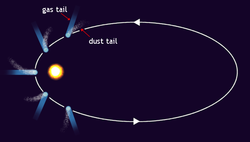
- Antitail
-
 Comet Lulin antitail to the left, ion tail to right
Comet Lulin antitail to the left, ion tail to right
An Antitail is a term used in astronomy to describe one of the three tails, all pointing in different directions, which may appear to emanate from a comet as it passes close to the Sun. The antitail appears, when viewed from Earth, as a spike projecting from the comet's coma towards the sun, and thus geometrically opposite to the other tails: the ion tail and the dust tail. The antitail is formed of larger dust particles, which are less affected by the sun's radiation pressure or solar wind, and tend to remain in the comet's orbital plane and eventually form a disc. As the earth passes through the comet's orbital plane, this disc is seen side on, and appears as the characteristic spike.[1] The other side of the disc can sometimes be seen, though it tends to be lost in the dust tail. The antitail is therefore normally visible for a brief interval only when the Earth passes through the comet's orbital plane.[2][3]
Most comets don't develop sufficiently for an antitail to become visible but notable comet that displayed anti-tails include Comet Arend-Roland in 1957 and Comet Hale-Bopp in 1997.
See also
- The coma and tail at the main Comet article.
Notes
- ^ "Encyclopedia of science:antitail". http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/A/antitail.html.
- ^ Rao, Joe (6 February 2009). "Newfound Comet Lulin to Grace Night Skies". SPACE.com. http://www.space.com/spacewatch/090206-ns-comet-lulin.html. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- ^ Tosar, Borja; Paolo Candy. "What is an antitail". 3.bp.blogspot. http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_yM063m-CN3M/SZ9YzVzA0OI/AAAAAAAAANk/627phmwTv14/s1600-h/antitail.jpg. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
External links
- Emily Lakdawalla - Got binoculars? Spot a comet near Saturn tonight (Feb. 23, 2009)
- Online Encyclopedia of Science - Antitail
Comets Features Nucleus · Coma · Tails · Antitail · Dust trail

Types Extinct · Lost · Great · Main-belt · Sungrazing (Kreutz Sungrazers) · Interstellar
Lists See also Categories:- Comets
- Comet stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.