- Marie Laurencin
-
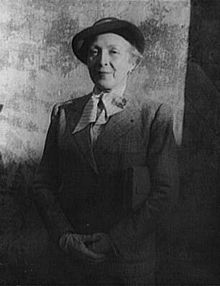 Marie Laurencin photographed by Carl Van Vechten, 1949
Marie Laurencin photographed by Carl Van Vechten, 1949
Marie Laurencin (October 31, 1885–June 8, 1956) was a French painter and printmaker. [1]
Contents
Biography
Laurencin was born in Paris, where she was raised by her mother and lived much of her life. At 18, she studied porcelain painting in Sèvres. She then returned to Paris and continued her art education at the Académie Humbert, where she changed her focus to oil painting.
During the early years of the 20th century, Laurencin was an important figure in the Parisian avant-garde and a member of the circle of Pablo Picasso. She became romantically involved with Picasso's friend, the poet Guillaume Apollinaire, and has often been identified as his muse. In addition, Laurencin had important connections to the salon of the American expatriate and famed lesbian writer Natalie Clifford Barney.
During the First World War, Laurencin left France for exile in Spain with her German-born husband, Baron Otto von Waëtjen, since through her marriage she had automatically lost her French citizenship. The couple subsequently lived together briefly in Düsseldorf. After they divorced in 1920, she returned to Paris, where she lived for the rest of her life and where she achieved great success as an artist.
Work
Laurencin's works include paintings, watercolors, drawings, and prints. She is known as one of the few female Cubist painters, with Sonia Delaunay, Marie Vorobieff, and Franciska Clausen[citation needed]. While her work shows the influence of Cubist painters Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, who was her close friend, she developed a unique approach to abstraction which often centered on the representation of groups of women and female portraits. Her work lies outside the bounds of Cubist norms in her pursuit of a specifically feminine aesthetic by her use of pastel colors and curvilinear forms. Laurencin's insistence on the creation of a visual vocabulary of femininity, which characterized her art until the end of her life, can be seen as a response to what some consider to be the arrogant masculinity of Cubism.
In 1983, on the one hundredth anniversary of Laurencin's birth, the Musée Marie Laurencin opened in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. The museum is home to more than 500 of her works and an archive.
External links
- Marielaurencin.com
- Musée Marie Laurencin, Japan.
- Artcyclopedia.com: Marie Laurencin
- Elizabeth Otto (2002). "Memories of Bilitis: Marie Laurencin beyond the Cublist Context," Genders 36. [1]
Bibliography
- Gere, Charlotte . Marie Laurencin, London - Paris, Flammarion, 1977
- Groult, Flora . Marie Laurencin, Paris, Mercure de France, 1987
- Kahn, Elizabeth Louise. "Marie Laurencin: Une Femme Inadaptée" in Feminist Histories of Art Ashgate Publishing, 2003.
- Marchesseau, Daniel. Marie Laurencin, Tokyo, éd. Kyuryudo & Paris, Hazan, 1981
- Marchesseau, Daniel. Marie Laurencin, Catalogue raisonné de l'œuvre gravé, Tokyo, éd. Kyuryudo, 1981
- Marchesseau, Daniel. Marie Laurencin, Catalogue raisonné de l'œuvre peint, 2 vol. Tokyo, éd. Musée Marie Laurencin, 1985 & 1999
- Marchesseau, Daniel. Marie Laurencin, Cent Œuvres du musée Marie Laurencin, Martigny, Fondation Pierre Gianadda, 1993
- Otto, Elizabeth. "Memories of Bilitis: Marie Laurencin beyond the Cublist Context," Genders 36 (2002). [2]
- Pierre, José. Marie Laurencin, Paris, France-Loisirs, 1988
Archives
- Fonds Marie Laurencin, Bibliothèque littéraire Jacques Doucet, Université de Paris
Notes
- ^ Maurice Raynal: Modern French Painters, Ayer Publishing, 1928, ISBN 978-0-40500735-4, p. 108
Categories:- 1885 births
- 1956 deaths
- Artists from Paris
- French engravers
- French painters
- Modern painters
- Modern printmakers
- French women artists
- Cubist artists
- Women painters
- French painter, 19th century birth stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
