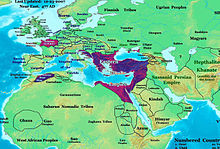
- Roman-Moorish kingdoms
-
Main article: Praetorian prefecture of Africa
Roman-Moorish kingdoms existed in much of present-day Morocco and Algeria between the end of effective Roman rule in the area and the Byzantine and Arab invasions of Africa. Direct Roman rule became confined to a few coastal cities (such as Ceuta in Mauretania Tingitana and Cherchell in Mauretania Caesariensis) from the late 3rd century in Mauretania Tingitana[1] and after the Vandal invasion of 429 in Mauretania Caesariensis.[2] Historical sources about inland areas are sparse, but these were apparently controlled by local Berber rulers who, however, maintained a degree of Roman culture, including the local cities, and usually nominally acknowledged the suzerainity of the Roman Emperors.[3] In an inscription from Altava in western Algeria, one of these rulers, Masuna, described himself as rex gentium Maurorum et Romanorum (king of the Roman and Moorish peoples).[4] Altava was later the capital of another ruler, Garmul or Garmules, who resisted Byzantine rule in Africa but was finally defeated in 578.[5] The Byzantine historian Procopius also mentions another independent ruler, Mastigas, who controlled most of Mauretania Caesariensis in the 530s.
The area was later reunited with the Byzantine Empire as a result of Justinian's campaigns of c. 533 AD; it was conquered by the Arabs at the end of the next century.
See also
Sources
- ^ Wickham, Chris (2005). Framing the Early Middle Ages: Europe and the Mediterranean, 400 - 800. Oxford University Press. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-19-921296-5. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ev8mb_Inv5sC&pg=PA18.
- ^ Wickham, Chris (2005). Framing the Early Middle Ages: Europe and the Mediterranean, 400 - 800. Oxford University Press. p. 335. ISBN 978-0-19-921296-5. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ev8mb_Inv5sC&pg=PA335.
- ^ Wickham, Chris (2005). Framing the Early Middle Ages: Europe and the Mediterranean, 400 - 800. Oxford University Press. p. 335. ISBN 978-0-19-921296-5. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ev8mb_Inv5sC&pg=PA335.
- ^ Wickham, Chris (2005). Framing the Early Middle Ages: Europe and the Mediterranean, 400 - 800. Oxford University Press. p. 335. ISBN 978-0-19-921296-5. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ev8mb_Inv5sC&pg=PA335.
- ^ Aguado Blazquez, Francisco (2005). El Africa Bizantina: Reconquista y ocaso. p. 46. http://www.biblioteca-tercer-milenio.com/sala-de-lectura/HistoriaUniversal/ImperioRomano/AfricaBizantina-conquistayocaso.pdf.
Categories:- Late Antiquity
- History of Algeria
- 5th century in Africa
- History of Morocco
- 6th century in Africa
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.