents in each but rather to draw lines along natural boundaries: Buffalo Bayou, Main Street, and Congress Street.[citation needed] In 1876 the city created the Sixth ward. It was bounded by the First Ward's southwest boundary and the Buffalo Bayou.[2]
The City of Houston abolished the ward system in the early 1900s.[4] In 1902, at the beginning of O.T. Hold's term as Mayor of Houston, the city's financial records were in poor shape, and independent auditors found that the city's coffers had a shortage of over $54,000 for the period 1899 to 1902. A 1975 Houston Post article said that the corruption that had been discovered lead voters to politically neuter the wards via en election on December 10, 1904. The city of Houston changed to a commission form of government. In November 1915 a newly-passed city ordinance officially abolished the wards.[2] On city maps, the wards continued to be used as geographic reference points until 1928. After 1928 other landmarks such as Memorial Park and River Oaks appeared in place of the wards as reference points.[3]
While the wards no longer exist legally, area residents still identify certain communities, especially that have been a part of the city since incorporation, as being "wards" of the city. The ward identification appears on signage and in casual conversation from Houstonians. The areas referred to as the wards as of 2004 are not exactly the same as the ones that were legally the wards until abolition. Will Howard, an assistant manager of the Texas and local history department of the Houston Public Library, said during that year "They are cultural entities today, not legal entities, and like any culture, they are almost obligated to change."[3]
First Ward
Main article: First Ward, HoustonSecond Ward
Main article: Second Ward, HoustonThird Ward
Main article: Third Ward, HoustonFourth Ward
Main article: Fourth Ward, HoustonFifth Ward
Main article: Fifth Ward, HoustonSixth Ward
Main article: Sixth Ward, HoustonReferences
- ^ "map0435.jpg." Texas State Library and Archives Commission. Retrieved on April 5, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f "Looking back wards." City Savvy Online (City of Houston). (northern hemisphere) Winter 2008. Retrieved on October 20, 2011.
- ^ a b c Kever, Jeannie. "Pride lives on in city's six historical wards." Houston Chronicle. September 7, 2004. Retrieved on October 20, 2011.
- ^ Wood, Roger. Down in Houston: Bayou City Blues. 2003, University of Texas Press. 1st Edition. 72.
External links
- Where the Wards are. Houston Chronicle. September 7, 2004. Last accessed November 19, 2006.
- Super Neighborhood # 63 Second Ward. Officially Recognized Super Neighborhood Councils, City of Houston. Last accessed November 19, 2006.
- About TSU > Community > Third Ward. Texas Southern University. Last accessed November 19, 2006.
- Super Neighborhood #67 Greater Third Ward
- Future development eyed for Lower Fifth Ward Houston Chronicle February 6, 2008
- Sixth Ward, Houston from the Handbook of Texas Online
- Fifth Ward Community Website
- First Ward Neighborhood Portrait
- OSWNA OSW Neighborhood Assoc.
- Sixth Ward
 City of HoustonNickname: Space City
City of HoustonNickname: Space CityTopics History | Geography | Climate | Politics | Mayors | Economy | Demographics | Culture | Architecture | Transportation | Education | Nicknames | Sister cities
Attractions Theater District | Bayou Place | Museum District | Houston Zoo | Hermann Park | Space Center Houston | the Galleria | Waterwall Park | Memorial Park | Discovery Green | Lee and Joe Jamail Skatepark | University of Houston
Business Districts Downtown | Uptown | Texas Medical Center | Greenway Plaza | Energy Corridor | Westchase | Memorial City | Greenspoint
See also: List of companies in HoustonCommunities Acres Homes | Addicks | Alief | Almeda | Bordersville | Boulevard Oaks | Braeburn | Braeswood Place | Brays Oaks | Blue Ridge | Chinatown | Clear Lake City | Denver Harbor | East Downtown | East End | East Houston | Genoa | Glenbrook Valley | Greater Sharpstown | Gulfton | Harrisburg | Hiram Clarke | Houston Heights | Independence Heights | Inwood Forest | Kingwood | Magnolia Park | Maplewood | Meyerland | Midtown | Montrose District | Museum District | Neartown | Near Northwest | North Shore | Northside | Oak Forest | River Oaks | Riverside Terrace | South Park | Spring Branch | Sunnyside | Upper Kirby
Historic wards: First Ward | Second Ward | Third Ward | Fourth Ward | Fifth Ward | Sixth Ward
See also: The six wards of HoustonNeighborhoods Afton Oaks | Brentwood | Briargrove Park | City Park | Clinton Park | Cloverland | Corinthian Pointe | Crestwood | Eastwood | Garden Oaks | Highland Village | Houston Gardens | Idylwood | Kashmere Gardens | Larchmont | Magnolia Grove | Montrose | Morningside Place | Near North Side | Nottingham Forest | Old Braeswood | Pecan Park | Port Houston | Rice Military | Robindell | Royal Oaks Country Club | Settegast | Sharpstown | Shenandoah | University Oaks | Walnut Bend | Westbury | West End | Westmoreland | Willow Meadows | Willowbend | Woodland Heights
See: List of Houston neighborhoodsEducation Public universities: University of Houston | University of Houston–Clear Lake | University of Houston–Downtown | Texas Southern University
Private universities: Rice University | Houston Baptist University | University of St. Thomas
Community colleges: Houston Community College | Lone Star College | San Jacinto College
See: List of colleges and universities in HoustonCategories:- History of Houston, Texas
- Neighborhoods in Houston, Texas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.