- Đurađ I Balšić
-
Đurađ I Died 13 January 1378
Shkodër, ZetaCause of death Natural causes Nationality Serb[1] Title Lord Term 1372 - 1378 Predecessor Balša I Successor Balša II Religion born Serbian Orthodox
Roman Catholic[2]Spouse Olivera Mrnjavčević
Teodora Dejanović DragašChildren Jelisaveta
Goisava
Jevdokija (Eudokia)
Konstantin (Košta)
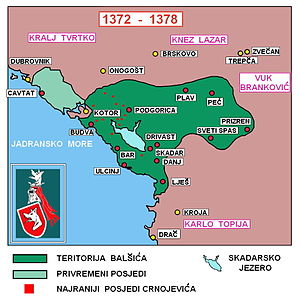
Đurađ (illegitimate)Parents Balša I Đurađ Balšić (Serbian Cyrillic: Ђурађ I) was the Lord of Zeta from 1362 - 13 January 1378. He was the eldest of the three sons of Balša I, and belonged to the House of Balšić.
Contents
Reign
He was the eldest son of Balša, a petty nobleman that held one village during the rule of Emperor Dušan the Mighty (r. 1331-1355), who was said to be "kin to Nemanja". The family started taking Lower Zeta sometime following the death of Dušan in 1355. In 1362 they murdered Đuraš Ilijić who was Head of Upper Zeta, the Balšići are henceforth recognized as Oblastni Gospodari (Lords) of Zeta, as evident in charters of Uroš the Weak (r. 1355-1371).
Campaign against Karlo Thopia
In 1363, Đurađ declared war against the Thopias, an Albanian noble family which controlled northern Albania. The Matarangos, an Albanian noble family which controlled southern Albania, were allied with the Balšićs as a result of a quarrel with the Thopias in the south. In the spring of 1364, Karlo Thopia took Đurađ captive due to a skirmish, ending Zetan involvement in the war. Đurađ was held captive until 1366 when Republic of Ragusa mediated peace and procured his release.
In January of 1368, a Ragusan document reported that the three Balšić brothers: Stracimir, Đurađ and Balša II, were preparing for a campaign against Karlo Thopia. They were camped on the Mati River, of which Karlo's lands lay south of. The fighting was apparently small-scale as two months later, Karlo had no difficulty capturing Dyrrhachium from the Angevins.[3]
Siege of Kotor
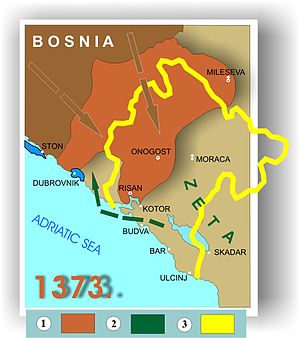
Hoping to acquire suzerainty over the town, Đurađ had waged war against Kotor in 1368. Kotor, as a result of warfare, was suffering economic decline. Accepting Zetan rule wasn't going to aid Kotor economically either. Kotor resisted Đurađ's assault after seeing the town of Bar paying an annual tribute of 2,000 ducats to Đurađ, previously paying 100 perpers to Serbia, expecting the same fate for Kotor. Kotor sought aid from Nikola Altomanović, but after his major defeat in Kosovo, he could provide little assistance. Kotor sought aid from the weak Tsar Uroš V and Venice. Neither provided much help as Venice was concerned that only their warships were on the Adriatic. In fact, Venice wrote to Tsar Uroš V in 1368, complaining that Serbia's armed ships were on the Adriatic, citing Bar, Budva nand Ulcinj to have them. They had also stated that this was also a violation of the Veneto-Serbian treaty and threatened to treat this ships as pirate vessels. However, Uroš replied to that letter, stating that these ships that Venice were complaining about belonged to Đurađ I Balšić, lord of Zeta.
Uroš was unhappy with Đurađ's actions as they were directed against Kotor, which was under Uroš' suzerainty. Concluding that Đurađ was a rebel, the Serbian court claimed no responsibility for Đurađ's actions that might violate the Veneto-Serbian treaty.
In 1369, Đurađ laid siege to Kotor. Kotor, having no choice, turned to Hungary for support and sought for Hungarian suzerainty. Hungary sent a nobleman from Zadar to be the Prince of Kotor. This action only increased Kotor's troubles, as it lost its trade privileges with Serbia for a time, causing a larger economic turmoil for Kotor. By spring 1370, probably through Venetian mediation, Đurađ had made peace with Kotor. However, in the same year, Nikola Altomanović attacked Kotor.[4]
Campaign against Nikola Altomanović
In 1371, Đurađ announced to Ragusan Republic that Vukašin Mrnjavčević and his son, Marko, along with their armies, were in Scutari with Đurađ, preparing an attack on Altomanović. Dubrovnik assisted their campaign by providing ships to transport men and supplies, since their campaign was in Dubrovnik's interests. However, the campaign never took place as Vukašin and Marko went to aid Vukašin's brother, Jovan Uglješa, in a campaign against the Turks, which ended up in total disaster, Uglješa being killed in the Battle of Maritsa. Altomanović thought was now in even more trouble. Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović of Serbia and Ban Tvrtko I of Bosnia allied themselves to defeat Nikola Altomanović. Desperate for a strong ally, Altomanović began negotiations with Đurađ. Most historians agree that in concluding negotiations, Đurađ gained the towns of Trebinje, Konavle and Dračevica from Altomanović, possibly a bribe to remain neutral within the war. Other historians, however, follow Mauro Orbini's account and argue that Đurađ never concluded such an agreement, rather conquered the towns he gained from the agreement himself after Altomanović was defeated in 1373.[5]
Rivalry with Prince Marko
After the Battle of Maritsa, Marko, the son of Vukašin Mrnjavčević, was crowned king and gained his father's lands. However, his friendship with the Balšićs soon crumbled. This was a result of Đurađ, in 1371, expelling his first wife Olivera, Marko's sister, and took Prizren from Marko. Lazar Hrebeljanović, prince of Moravian Serbia, conquered Priština in the same year. Đurađ took Peć a year later, stripping most of Marko's lands north of Šar mountain.[6]
Death
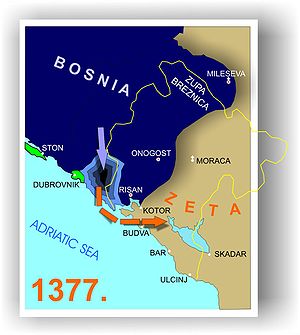
Đurađ I died on 13 January 1378 in Skadar. However, recent studies now conclude that Đurađ died in 1379 rather than in 1378. The rule of Zeta was passed down to his younger brother, Balša II. Đurađ's death caused quite a stir between Zeta's neighbours. Bosnian Ban Tvrtko I annexed Đurađ's territories bordering Dubrovnik in 1377, along with the remainder of Đurađ's coastal lands between the Bay of Kotor and the land previously annexed in 1377 at the time of his death. Tvrtko secured these possessions through Đurađ's death, free of worry of any counter-attack.
Vuk Branković also took this opportunity to gain Đurađ's land. Branković sent his forces into Metohija and seized Prizren, along with the rest of Đurađ's holdings in the region.[7]
Family and Children
Đurađ I was married to two women: Olivera Mrnjavčević (daughter of Vukašin Mrnjavčević) before 1364 and Teodora Dejanović/Dragaš (daughter of despot Dejan) after 1371. He had the following issue:
- Jelisaveta (d. 1443)
- Goisava (d. 1398), married Radič Sanković, lord of Nevesinje, Popovo Polje and Konavli
- Jevdokija (Eudokia), married to Esau de' Buondelmonti, despot of Epirus
- Konstantin (Košta) (d. 1402), local Zetan lord
- Đurađ (illegitimate)
References
Sources
- Sveta loza Stefana Nemanje, chapter 41: "Balša o kojem ćemo sada govoriti beše veoma siromašan zetski vlastelin i za života cara Stefana držao je samo jedno selo. Ali kad je umro car, a kako njegov sin Uroš nije bio valjan vladar, počeo je s nekoliko svojih prijatelja i sa svojim sinovima Stracimirom, Đurđem i Balšom da zauzima Donju Zetu."
"Posle toga krenuo je sa svojim ljudima na osvajanje Gornje Zete, koju je držao Đuraš Ilijić i njegovi rođaci. Đuraša ubiše Balšini sinovi, neke njegove rođake zarobiše, a ostali napustiše zemlju. I tako su Balšini sinovi zagospodarili i Gornjom Zetom" - Nicol, Donald MacGillivray (2010), The Despotate of Epiros 1267–1479: A Contribution to the History of Greece in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521130899, http://books.google.com/books?id=XIj0FfKto9AC
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994). The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Michigan: The University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472082604, 0472100793.
- Dr Željko Fajfrić - Sveta loza Stefana Nemanje, 1998
Preceded by
Balša IRuler of Zeta
1362 – 13 January 1378Succeeded by
Balša IICategories:- 1378 deaths
- 14th-century Serbian nobility
- Serbs of Montenegro
- History of Montenegro
- Rulers of Montenegro
- House of Balšić
- Montenegrin people stubs
- European royalty stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.