Mechanically-interlocked molecular architectures
- Mechanically-interlocked molecular architectures
-
Mechanically interlocked molecular architectures are connections of molecules not through traditional bonds, but instead as a consequence of their topology. This connection of molecules is analogous to keys on a key chain loop. The keys are not directly connected to the key chain loop but they cannot be separated without breaking the loop. On the molecular level the interlocked molecules cannot be separated without significant distortion of the covalent bonds that make up the conjoined molecules. Examples of mechanically interlocked molecular architectures include catenanes, rotaxanes, molecular knots, and molecular Borromean rings.
The synthesis of such entangled architectures has been made efficient through the combination of supramolecular chemistry with traditional covalent synthesis, however mechanically interlocked molecular architectures have properties that differ from both “supramolecular assemblies” and “covalently bonded molecules”. Recently the terminology "mechanical bond" has been coined to describe the connection between the components of mechanically interlocked molecular architectures. Although research into mechanically interlocked molecular architectures is primarily focused on artificial compounds, many examples have been found in biological systems including: cystine knots, cyclotides or lasso-peptides such as microcin J25 which are protein, and a variety of peptides. There is a great deal of interest in mechanically interlocked molecular architectures to develop molecular machines by manipulating the relative position of the components.
Examples of mechanically interlocked molecular architectures
References
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Molecular switch — A molecular switch is a molecule that can be reversibly shifted between two or more stable states.[1] The molecules may be shifted between the states in response to changes in e.g. pH, light, temperature, an electrical current, microenvironment,… … Wikipedia
Molecular machine — Part of a series of articles on Molecular Nanotechnology … Wikipedia
Supramolecular chemistry — refers to the area of chemistry that focuses on the noncovalent bonding interactions of molecules. [cite journal | author=Lehn JM | title=Supramolecular chemistry | journal=Science | volume=260 | issue=5115 | year=1993 | pages=1762–3 |… … Wikipedia
James Fraser Stoddart — Infobox Scientist name = J Fraser Stoddart caption = James Fraser Stoddart birth date = Birth date and age|1942|5|24|mf=y birth place = Edinburgh, Scotland, UK death date = death place = residence = UK, U.S. nationality = Scottish field =… … Wikipedia
James Fraser Stoddart — Naissance 24 mai 1942 Edinburgh (Écosse) Nationalité Britannique Champs Chimie … Wikipédia en Français
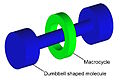
Rotaxane — A rotaxane is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture consisting of a dumbbell shaped molecule which is threaded through a macrocycle (see graphical representation). The name is derived from the Latin for wheel (rota) and axle (axis).… … Wikipedia
Jean Pierre Sauvage — is a French chemist, a pioneer in the field of mechanically interlocked molecular architectures.Sauvage was born in Paris in 1944. He obtained his Ph. D. from the university of Strasbourg under the supervision of J. M. Lehn. After postdoctoral… … Wikipedia
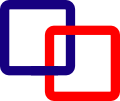
Catenane — [ thumbnail|230px|Schematic animation of the template directed synthesis of the bis bipyridinium cyclophane / paraphanylene crown ether [2] catenane described in the text.] A catenane is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture… … Wikipedia
Interlock (disambiguation) — Interlock can refer to the following:*Interlock (band) an industrial/alternative metal band *Interlock (engineering) *Interlocking (railway signaling) *Interlock (cinema projection) *Interlocking tower *an interlocked hutch in a synchrotron… … Wikipedia
Mechanical bond — The mechanical bond is a type of chemical bond found in mechanically interlocked molecular architectures such as catenanes and rotaxanes. Unlike classical molecular structures, interlocked molecules consist of two or more separate components… … Wikipedia