- NOAAS Rude (S 590)
-

NOAA Ships Rude (S 590) and Heck (S 591)Career (United States)  _
_

Name: NOAAS Rude (S 590) Namesake: Captain Gilbert T. Rude (1881-1962), a U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey officer Builder: Jackobson Shipyard, Oyster Bay, New York Launched: August 1966 Completed: December 1966 Commissioned: March 1967 Decommissioned: 25 March 2008 Honors and
awards:Department of Commerce Silver Medal 1978 Status: Inactive in NOAA Atlantic Fleet Notes: Served in U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey as USC&GS Rude 1967-1970
Served in National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as NOAAS Rude from 1970General characteristics Type: hydrographic survey ship Tonnage: 150 gross register tons (domestic tonnage) Displacement: 220 tons (ITC tons) Length: 90 ft (27 m) Beam: 22 ft (6.7 m) (moulded) Draft: 7.2 ft (2.2 m) Installed power: 850 shp (0.63 MW) Propulsion: Two Cummins 425 hp (0.317 MW) geared diesel engines, 2 shafts, 3,900 US gallons (15,000 L) fuel Speed: 10 knots (19 km/h) (cruising) Range: 1,000 nautical miles (1,900 km) Endurance: 5 days Boats and landing
craft carried:One launch Complement: 11 (4 NOAA Corps officers, 1 licensed engineer, and 6 other crew members) Notes: 120 kilowatts electrical power NOAAS Rude (S 590) is an American hydrographic survey ship. She served in the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey from 1967 to 1970 and has served in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) since 1970.
She was built at the Jackobson Shipyard in Oyster Bay, New York. She was launched in August 1966, commissioned in March 1967, and decommissioned on March 25, 2008.[1]
The RUDE (pronounced "Rudy") is named for Gilbert T. Rude, former Chief of the Division of Coastal Surveys, U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey. The hull of the ship is 90 feet (27.4 m) long, the smallest in the NOAA fleet. The ship has a total of 11 bunk spaces. The ship's mess room can seat 7. She carries a complement of 4 NOAA Corps officers, 7 crew, including 1 licensed engineer.
The deck equipment features one winch and one telescoping boom crane. This equipment gives the RUDE a lifting capacity of up to 7,500 pounds (3,400 kg) as well 500 feet (150 m) of cable that can pull up to 250 pounds (113 kg).
For her primary mission of inshore hydrographic surveys, the ship is equipped with a differential global positioning system (DGPS), a multibeam sonar system, and side-scan sonar (SSS). She is also equipped for diving operations to allow human investigation of submerged obstacles. A 19-foot (5.7 m) fiberglass launch is available for utility or rescue operations.
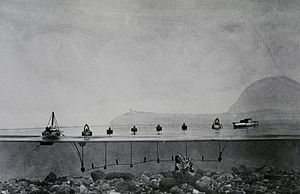 A United States Coast and Geodetic Survey diagram of ca. 1920 of wire drag hydrographic survey operations as carried out by Rude and her sister ship Heck. The basic principle is to drag a wire attached to two vessels; if the wire encounters an obstruction it will come taut and form a "V."
A United States Coast and Geodetic Survey diagram of ca. 1920 of wire drag hydrographic survey operations as carried out by Rude and her sister ship Heck. The basic principle is to drag a wire attached to two vessels; if the wire encounters an obstruction it will come taut and form a "V."
Rude was originally used as a wire drag vessel with a 'sister ship' of identical design named HECK. They worked together under a single command conducting wire drag surveys clearing large swaths between them with a submerged wire prior to electronic technologies that allow a single vessel to do the same work using side-scan or multibeam sonar. In 1989, they began working independently thanks to the improved technology. The HECK was deactivated in 1995.
Contents
Search and rescue
In 1978, Rude and Heck came to the assistance of the burning research vessel Midnight Sun, rescuing Midnight Sun's crew and scientists and saving the vessel from total loss. Rude's crew took aboard all 20 of Midnight Sun's crew members and scientists, who were afloat in life rafts near Midnight Sun, administered first aid to them, and transported them to shore. Heck's crew, meanwhile, fought the fire aboard Midnight Sun for 20 consecutive hours and saved Midnight Sun from sinking. For their efforts in saving Midnight Sun and her crew, the crews of Rude and Heck received the 1978 Department of Commerce Silver Medal.
Rude was sometimes called upon to assist the U.S. Coast Guard and Navy in search, rescue, and recovery operations. She located the TWA Flight 800 wreckage off of Moriches, New York, in 1996, and, more recently, located John F. Kennedy Jr.'s plane wreckage off Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts.
See also
References
External links
- "NOAA Ship RUDE". October 2005. http://www.moc.noaa.gov/ru/index.htm. Retrieved May 10, 2006.
- "Coast and Geodetic Survey Ships". April 2007. http://www.history.noaa.gov/ships/heck.html. Retrieved April 13, 2007.
List of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration shipsCategories:- Ships of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- Survey ships of the United States
- Rude class hydrographic survey ships
- Ships built in New York
- 1966 ships
- Virginia-related ships
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
