- Neoflavonoid
-
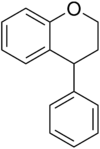
Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds[1]. While flavonoids (in the narrow sense) have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, neoflavonoids have the 4-phenylchromen backbone with no hydroxyl group substitution at position 2.
Contents
Types
Neoflavonoids include 4-arylcoumarins (neoflavones), 4-arylchromanes, dalbergiones and dalbergiquinols.
- Neoflavones[2] are derived from the 4-phenylcoumarin (or 4-Aryl-coumarin) backbone (C15H12O2, molar mass : 224.25g/mol, exact mass : 224.083729)[3]. The first neoflavone isolated from natural sources in 1951 was calophyllolide from Calophyllum inophyllum seeds[4].
- Neoflavenes possess the 4-phenylchromen backbone (chemical formula : C15H10O2, exact mass : 222.0680792). Dalbergichromene, extracted from the stem-bark and heartwood of Dalbergia sissoo, is an example of such compounds[5]
Other examples
- Coutareagenin (5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2H-benzo-1-pyran-2-on) found in Hintonia latiflora[6]
- Dalbergin
- Nivetin isolated from Echinops niveus[7]
References
- ^ The neoflavanoids, a new class of natural products. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, Volume 22, Number 12 / december 1966
- ^ Revised structure of neoflavone in Coutarea hexandra. Munekazu Iinuma, Toshiyuki Tanaka, Koji Hamada, Mizuo Mizuno, Fujio Asai, Gesa Reher and Ljubomir Kraus, Phytochemistry, Volume 26, Issue 11, 1987, Pages 3096-3097.
- ^ Structures of 4-Aryl-coumarin (Neoflavone) Dimers Isolated from Pistacia chinensis BUNGE and Their Estrogen-like Activity. Satoshi NISHIMURA, Motohiko TAKI, Sachiko TAKAISHI, Yasuteru IIJIMA and Toshiyuki AKIYAMA, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 48(4) 505—508 (2000)
- ^ Neoflavones. 1. Natural Distribution and Spectral and Biological Properties. M. M. Garazd, Ya. L. Garazd and V. P. Khilya, Chemistry of Natural Compounds, Volume 39, Number 1 / janvier 2003.
- ^ Dalbergichromene : A new neoflavonoid from stem-bark and heartwood of Dalbergia sissoo. Mukerjee S. K., Saroja T. and SeshadriT. R., Tetrahedron, Volume 27, Issue 4, 1971, Pages 799-803
- ^ Effects of the neoflavonoid coutareagenin, one of the antidiabetic active substances of Hintonia latiflora, on streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in rats. Korec R., Sensch K. H., Zoukas T., Symposium der Paul-Martini-Stiftung in Verbindung mit der Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur, Mainz, Germany (12/11/1999) 2000, vol. 50, no 2, pp. 189-224 (33 ref.), pp. 122-128
- ^ Nivetin, a neoflavonoid from Echinops niveus. Singh P. and Pandey V.B., Phytochemistry, Volume 29, Issue 2, 1990, Pages 680-681
External links
Types of Flavonoids Flavonoids Flavones | Flavonols (Pyranoflavonols, Furanoflavonols) | Flavanones | Flavanonols | Flavans | Flavan-3-ols | Flavan-4-ols | Flavan-3,4-diols | Anthocyanidins (Anthocyanins) | Condensed tanninsIsoflavonoids Isoflavones (Pyranoisoflavones) | Isoflavans | PterocarpansNeoflavonoids Aurones Aureusidin | LeptosidinOther categories C-methylated flavonoids | O-methylated flavonoids | Flavonolignans | Furanoflavonoids | Pyranoflavonoids | Methylenedioxyflavonoids | Prenylated flavonoids | CastavinolsFlavonoid biosynthesis This article about a natural phenol is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.