- Nyquist ISI criterion
-
In communications, the Nyquist ISI criterion describes the conditions which, when satisfied by a communication channel, result in no intersymbol interference or ISI. It provides a method for constructing band-limited functions to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference.
When consecutive symbols are transmitted over a channel by a linear modulation (such as ASK, QAM, etc.), the impulse response (or equivalently the frequency response) of the channel causes a transmitted symbol to be spread in the time domain. This causes intersymbol interference because the previously transmitted symbols affect the currently received symbol, thus reducing tolerance for noise. The Nyquist theorem relates this time-domain condition to an equivalent frequency-domain condition.
The Nyquist criterion is closely related to the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, with only a differing point of view.
Contents
Nyquist criterion
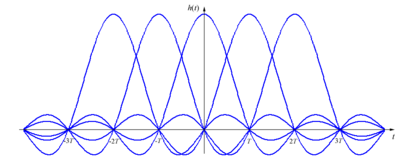
If we denote the channel impulse response as h(t), then the condition for an ISI-free response can be expressed as:
for all integers n, where Ts is the symbol period. The Nyquist theorem says that this is equivalent to:
 ,
,
where H(f) is the Fourier transform of h(t). This is the Nyquist ISI criterion.
This criterion can be intuitively understood in the following way: frequency-shifted replicas of H(f) must add up to a constant value.
In practice this criterion is applied to baseband filtering by regarding the symbol sequence as weighted impulses (Dirac delta function). When the baseband filters in the communication system satisfy the Nyquist criterion, symbols can be transmitted over a channel with flat response within a limited frequency band, without ISI. Examples of such baseband filters are the raised-cosine filter, or the sinc filter as the ideal case.
Derivation
To derive the criterion, we first express the received signal in terms of the transmitted symbol and the channel response. Let the function h(t) be the channel impulse response, x[n] the symbols to be sent, with a symbol period of Ts; the received signal y(t) will be in the form (where noise has been ignored for simplicity):
![y(t) = \sum_{n = -\infty}^{\infty} x[n] \cdot h(t - n T_s)](a/36a72d3ded411832fe98c9964803be51.png) .
.
Sampling this signal at intervals of Ts, we can express y(t) as a discrete-time equation:
![y[k] = y(k T_s) = \sum_{n = -\infty}^{\infty} x[n] \cdot h[k - n]](c/7cce92f23e38e1a437d63265e9b599b0.png) .
.
If we write the h[0] term of the sum separately, we can express this as:
![y[k] = x[k] \cdot h [0] + \sum_{n \neq k} x[n] \cdot h[k - n]](3/633d7f6bcccbb5418ea4481982ca95db.png) ,
,
and from this we can conclude that if a response h[n] satisfies
![h[n] = \begin{cases} 1; & n = 0 \\ 0; & n \neq 0 \end{cases}](1/1210849d9db1bbb7d816df26464311c4.png) ,
,
only one transmitted symbol has an effect on the received y[k] at sampling instants, thus removing any ISI. This is the time-domain condition for an ISI-free channel. Now we find a frequency-domain equivalent for it. We start by expressing this condition in continuous time:
for all integer n. We multiply such a h(t) by a sum of Dirac delta function (impulses) δ(t) separated by intervals Ts This is equivalent of sampling the response as above but using a continuous time expression. The right side of the condition can then be expressed as one impulse in the origin:
Fourier transforming both members of this relationship we obtain:
and
 .
.
This is the Nyquist ISI criterion and, if a channel response satisfies it, then there is no ISI between the different samples.
See also
- Intersymbol interference
- Nyquist rate
- Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem
- Pulse shaping
- Raised-cosine filter
References
- John G. Proakis, "Digital Communications, 3rd Edition", McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1995. ISBN 0-07-113814-5
- Behzad Razavi, "RF Microelectronics", Prentice-Hall, Inc., 1998. ISBN 0-13-887571-5
Categories:- Telecommunication theory
- Digital signal processing
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.