- Mentzelia multiflora
-
Mentzelia multiflora 
Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Asterids Order: Cornales Family: Loasaceae Genus: Mentzelia Species: M. multiflora Binomial name Mentzelia multiflora
Nutt. & A. Gray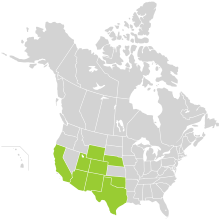
Mentzelia multiflora, commonly known as Adonis blazingstar, Adonis stickleaf, desert blazingstar, Prairie stickleaf and manyflowered mentzelia is a herbaceous perennial wildflower of the family Loasaceae native to the Southwestern United States, California, and northwestern Mexico. It is a blazingstar and is a member of the Mentzelia genus, the stickleafs.[1][2]
Contents
Description
This species grows to about 2–2 1/2 feet tall, has shiny white stems and numerous branches. Its sticky, bright green leaves are covered with hairs containing minute barbs. The flowers are around 5 cm (2 in) in diameter, are yellow in colour and normally have ten petals. The flowers open in late afternoon and close in the morning.[1][3] The flowers are hermaphrodite and flower from July to August.
Taxonomy
Mentzelia multiflora was first described by the botanists Thomas Nuttall and Asa Gray.
Distribution
Mentzelia multiflora is found in the western United States and northern Mexico from Montana and North Dakota, south to Sonora and Chihuahua.[4] This species prefers dry, sandy well-drained soil. They require direct sunlight and cannot grow in the shade.[5]
Uses
The plant is used as a Native American medicine to treat toothache. It is also a diuretic. The roots and leaves have been used to treat tuberculosis.[5]
Varieties
Mentzelia multiflora var. integra M.E. Jones
Mentzelia multiflora var. longiloba (J. Darl.) Kartesz[6][7]References
- ^ a b "NPIN: Mentzelia multiflora (Adonis blazingstar)". Wildflower.org. 2010-05-28. http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=MEMU3. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "Centennial Museum and Gardens - Home". Museum.utep.edu. http://museum.utep.edu/chih/gardens/plants/GtoM/mentzeliamult.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "Vascular Plants of the Gila Wilderness- Mentzelia multiflora". Wnmu.edu. http://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages2/gilaflora/mentzelia_multiflora.html. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "ITIS Standard Report Page: Mentzelia multiflora". Itis.gov. http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=503788. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ a b http://www.ibiblio.org/pfaf/cgi-bin/arr_html?Mentzelia+multiflora
- ^ "Welcome to the PLANTS Database | USDA PLANTS". Plants.usda.gov. 2010-07-26. http://plants.usda.gov. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ [http://ucjeps.berkeley.edu/cgi-bin/get_JM_treatment.pl?4990,4994,0,5011 Jepson
Further reading
- F. Chittendon. RHS Dictionary of Plants plus Supplement. 1956 Oxford University Press 1951
- Munz. A California Flora. University of California Press 1959
- Kunkel. G. Plants for Human Consumption. Koeltz Scientific Books 1984 ISBN 3-87429-216-9
- Huxley. A. The New RHS Dictionary of Gardening. 1992. MacMillan Press 1992 ISBN 0-333-47494-5
- Whiting. A. F. Ethnobotany of the Hopi North Arizona Society of Science and Art 1939
- Moerman. D. Native American Ethnobotany Timber Press. Oregon. 1998 ISBN 0-88192-453-9
External links
Categories:- Mentzelia
- North American desert flora
- Flora of the Southwestern United States
- Flora of Northwestern Mexico
- Flora of the California desert regions
- Flora of the Sonoran Deserts
- Traditional Native American medical plants
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
