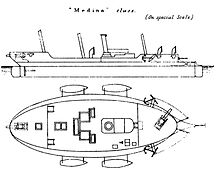
- Medina class gunboat
-

Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company, JarrowOperators:  Royal Navy
Royal NavyPreceded by: Ant-class gunboat Succeeded by: gunboat Built: 1876 - 1877 In commission: 1877 - 1923 Completed: 12 General characteristics Displacement: 386 tons (designed)
363 tons (actual)[1]Length: 110 ft 0 in (33.5 m)[1] Beam: 34 ft 1 in (10.4 m)[1] Draught: 9 ft 6 in (2.9 m)[1] Depth of hold: 5 ft 6 in (1.7 m)[1] Installed power: 60 nominal horsepower
310 ihp (230 kW)Propulsion: - 2 x 2-cylinder horizontal single-expansion steam engines
- Twin screws
Sail plan: Barquentine
(2 pole masts from 1892)Speed: 91⁄2 kn (17.6 km/h) Complement: 51 Armament: As built:
- 3 x 6.3-inch (160-mm) 64-pdr muzzle-loading rifles
Later:
- 2 (or 3) x 4.7-inch quick-firing guns
The Medina-class gunboat was a class of 12 Royal Navy Rendel (or "flat-iron") gunboats mounting three 6.3-inch guns, built between 1876 and 1877.[1] Flat-iron gunboats were normally built without masts or rigging, but the Medinas carried a full barquentine rig. Their robust iron hulls meant that they lingered on as diving tenders, barges and lighters, with five of them working into the 1920s.
Contents
Design
The Medina class were a development of the Rendel (or "flat-iron") gunboat, a series of small vessels with low freeboards which mounted a small number of relatively large guns. Although the Medinas were exceptionally provided with masts to extend their range and independence, in essence they were available for similar operations to their un-masted sisters; offensive action against shore defences. Their ungainly appearance led them to be described by the naval historian Antony Preston as "the most grotesque craft ever seen".[2] All 12 vessels of the class were built at Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company in Jarrow and were named after rivers. They were constructed entirely of iron and were fitted with an unusual bow rudder.[1]
Armament
As built, ships of the class mounted three 6.3-inch (160-mm) 64-pdr 64-cwt muzzle-loading rifles. By 1892 Trent had been fitted with a pair of 4.7-inch quick-firing guns.[3]
Propulsion
All the ships of the class were fitted with a pair of R and W Hawthorn 2-cylinder horizontal single-expansion steam engines of 60 nominal horsepower. They developed 310 indicated horsepower (230 kW), giving a speed of about 91⁄2 kn (17.6 km/h).[1]
Sail plan
All ships of the class were built with three masts[1] and a barquentine rig of sails. Surviving members of the class had their sailing rig replaced by a pair of pole masts in the 1890s.[3]
Operational lives
Some of the ships of the class were appointed as tenders to battleships as soon as they were built: Medina tender to Duke of Wellington and Medway to Excellent, the gunnery school at Portsmouth. Spey was fitted in 1900 with three 4.7-inch guns for service at the gunnery school.[4]
Dee and Don served in the Mediterranean in 1886 as part of an International squadron dominated by the Royal Navy. They both remained at Malta in various capacities for the rest of their lives.[5][6] Tay had her armament reduced to a single 9-pounder gun and by 1914 was a tender to HMS Vivid, the Royal Navy barracks at Devonport.[7] Esk and Tweed both served in Hong Kong in the 1890s, being sold there in the 1900s.[8][9]
In all cases the crews were not expected to live onboard their cramped ships when not at sea, with living space provided in accommodation hulks or the battleships to which the gunboats were tenders.
Ships
Name Ship Builder Launched Fate Jarrow 3 August 1876 Sold at Bermuda in 1904 Dover 22 October 1920 Bristol 9 July 1907 Malta 1892-1902 and sold there on 10 July 1902 Hong Kong in April 1903 edit] References - ^ a b c d e f g h i Winfield (2004) p.281
- ^ Gunboat (2007) p.167
- ^ a b "HMS Trent at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/T/04871.html. Retrieved 2011-05-31.
- ^ "HMS Spey at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/S/04352.html. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "HMS Dee at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/D/01310.html. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "HMS Don at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/D/01424.html. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "HMS Tay at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/T/04582.html. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "HMS Esk at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/E/01641.html. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "HMS Tweed at the Naval Database". http://www.pbenyon.plus.com/18-1900/T/04909.html. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- Winfield, Rif; Lyon, David (2004). The Sail and Steam Navy List: All the Ships of the Royal Navy 1815–1889. Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-032-6. OCLC 52620555.
- Preston, Anthony; Major, John (2007). Send a Gunboat, The Victorian Navy and Supremacy at Sea, 1854 1904 (2nd ed.). Conway Maritime. ISBN 9780851779232.
Medina-class gunboat Categories:- Small combat vessel classes
- Medina class gunboats
- Victorian era gunboats of the United Kingdom
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
List of World War II topics (I) — # I ll Remember April (film) # I Airborne Corps (United Kingdom) # I Armored Corps (United States) # I Canadian Corps # I Corps (Australia) # I Corps (France) # I Corps (Germany) # I Corps (United Kingdom) # I Corps (United States) # I Hua Huang… … Wikipedia
List of shipwrecks — Contents 1 Africa 1.1 East Africa 1.2 North Africa 1.2.1 Algeria … Wikipedia
Mexican Navy — (Armada de México) Mexican Navy Emblem Active January 19, 1821 Countr … Wikipedia
Peruvian Navy — Marina de Guerra del Perú Coat of arms of the Peruvian Navy Active October 8, 1821 today Country … Wikipedia
Peninsular War — For the 1862 American Civil War campaign, see Peninsula Campaign. Peninsular War Part of the Napoleonic Wars … Wikipedia
Iraq — /i rak , i rahk /, n. a republic in SW Asia, N of Saudi Arabia and W of Iran, centering in the Tigris Euphrates basin of Mesopotamia. 22,219,289; 172,000 sq. mi. (445,480 sq. km). Cap.: Baghdad. Also, Irak. * * * Iraq Introduction Iraq Background … Universalium
Mayaguez incident — Part of the Vietnam War … Wikipedia
Denmark — This article is about the country. For other uses, see Denmark (disambiguation). Denmark Danmark … Wikipedia
List of patrol vessels of the United States Navy — This is a list of patrol vessels of the United States Navy.PC Patrol Craft Coastal ;By hull number * * * * * * * * * * * * * *;By name * * * * * * * * * * * * * * PHM, PGH, PCH Hydrofoil VesselsPHM Patrol Missile Hydrofoil* USS Pegasus (PHM 1),… … Wikipedia