- Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda
-
Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda Part of the Eastern Front of World War II
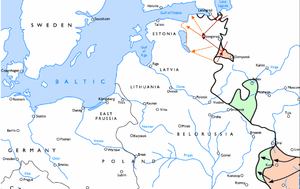
Soviet plan for Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda in the context of the wider offensive in the northern and central parts of the front.Date February 10–April 1, 1943 Location Southern shore of Lake Ladoga , near present-day Saint Petersburg and near Demyansk, Russia Result Stalemate Belligerents  Germany
Germany Soviet Union
Soviet UnionCommanders and leaders  Georg von Küchler
Georg von Küchler Georgy Zhukov
Georgy ZhukovNaval warfare
- Baltic Sea
- Black Sea
- Arctic
1941
1942
- Battles of Rzhev
- Toropets and Kholm
- Demyansk
- Velikiye Luki
- Mars
- 2nd Kharkov
- Case Blue
- Stalingrad
1943
1944
- Dnieper and Carpathian
- Leningrad and Novgorod
- Narva
- Hube's Pocket
- Crimea
- Jassy-Kishinev
- Karelia
- Bagration
- Lvov and Sandomierz
- 2nd Jassy-Kishinev
- Baltics
- Debrecen
- Petsamo and Kirkenes
- Hungary
1945
Leningrad and the Baltics 1941–1944June in Lithuania – Summer in Estonia – Evacuation of Tallinn – Nazi occupation – Toropets-Kholm – Demyansk – Sinyavino – Iskra – Polyarnaya Zvezda – Relief of the siege – Narva – Karelian isthmus – Vilnius – Kaunas – Southern Estonia – Riga – Northern Estonia – Attempt to restore independence of Estonia – Moonsund – Re-occupation of Estonia – Courland – Re-occupation of LatviaOperation Polyarnaya Zvezda (Russian: Операция Полярная звезда, Operatsia Polyarnaya Zvezda; English translation: Operation Polar Star) was an operation conducted by the Soviet Leningrad, Volkhov and Northwestern Fronts in February and March 1943. The operation was planned in the wake of the successful Operation Iskra. The operation was planned by Georgy Zhukov and envisaged two separate encirclements. One to be carried out in the north by the Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts near Mga and further south, by the Northwestern Front, near Demyansk.
The operation succeeded in recapturing Demyansk salient but failed to encircle the German forces. The northern part of the operation failed, without gaining much ground altogether. With the battles south near Kharkov and, later, Kursk using reinforcements for both sides, the frontline near Leningrad stabilised until July 1943
Contents
Background
Preparations
Battle
Northern part
Southern part
Action in March
Aftermath
Notes
References
- Glantz, David M. (2002). The Battle for Leningrad 1941–1944. Kansas University Press. ISBN 0-7006-1208-4.
- Glantz, David M. (2009). After Stalingrad: The Red Army's Winter Offfensive 1942-1943. Helion and Company. ISBN 978-1-906033-26-2.
- Исаев, Алексей Валерьевич (2006). Когда внезапности уже не было. История ВОВ, которую мы не знали. (in Russian). М. Яуза, Эксмо. ISBN 5-699-11949-3. http://militera.lib.ru/h/isaev_av6/.
Categories:- Battles and operations of World War II
- Battles and operations of the Soviet–German War
- Military operations of World War II involving Germany
- Battles involving Spain
- Strategic operations of the Red Army in World War II
- Battles involving the Soviet Union
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.