- GER Decapod
Infobox Locomotive
railroad=Great Eastern Railway
name="Decapod"
powertype=Steam
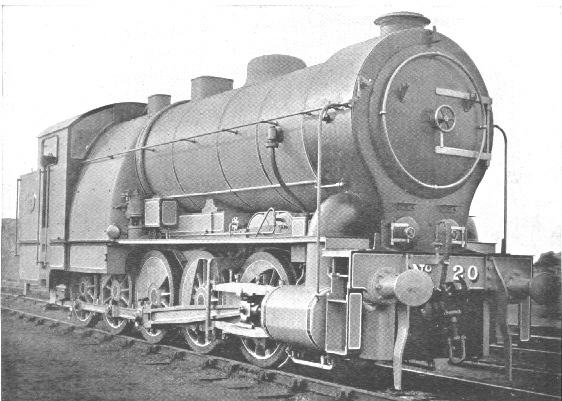
whytetype=0-10-0 ; rebuilt in 1906 as0-8-0
builddate=1902
designer=James Holden
cylindercount=3
weight=80 tons
driversize=4 ft 6 in (1371.6 mm)
cylindersize=18½ in dia x 24 in stroke
boiler=length: 15 ft 6 in
inside dia: 5 ft 3 in
tubearea=395 x 1¾ in dia
tractiveeffort=38,788 lbs
totalsurface=2,873.3 ft²
fireboxarea=131.7 ft²
disposition=scrapped
TheGreat Eastern Railway 's Decapod was an experimentalsteam locomotive with an0-10-0 wheel arrangement . It was the first ten coupled steam locomotive inGreat Britain .Background
The locomotive was built for purely political purposes in order to block the passage through Parliament of a new rival scheme for an electric railway.The Decapod was built in 1902 to a design by the GER Chief Draughtsman, Fred Russell [http://www.steamindex.com/people/holden.htm#russell] under the supervision of the Chief Superintendent, James Holden. The aim was to demonstrate the ability of a steam locomotive to
accelerate passenger trains at a rate comparable to electric traction and theelectric tram s with which the GER was also in competition over short distances.The locomotive was far larger than any locomotive previously built in Britain for home service. It had 10 four-foot-six-inch
driving wheel s. which gave hightractive effort . Three cylinders were used because there was insufficient room for 2 cylinders large enough to develop the required tractive effort without going up to a higher boiler pressure. Even so, it still had to have a pressure of 200 psi (1,378 KPa) [Ahrons E.L., The British Steam Railway Locomotive, 1825-1925: Locomotive Publishing Co. 1925 (republished Ian Allan, 1963)] to achieve the required result.Technical details
There were three separate grates and ash pans, one on each side outside the frames and a third between, giving an aggregate area of 42sq. ft. The trailing drivers were given a side play of ½", the coupling rods being fitted with ball and socket joints. As the cranks of the three cylinders were set at 120 degrees in relation to each other, perfect balancing of the reciprocating parts was secured. In order to minimise the drivers slipping, compressed air sanders were fittedFact|date=November 2007.
Performance and subsequent career
The specification required that the locomotive should accelerate 315 ton (305 tonne) train from a stand to convert|30|mi/h|km/h|0|sing=on|lk=on in 30 seconds. According to Ahrons, "Holden's engine actually accelerated a new train of 18 carriages weighing 335 tons (340
tonnes ) at a rate of 1.4 feet/second in very windy weather".Axle load at 16.75 tons (17 tonnes), was not excessive, but weight per foot run of wheelbase was very high and using a class of these engines would have necessitated considerable strengthening of bridges; thus whilst it achieved its aims, nothing resulted from the experiment. The locomotive was therefore surplus to requirements and In 1906 it was converted into an
0-8-0 freight tender engine, the only eight coupled engine of the GER and was scrapped as non-standard after a short working life.0-10-0 Developments
The
Midland Railway produced the second 0-10-0 locomotive in 1919 with itsMR 0-10-0 Lickey Banker . The third ten coupled engine however would not appear until 1943 in the guise of a class of2-10-0 s built by the War Department, the Austerity 2-10-0. These were followed in 1954 by the last class of British ten coupled engines, theBR standard class 9F .notes
External links
* http://mikes.railhistory.railfan.net/r075.html
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
