- Bavarian Geographer
-
The Bavarian Geographer (Latin: Geographus Bavarus) is a conventional name given by Jan Potocki in 1796[1] to the author of an anonymous medieval document Descriptio civitatum et regionum ad septentrionalem plagam Danubii ("Description of Cities and Lands North of the Danube").
The short document was discovered in 1772 in the Bavarian State Library, Munich by Louis XV's ambassador to the Saxon court, Comte Louis-Gabriel Du Buat-Nançay.[2] It had been acquired by the Wittelsbachs with the collection of the antiquarian Hermann Schädel (1410–85) in 1571. The document was much discussed in the early 19th-century historiography, notably by Nikolai Karamzin and Joachim Lelewel.[3]
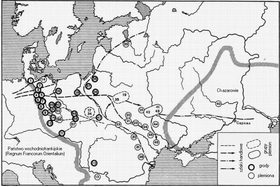
The document contains a list of the tribes in Central-Eastern Europe east of the Elbe and north of the Danube to the Volga rivers to the Black and Caspian Sea (most of them of Slavonic origin, with Ruzzi, and others such as Vulgarii, etc.). Absent on the list are Polans, Pomeranians and Masovians, tribes first of whom are believed to have settled along the shores of the Warta river during the 8th century.[4]
There is also some information about the number of strongholds (civitates) possessed by some of the tribes. Henryk Łowmiański demonstrated that the list consists of two parts, which may be datable to different periods and attributed to distinct authors.[5]
The provenance of the document is disputed. Although early commentators suggested that it could have been compiled in Regensburg,[6] the list seems to have been taken from Codex Reginbertinus II, recorded in the 9th century in the library of the Reichenau Abbey and named after a local librarian.[7] Based on these findings, Bischoff attributes it to a monk active at Reichenau from the 830s to 850s.[8]
Nazarenko finds it more probable that the list was composed in the 870s, when Saint Methodius is believed to have resided at Reichenau. The document may have been connected with his missions in the Slavic lands.[9]
References
- ^ J. Potocki. Fragments historiques et geographiques sur la Scythie, Sarmatie, et les Slaves. Brunsvic, 1796.
- ^ Le comte du Buat. Histoire ancienne des peuples de l'Europe. T. 11. Paris, 1772.
- ^ J. Lelewel. Winulska Sławiańszczyzna z Geografa bawarskiego, Tygodnik Wileński, nr 47, z dn. 8 paźdzernika 1816, s. 333, i w nastęnych numerach 48–50. Also: Joachim Lelewel, Geographe du Moyen Age III, Bruxelles 1852, s.21–45.
- ^ Andrzej Buko: Archeologia Polski wczesnośredniowiecznej : odkrycia, hipotezy, interpretacje. Warszawa, 2005.
- ^ Henryk Łowmiański, O identyfikacji nazw Geografa bawarskiego, Studia Źródłoznawcze, t. III: 1958, s.1–22.
- ^ Henryk Łowmiański, O pochodzeniu Geografa bawarskiego, Roczniki Historyczne, R. 20, 1955, s.9–58
- ^ The codex contains Boethius's treatise on geometry. See: Novy R. Die Anfänge des böhmischen Staates, 1: Mitteleuropa im 9. Jh. Praha, 1969.
- ^ Bischoff B. Die südostdeutchen Schreibschulen und Bibliotheken in der Karolingerzeit. Bd. 1.2. Aufl. Wiesbaden, 1960.
- ^ А.В. Назаренко. Древняя Русь на международных путях: Междисциплинарные очерки культурных, торговых, политических связей IX–XII веков. Moscow, 2001. Pages 52–70.
Further reading
- Le comte du Buat, Histoire ancienne des peuples de l'Europe, T. 11. Paris 1772
- J. Potocki, Fragments historiques et geographiques sur la Scythie, Sarmatie, et les Slaves, Brunsvic 1796
- V. von Keltsch, Der bairische Geograph, Alpreussische Monatsschr., 23 (1886), s. 507 n.
- A. Králiček, Der s.g. bairische Geograph und Mahren, Zeitschr d. Vereins f. die Geschichte Mahrens u. Schlesiens II (1898), pp. 216–235, 340–360
- S. Zakrzewski, Opis grodów i terytoriów z północnej strony Dunaju czyli tzw. Geograf bawarski, Lwów 1917
- E. Kucharski, Polska w zapisce karolińskiej zwanej niewłaściwie "Geografem bawarskim", [w:] Pamiętnik IV powszechnego Zjazdu historyków polskich, t. I, Lwów 1925, sekcja II, s. 111;
- E. Kucharski, Zapiska karolińska zwana niewłaściwie "Geografem bawarskim", Sprawozdania Tow. Nauk. we Lwowie, t. V (1925), s. 81–86
- A. V. Nazarenko. Nemetskie latinoyazychnye istochniki IX–XI vekov: teksty, perevod, kommentarii. Moscow, 1993
- W. Fritze, Die Datierung des Geographus Bavarus, Zschr f. Slavische Philologie, 21, Heft 2 (1952), pp. 326–242
- Henryk Łowmiański, O pochodzeniu Geografa bawarskiego, Roczniki Historyczne, R. 20, 1955, s. 9–58; reed: w: Studia nad dziejami Słowiańszczyzny, Polski i Rusi w wiekach średnich, Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu im. Dama Mickiewicza, Poznań 1986, s. 104–150, ISSN 0554-8217
- Henryk Łowmiański, O identyfikacji nazw Geografa bawarskiego, Studia Źródłoznawcze, t. III: 1958, s. 1–22; reed: w: Studia nad dziejami Słowiańszczyzny, Polski i Rusi w wiekach średnich, Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu im. Dama Mickiewicza, Poznań 1986, s. 151–181, ISSN 0554-8217
- Gerhard Billig, Zur Rekonstruktion der ältesten slawischen Burgbezirke im obersächsisch-meißnischen Raum auf der Grundlage des Bayerischen Geographen, Neues Archiv für sächsische Geschichte 66 (1995), pp. 27–67
- Jerzy Nalepa, O nowszym ujęciu problematyki plemion słowiańskich u "Geografa Bawarskiego". Uwagi krytyczne, Slavia Occidentalis, T. 60 (2003), s. 9–6
External links
Categories:- 9th-century geographers
- Medieval German geographers
- Latin texts
- Slavic people
- 9th century
- Anonymous works
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.