- DM domain
-
DM domain 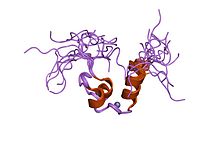
drosophila melanogaster doublesex (dsx), nmr, 18 structures Identifiers Symbol DM Pfam PF00751 InterPro IPR001275 SMART SM00718 SCOP 1rvv Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary In molecular biology the DM domain is a protein domain first discovered in the doublesex proteins of Drosophila melanogaster and is also seen in proteins from Caenorhabditis elegans.[1] In D. melanogaster the doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides.[2] These proteins are believed to function as transcription factors on downstream sex-determination genes, especially on neuroblast differentiation and yolk protein genes transcription.[3][4] The DM domain binds DNA as a dimer, allowing the recognition of pseudopalindromic sequences .[2][5][6] The NMR analysis of the DSX DM domain [6] revealed a novel zinc module containing 'intertwined' CCHC and HCCC zinc-binding sites. The recognition of the DNA requires the carboxy-terminal basic tail which contacts the minor groove of the target sequence.
References
- ^ Raymond CS, Shamu CE, Shen MM, Seifert KJ, Hirsch B, Hodgkin J, Zarkower D (February 1998). "Evidence for evolutionary conservation of sex-determining genes". Nature 391 (6668): 691–5. doi:10.1038/35618. PMID 9490411.
- ^ a b Erdman SE, Chen HJ, Burtis KC (December 1996). "Functional and genetic characterization of the oligomerization and DNA binding properties of the Drosophila doublesex proteins". Genetics 144 (4): 1639–52. PMC 1207715. PMID 8978051. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1207715.
- ^ Burtis KC, Coschigano KT, Baker BS, Wensink PC (September 1991). "The doublesex proteins of Drosophila melanogaster bind directly to a sex-specific yolk protein gene enhancer". EMBO J. 10 (9): 2577–82. PMC 452955. PMID 1907913. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=452955.
- ^ Shen MM, Hodgkin J (September 1988). "mab-3, a gene required for sex-specific yolk protein expression and a male-specific lineage in C. elegans". Cell 54 (7): 1019–31. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(88)90117-1. PMID 3046751.
- ^ Yi W, Zarkower D (February 1999). "Similarity of DNA binding and transcriptional regulation by Caenorhabditis elegans MAB-3 and Drosophila melanogaster DSX suggests conservation of sex determining mechanisms". Development 126 (5): 873–81. PMID 9927589.
- ^ a b Zhu L, Wilken J, Phillips NB, Narendra U, Chan G, Stratton SM, Kent SB, Weiss MA (July 2000). "Sexual dimorphism in diverse metazoans is regulated by a novel class of intertwined zinc fingers". Genes Dev. 14 (14): 1750–64. PMC 316782. PMID 10898790. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=316782.
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR001275
Categories:- Protein families
- Protein domains
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
