- Glycolonitrile
-
Glycolonitrile 

 2-HydroxyacetonitrileOther namesFormaldehyde cyanohydrin; Hydroxyacetonitrile; Glycolic nitrile; Cyanomethanol; Hydroxymethylnitrile
2-HydroxyacetonitrileOther namesFormaldehyde cyanohydrin; Hydroxyacetonitrile; Glycolic nitrile; Cyanomethanol; HydroxymethylnitrileIdentifiers CAS number 107-16-4 
PubChem 7857 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C(C#N)O
Properties Molecular formula C2H3NO Molar mass 57.05 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Glycolonitrile, also called hydroxyacetonitrile or formaldehyde cyanohydrin, is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2CN. It is the simplest cyanohydrin and it is derived from formaldehyde.[1] Because glycolonitrile decomposes readily into formaldehye and hydrogen cyanide, it is listed as an extremely hazardous substance.
Contents
Synthesis
Glycolonitrile can be synthesized by reacting formaldehyde with hydrogen cyanide under acidic conditions. This reaction takes place spontaneously even under aqueous conditions.[2]
Properties
Chemical properties
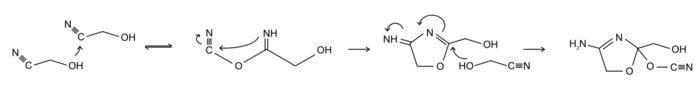
Gylcolonitrile polymerizes under alkaline conditions above pH 7.0. Arrhenius et al. have proposed the following mechanism for polymerization:[2]
As the product of polymerization is an amine with a basic character, the reaction is self-catalysed, gaining in speed with ongoing conversion.
References
- ^ Gaudry, R. (1955), "Glycolonitrile", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv3p0436; Coll. Vol. 3: 436
- ^ a b Arrhenius et al., J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 5522-5525
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.