- Project Mogul
-
Project Mogul (sometimes referred to as Operation Mogul) was a top secret project by the US Army Air Forces involving microphones flown on high altitude balloons, whose primary purpose was long-distance detection of sound waves generated by Soviet atomic bomb tests. The project was carried out from 1947 until early 1949. The project was moderately successful, but was very expensive and was superseded by a network of seismic detectors and air sampling for fallout which were cheaper, more reliable, and easier to deploy and operate.
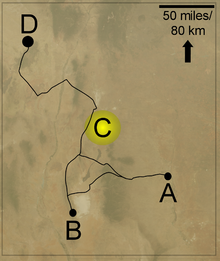 Wreckage said by the Air Force to be consistent with launch number four was found 75 miles northwest of Roswell[1]
Wreckage said by the Air Force to be consistent with launch number four was found 75 miles northwest of Roswell[1]
A. Roswell B. Alamogordo C. Area of wreckage D. AlbuquerqueProject Mogul was conceived by Dr. Maurice Ewing who had earlier researched the deep sound channel in the oceans and theorized that a similar sound channel existed in the upper atmosphere: a certain height where the air pressure and temperature result in minimal speed of sound, so that sound waves would propagate and stay in that channel due to refraction. The project involved arrays of balloons carrying disc microphones and radio transmitters to relay the signals to the ground. It was supervised by Dr. James Peoples, who was assisted by Dr. Albert P. Crary.
One of the requirements of the balloons was that they maintain a relatively constant altitude over a prolonged period of time. (See aerostat.) Thus instrumentation had to be developed to maintain such constant altitudes, such as pressure sensors controlling the release of ballast.
The early Mogul balloons consisted of large clusters of rubber meteorological balloons. However, these were quickly replaced by enormous balloons made of polyethylene plastic. These were more durable, leaked less helium, and also were better at maintaining a constant altitude than the early rubber balloons. Constant altitude control and polyethylene balloons were the two major innovations of Project Mogul.
Project Mogul was the forerunner of the Skyhook balloon program, which started in the late 1940s, as well as another espionage program involving overflights and photo-surveillance of the Soviet Union in the early 1950s, called Project Moby Dick.[2] The latter raised storms of protest from the Soviets. The balloons were also used for cosmic ray experiments.
In 1994/5, the Air Force published a report which concluded that Mogul Flight #4, launched from Alamogordo, New Mexico, on June 4, 1947, was what crashed near Roswell, New Mexico, and formed the source of the debris which sparked the Roswell UFO Incident.[3]
References
- ^ Report on Project Mogul Synopsis of Balloon Research Findings by James McAndrew, 1st Lt, USAFR
- ^ Sagan, Carl. The Demon-Haunted World, p. 83.
- ^ Tim Printy. Popular Roswell Myths. Myth #24
External links
- Physics lecture video in which Prof. Richard A. Muller gives a detailed explanation of the science of Project Mogul (Youtube)
Categories:- Balloons (aircraft)
- Military projects
- Roswell UFO incident
- Soviet Union–United States relations
- Projects of the United States Air Force
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
