- Devil's Footprints
-
The Devil's Footprints is a name given to a phenomenon that occurred in February 1855 around the Exe Estuary in South Devon, England. After a heavy snowfall, trails of hoof-like marks appeared overnight in the snow covering a total distance of some 40 to 100 miles. The footprints were so called because some people believed that they were the tracks of Satan, as they were allegedly made by a cloven hoof. Many theories have been put forward to explain the incident, and some aspects of its veracity have also been called into question.
Contents
Incident
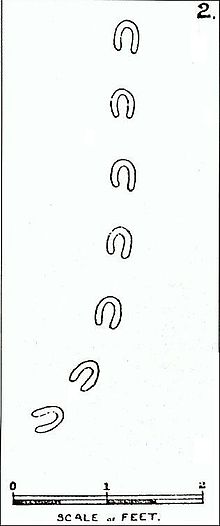
On the night of 7–8 February 1855 and one or two later nights,[1] after a heavy snowfall, a series of hoof-like marks appeared in the snow. These footprints, most of which measured around four inches long, three inches across, between eight and sixteen inches apart and mostly in a single file, were reported from over thirty locations across Devon and a couple in Dorset. It was estimated that the total distance of the tracks amounted to between 40 and 100 miles.[2] Houses, rivers, haystacks and other obstacles were travelled straight over, and footprints appeared on the tops of snow-covered roofs and high walls which lay in the footprints' path, as well as leading up to and exiting various drain pipes of as small as a four-inch diameter.[2]
The area in which the prints appeared extended from Exmouth, up to Topsham, and across the Exe Estuary to Dawlish and Teignmouth.[3] R.H. Busk, in an article published in Notes and Queries in 1890, stated that footprints also appeared further afield, as far south as Totnes and Torquay, and that there were other reports of the prints as far away as Weymouth (Dorset) and even Lincolnshire.[4]
There were also attendant rumours about sightings of a "devil-like figure" in the Devon area during the scare. Many townspeople armed themselves and attempted to track down the beast responsible, without success.[citation needed]
Evidence
There is little first-hand evidence of the phenomenon. The only known documents came to light after the publication in 1950 of an article in the Transactions of the Devonshire Association asking for further information about the event.[5] This resulted in the discovery of a collection of papers belonging to Reverend H. T. Ellacombe, the vicar of Clyst St George in the 1850s. These papers included letters addressed to the vicar from his friends, among them the Reverend G. M. Musgrove, the vicar of Withycombe Raleigh; the draft of a letter to The Illustrated London News marked 'not for publication'; and several apparent tracings of the footprints.[2][6]
Over many years the noted researcher Mike Dash collated all the available primary and secondary source material into a paper entitled The Devil's Hoofmarks: Source Material on the Great Devon Mystery of 1855 which was published in Fortean Studies in 1994.[7]
Theories
Many explanations have been put forward for the incident. Some investigators are sceptical that the tracks really extended for over a hundred miles, arguing that no-one would have been able to follow their entire course in a single day. Another reason for scepticism, as Joe Nickell points out, is that the eye-witness descriptions of the footprints varied from person to person.[8]
In his Fortean Studies article, Mike Dash concluded that there was no one source for the "hoofmarks": some of the tracks were probably hoaxes, some were made by "common quadrupeds" such as donkeys and ponies, and some by wood mice (see below). He admitted, though, that these cannot explain all the reported marks and "the mystery remains".[9]
Balloon
Author Geoffrey Household suggested that "an experimental balloon" released by mistake from Devonport Dockyard had left the mysterious tracks by trailing two shackles on the end of its mooring ropes. His source was a local man, Major Carter, whose grandfather had worked at Devonport at the time. Carter claimed that the incident had been hushed up because the balloon also wrecked a number of conservatories, greenhouses, and windows before finally descending to earth in Honiton.[10]
While this could explain the shape of the prints, sceptics have disagreed about whether the balloon could have travelled such a random zigzag course without its trailing ropes and shackles becoming caught in a tree or similar obstruction.
Hopping mice
Mike Dash suggested that at least some of the prints, including some of those found on rooftops, could have been made by hopping rodents such as wood mice. The print left behind after a mouse leaps resembles that of a cloven animal, due to the motions of its limbs when it jumps. Dash stated that the theory that the Devon prints were made by rodents was originally proposed as long ago as March 1855, in The Illustrated London News.[7]
Hysteria
It is also often suggested that the footprints were merely a case of mass hysteria, caused by the sighting of various animal tracks and lumping them together as one.[citation needed]
Kangaroo
In a letter to the Illustrated London News in 1855, Rev. G. M. Musgrave wrote: "In the course of a few days a report was circulated that a couple of kangaroos escaped from a private menagerie (Mr. Fische's, I believe) at Sidmouth." It seems, though, that nobody ascertained whether the kangaroos had escaped, nor how they could have crossed the Exe estuary,[11] and Musgrave himself said that he only came up with the story to distract his parishioners' concerns about a visit from the devil:
I found a very apt opportunity to mention the name of kangaroo, in allusion to the report then current. I certainly did not pin my faith to that version of the mystery ... but the state of the public mind of the villagers ... dreading to go out after sunset ... under the conviction that this was the Devil's work ... rendered it very desirable that a turn should be given to such a degraded and vitiated notion ... and I was thankful that a kangaroo ... [served] to disperse ideas so derogatory...Similar incidents
Reports of similar anomalous, obstacle-unheeded footprints exist from other parts of the world, although none is of such a scale as that of the case of the Devil's Footprints. This example was reported 15 years earlier in The Times:
Among the high mountains of that elevated district where Glenorchy, Glenlyon and Glenochay are contiguous, there have been met with several times, during this and also the former winter, upon the snow, the tracks of an animal seemingly unknown at present in Scotland. The print of the foot in every respect is an exact resemblance of that of a foal of considerable size, with this small difference perhaps, that the sole seems a little longer or not so round; but, as no one has had the good fortune as yet to have obtained a glimpse of this creature, nothing more can be said of its shape or dimensions; only it has been remarked, from the depth to which the feet sunk in the snow, that it must be a beast of considerable size; it has been observed also, that its walk is not like that of the generality of quadrupeds, but that it is more like the bounding or limping of a hare when not scared or pursued. It is not in one locality only that its tracks have been met with, but through a range of at least twelve miles...In the Illustrated London News of 17 March 1855, a correspondent from Heidelberg wrote, "upon the authority of a Polish Doctor in Medicine", that on the Piaskowa-góra (Sand Hill) a small elevation on the border of Galicia, but in Congress Poland, such marks are to be seen in the snow every year, and sometimes in the sand of this hill, and "are attributed by the inhabitants to supernatural influences".
On the night of 12 March 2009 marks claimed to be similar to those left in 1855 were found in Devon.[13]
See also
- Jersey Devil – the appearance in January 1909 of similar mysterious footprints in New Jersey, USA
- Phantom kangaroo
- The Great Thunderstorm, Widecombe – another legend of the Devil in Devon
- Urban legend
References
- ^ "Topsham. The two-legged wonder". Western Times. 24 February 1855.
- ^ a b c Dash, 1994. Introduction.
- ^ The Times 16-2-1855
- ^ Busk, R.H. (25 January 1890). "Phenomenal Footprints in the Snow, S. Devon". Notes and Queries s7-IX (213): 70. (Cited as Document 17 in Dash 1994)
- ^ Brown, Theo (1950). "The Great Devon Mystery of 1855 or "The Devil in Devon" (Forty-seventh Report on Folklore)". Report & Transactions of the Devonshire Association 82: 107–12.
- ^ Brown, Theo (1952). "A Further Note on "The Great Devon Mystery"". Report & Transactions of the Devonshire Association 84: 163–71.
- ^ a b Dash, 1994.
- ^ Joe Nickell, Real Life X-Files: Investigating the Paranormal.
- ^ Dash, 1994. Summary.
- ^ Household, Geoffrey (ed.) (1985). The Devil's Footprints : The Great Devon Mystery as it was Reported in the Newspapers of 1855. Exeter: Devon Books. ISBN 0861147537.
- ^ "Professor Owen on the foot-marks in the snow in Devon." Illustrated London News, 26 (March 4, 1855): 214.
- ^ Cited in Dash, 1994.
- ^ The Sun, 13 March 2009
Sources
- Dash, Mike (1994). "The Devil’s Hoofmarks". Fortean Studies (online at Academia.edu) 1: 71–150. http://independent.academia.edu/MikeDash/Papers/193347/The_Devils_Hoofmarks_Source_Material_on_the_Great_Devon_Mystery_of_1855#.
Further reading
Categories:- Paranormal
- Forteana
- 1855 in England
- History of Devon
- Devon folklore
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.