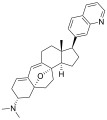
- Cortistatins
-
This article is about the class of alkaloids. For the neuropeptide, see cortistatin (neuropeptide).
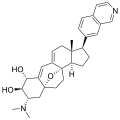
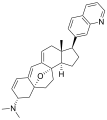
Cortistatin A 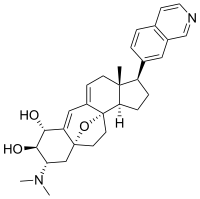 (1R,2R,3S,5R,8β,17β)-3-(Dimethylamino)-17-(isoquinolin-7-yl)-5,8-epoxy-9,19-cyclo-9,10-secoandrosta-9(11),10-diene-1,2-diolOther namesCortistatine A
(1R,2R,3S,5R,8β,17β)-3-(Dimethylamino)-17-(isoquinolin-7-yl)-5,8-epoxy-9,19-cyclo-9,10-secoandrosta-9(11),10-diene-1,2-diolOther namesCortistatine AIdentifiers CAS number 882976-95-6 
PubChem 11561907 ChemSpider 9736681 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C[C@]12CC=C3C=C4[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C[C@]45CC[C@@]3([C@@H]1CC[C@@H]2c6ccc7ccncc7c6)O5)N(C)C)O)O
- InChI=1S/C30H36N2O3/c1-28-10-8-21-15-23-26(33)27(34)24(32(2)3)16-29(23)11-12-30(21,35-29)25(28)7-6-22(28)19-5-4-18-9-13-31-17-20(18)14-19/h4-5,8-9,13-15,17,22,24-27,33-34H,6-7,10-12,16H2,1-3H3/t22-,24+,25-,26-,27-,28-,29-,30-/m1/s1
Key: KSGZCKSNTAJOJS-DZBMUNJRSA-N
InChI=1/C30H36N2O3/c1-28-10-8-21-15-23-26(33)27(34)24(32(2)3)16-29(23)11-12-30(21,35-29)25(28)7-6-22(28)19-5-4-18-9-13-31-17-20(18)14-19/h4-5,8-9,13-15,17,22,24-27,33-34H,6-7,10-12,16H2,1-3H3/t22-,24+,25-,26-,27-,28-,29-,30-/m1/s1
Key: KSGZCKSNTAJOJS-DZBMUNJRBJ
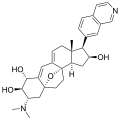
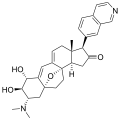
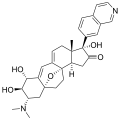
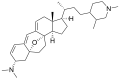
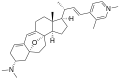
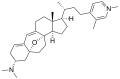
Properties Molecular formula C30H36N2O3 Molar mass 472.62 g mol−1 Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references The cortistatins are a group of steroidal alkaloids first isolated in 2006 from the marine sponge Corticium simplex.[1] The cortistatins inhibit proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with high selectivity, with cortistatin A being the most potent compound in the class.[2]
The unique chemical structure and potent biological activity of these compounds have stimulated interest in their total synthesis and further biological evaluation.[3][4]
Chemical structures
References
- ^ Aoki, S; Watanabe, Y; Sanagawa, M; Setiawan, A; Kotoku, N; Kobayashi, M (2006). "Cortistatins A, B, C, and D, anti-angiogenic steroidal alkaloids, from the marine sponge Corticium simplex". Journal of the American Chemical Society 128 (10): 3148–9. doi:10.1021/ja057404h. PMID 16522087.
- ^ Aoki, S; Watanabe, Y; Tanabe, D; Arai, M; Suna, H; Miyamoto, K; Tsujibo, H; Tsujikawa, K et al. (2007). "Structure-activity relationship and biological property of cortistatins, anti-angiogenic spongean steroidal alkaloids". Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 15 (21): 6758–62. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.08.017. PMID 17765550.
- ^ Chen, David Yu-Kai; Tseng, Chih-Chung (2010). "Chemistry of the cortistatins–a novel class of anti-angiogenic agents". Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 8 (13): 2900. doi:10.1039/C003935G.
- ^ Hardin Narayan, Alison R.; Simmons, Eric M.; Sarpong, Richmond (2010). "Synthetic Strategies Directed Towards the Cortistatin Family of Natural Products". European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2010 (19): 3553. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201000247.
Categories:- Steroids
- Alkaloids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.