- Openkore
-
OpenKore - Custom Ragnarok Online client 
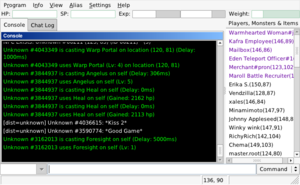
Screenshot of wxWidgets GUI on wxGTKOriginal author(s) VCL and others[1] Developer(s) OpenKore developers[1] Initial release November 12, 2003[1] Stable release 2.0.7[2] / July 29, 2009[2] Development status Active[3] Written in Perl, C, C++ and others[4] Operating system BSD, Linux, Mac OS and Windows[2] Size 5.9 MB
19.2 MB (with Windows binaries)Available in English, Indonesian, Korean, Portuguese, Russian, Thai, Tagalog, Traditional Chinese, Chinese Type Internet bot[2] License GNU General Public License [2] Website openkore.com OpenKore is a custom client and an advanced automated assistant for the MMORPG Ragnarok Online. It's free software and licensed under the GNU General Public License. OpenKore is mainly written in Perl, but some code is also in C++ XS modules. The Perl interpreter allows for a cross-platform usability and an ability to work with the source code without recompiling or even interrupting the program. OpenKore is not associated with Gravity (developers of Ragnarok Online).[1]
Contents
History
The OpenKore project was started by VCL in late November 2003. At the moment, there was original Kore, probably the only well-known free software Ragnarok Online bot, but due to lack of organization, many forks and modifications existed. OpenKore is based on Skore-revamped, which is a modified version of Skore (Solos Kore), which is a fork of the original Kore developed by Kura[5]. It was started as an attempt to unite contributors to Kore forks, and that was quite successful. Gradually, other Ragnarok Online bot projects have phased out, mostly due to server-side updates and lack of development. Many developers have come from other inactive Ragnarok Online bot program projects (e.g. ApezBot, Kore, Modkore, Revemu, Skore, etc.) to develop on OpenKore.[1]
Nearing the end of 2008, the Openkore project is the only Ragnarok Online bot that currently provides support to many Ragnarok Online servers and continual development on an international level. As of November 8, 2010, Openkore releases has been downloaded from SourceForge.net approximately more than 6,071,820 times since its availability in 2003.[6]
After version 2.0.7's release in mid-2009, there were no releases for a long time, with recommendation[7] to use trunk instead due to server updates, bug fixes and new features.
Features
OpenKore acts as a Ragnarok Online game client and can perform anything a player's character can do manually in the game client. It's highly configurable and tweakable; reasonable default configuration provided as well.[8][9]
The software can be configured to automatically and repeatedly perform assigned tasks without human involvement. The automated actions are state-based and with the macro plug-in be also script-based. These automations cover almost every action available in the game client. When a bot program is running, it continuously reports the latest information and the current status of the game, e.g., a character’s location, the current action, the “hit” point, and information about nearby monsters. Openkore allows users to give commands anytime, regardless of the prearranged actions by scripts, i.e., the bot is script-based and interactive. Basically, Openkore is meant to automate and simplify actions by the user of the software within the Ragnarok Online environment through the use of extensive scripting.[10]
Controls
There are several interfaces which all have console log with the latest information and console input for commands which cover current status inspection, manual actions and AI management. The most basic interface is just a console application. There is also slightly more tuned Curses-based console interface and wxWidgets-based GUI with graphical map display etc.
Automation Features
These features are generally triggered by state-based triggers and can be tuned in many aspects.
- Walk seamlessly between maps, automatically finding the shortest, cheapest or safest path
- Automatically find (randomly wandering or teleporting) and attack monsters
- Automatically use items and skills
- Automatically manage (loot, gather, buy, sell, drop) items in inventory, cart and storage
- Automatically find (party members only) and follow another character, mimicking his movements, attacks and other actions
- Automatically manage various requests (party, guild, deal)
- Avoiding monsters, players, GMs, tough damage, death
- Automatically chat with players with self-training chat plugin
- Control semi-independent entities such as Homunculus and Mercenary using semi-independent AI
Logging Features
- Log the number of monsters killed
- Log private, public and guild chats
- Log console
- Log raw network packets
- Automatically visit vendors, collect data on offers and store it in database with a web interface (plugin)
- Automatically collect data on other players (levels, equipment, parties, guilds)
Miscellaneous Features
- Hook on game client's connection to the game server, using the client as the ultimate view and control tool and acting as a packet editor ("XKore 1")
- Integrated game server game client can connect to without interrupting ("XKore 2")
- Remote controlling via socket (included) or IRC (plugin)
- Anti spam (plugin)
- Sound alerts (plugin)
- Growl and Snarl alerts (plugin)
Plugins and Scripting
Third-party plugins, written in Perl, can add and modify available functions using provided API (hooks) or reflective features of Perl.
Macro plugin provides a simple way to create a script-based triggers and action sequences.
Community
OpenKore's community is diverse with contributions to the project coming from communities that are English[11], French, German, Indonesian, Korean, Portuguese, Russian[12], Spanish, Filipino, Thai, Traditional Chinese, and Vietnamese. This diverse range of cultures enables OpenKore to provide international support for various Ragnarok Online servers all over the world. Currently, OpenKore supports bRO, iRO, idRO, inRO, mRO, pRO, rRO and most private servers.;[13] euRO was supported when it shut down.
Impact and Reception
Bots, unlike normal players, can play and do repetitive actions endlessly long, including gaining experience points, ingame items and currency, which can affect so-called balance of the game. They can affect real economy, as well as human players, due to these things being sold for real money. High amount of obvious bots (not well-configured) may negatively change the gaming experience for human players[8][9], but due to being obvious they can be banned easily as well. If server staff is concerned about botting issue, negative effects can be reduced to the minimum.
OpenKore itself is just an alternative client and tries to conform to common game rules and ethics: it doesn't kill steal and doesn't loot, there isn't any options or plugins for that and it's forbidden to ask about it at OpenKore forums[14]. However, there isn't any strict countermeasures against implementing it, as it's pointless to do in free software.
With free software game clients, everyone can enrich the overall gaming experience. Many harmless features added, like efficient and configurable spam blocking, automatic reconnection after disconnect and play statistics. Various types of bot-based services exist, for example market search (found in other games and finally implemented in Ragnarok Online too, but poorly), global events/quests availability viewer, buff and teleport service. Bots can act as a flexible NPCs for client-side controlled quests.
Some anti-bot measures expose complete incompetence and/or indifference of game management on official servers, for example, installation of protection systems[15] which are already circumvented by OpenKore for years[16] and so only introduce additional problems for all players.
Botting isn't the only problem that exist in official servers. Server software bugs causing disconnects and downtime, server exploits and corrupted server management (game masters) lead to more serious problems then just having alternative game clients.
Related Projects
- ModKore, another fork of Kore, went closed source and is not supported anymore
- VisualKore, OpenKore variant with simplified configuration and interface, is not supported anymore. Some of its features were implemented in OpenKore
- Ragnarok Online Plugin System[17], game client plugin framework
- RCX (RoCha)[18], nonfree software which extends game client without automation features
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e "About OpenKore". http://openkore.com/index.php/OpenKore. Retrieved 2008-11-29.
- ^ a b c d e "OpenKore | Download OpenKore software for free at SourceForge.net". 2003-11-07. http://sourceforge.net/projects/openkore.
- ^ "Openkore - CIA.vc". http://cia.vc/stats/project/openkore.
- ^ "OpenKore - Ohloh". http://www.ohloh.net/p/openkore/analyses/latest.
- ^ "Kore Ragnarok bot project". http://kore.sourceforge.net/.
- ^ "SourceForge.net: Openkore - Download History Statistics". 2003-11-07. http://sourceforge.net/project/stats/detail.php?group_id=94364&ugn=openkore&type=prdownload&mode=alltime&file_id=0. Retrieved 2010-11-08.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". http://openkore.com/index.php/FAQ.
- ^ a b Adam Cornelissen; Franc Grootjen (October 2008). "A Modern Turing Test: Bot Detection in MMORPGs" (PDF). Proceedings 20th Belgian-Netherlands Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Enschede: University of Twente): 49–55. ISSN 1568-7805. http://franc.grootjen.nl/wp-content/uploads/2009/01/bnaic08.pdf.
- ^ a b Marlieke van Kesteren; Jurriaan Langevoort; Franc Grootjen (October 2009). "A step in the right direction: Botdetection in MMORPGs using movement analysis" (PDF). Proceedings of the 21st Belgian-Dutch Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Eindhoven). http://franc.grootjen.nl/wp-content/uploads/2009/12/bnaic2009.pdf.
- ^ Chen, K.T.; Jiang, J.W.; Huang, P.; Chu, H.H.; Lei, C.L.; Chen, W.C. (2006-06-01). Identifying MMORPG Bots: A Traffic Analysis Approach. ACM. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1178829.
- ^ "OpenKore community forums". http://forums.openkore.com/.
- ^ "Клуб любителей пляски с бубном вокруг Openkore [Club dancing with a tambourine around Openkore]" (in Russian). http://rofan.ru/.
- ^ "Openkore - List of (un)supported servers". 2003-11-07. Archived from the original on 2008-06-19. http://web.archive.org/web/20080619163409/http://www.openkore.com/wiki/index.php/List_of_(un)supported_servers. Retrieved 2008-11-29.
- ^ "Global Forum Rules". http://forums.openkore.com/viewtopic.php?t=129.
- ^ "Новая система защиты HackShield для игрового клиента [The new protection system for the game client HackShield]" (in Russian). Gravity CIS, Inc.. 22.06.2009. http://www.raggame.ru/news.asp?id=863.
- ^ "Copy CVS's Base::Server to the 1.6 branch; add Poseidon to CVS". 31.01.2006. http://openkore.svn.sourceforge.net/viewvc/openkore?view=revision&revision=3844.
- ^ "Ragnarok Online Plugin System". http://rops.ragial.com/.
- ^ "RCX temporary". http://rcx.planetleaf.com/.
Further reading
- eAthena
External links
Categories:- 2003 software
- Free cross-platform software
- Free multilingual software
- Portable software
- Network analyzers
- Console application
- Curses (programming library)
- Software that uses wxWidgets
- Free software programmed in Perl
- Competitive video gaming
- Video game cheating
- Ragnarok Online
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.