- Classification System for Serial Criminal Patterns
-
The Classification System for Serial Criminal Patterns (CSSCP) is an artificial intelligence computer system that assists law enforcement officials in identifying links between serial crimes.[1] Working in conjunction with a neural network called a Kohonen network, CSSCP finds patterns in law enforcement databases by analyzing the characteristics of an offender, the criminal activities that have occurred, and the objects used in a crime. Once the links between crimes have been identified by CSSCP, law enforcement officials can then use the data that is produced to build leads or solve criminal cases. Through its capability to run autonomously, the CSSCP has proven that it can operate non-stop without any human interaction and can achieve results with much more accuracy and efficiency than a human.[2]Contents
Background
The Classification System for Serial Criminal Patterns was started by Professor Thomas Muscarello and Professor Kamal Dahbur at DePaul University in Chicago, Illinois in 1996 with the help of a Chicago Police Detective (Thomas Muscarello, personal communication, October, 2011). Muscarello and Dahbur recognized the need for their hybrid system as a result of recognized deficiencies in police practices. These deficiencies were said to be as a result of the police's difficulties in analyzing data and transforming it into information that could be useful in the investigation of crimes.[3] In addition to assisting law enforcement officials interpret data, the CSSCP was also designed to help investigators determine which criminal data was critical to an investigation and which format it should be stored in.
Although a similar project was previously undertaken by Timothy O'Shea, Muscarello and Dahbur noticed that problems existed with this proposed system because it relied on limited pre-processing and complex algorithms that lead to computational problems.[3]
The objective of Professor Muscarello and Professor Dahbur was to create an "automated methodology that can systematically identify groups of records as potential patterns for serial criminals, with a good degree of accuracy".[3]
System Design
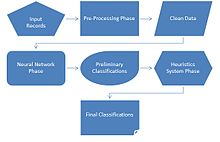
The CSSCP program was designed to work in three separate phases in conjunction with a Kohonen network. The three phases of CSSCP include:
-
- Pre-processing phase
- Neural network phase
- Heuristics system phase
Pre-Processing Phase
The Pre-Processing Phase of CSSCP is considered to be the most important phase of the system because it is the phase in which data is structured and put in a format that can be used by the neural network.[3] This phase is where CSSCP will analyze the records it's provided, detect patterns among the data, and assign the data values according to the algorithm chosen. The pre-processing phase relies heavily on accurate and complete input data in order for the output data (results) to also be accurate and complete.
Within the pre-processing phase of CSSCP there are four major functions that take place in order to ensure that input data is processed correctly for the next phases. The four functions include:
-
- Providing categories for missing values- In CSSCP, when a characteristic of a crime comes up that has not been previously assigned a value, the pre-processing phase will ensure that a category is created to account for that value so that it can be grouped with other characteristics of the same value in the future.
-
- Standardization- By standardizing all the values (both discrete and continuous), the data can be better analyzed and a measure can be given to their significance in relation to other values. The standardization of all attributes serves the very important purpose of closing down the gaps among their respective domains.[3]
-
- Categorizations & re-categorization- The Categorizing and re-categorizing of values and variables allows for users of CSSCP to determine a relationship between the values and variables and to create broader categories for data to be classified in. This function of CSSCP was created so that fewer categories could be used and so that the values could have more meaning to the user.
-
- Grouping- Grouping in CSSCP is conducted so that discovering patterns can be done more effectively. Grouping allows adjustments to be made to the variables so that patterns can be depicted.
Neural Network Phase
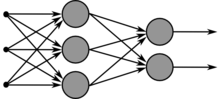
The Neural Network phase of CSSCP is where machine learning algorithms are used for clustering and prediction tasks.[3] The type of neural network used in CSSCP is called a Kohonen network. The Kohonen network is an unsupervised learning network that uses a simple algorithm to make computations without needing to know the type or number of classifications to be used.[4]
In the neural network phase, all the attributes and features of a case are grouped according to their given values (similarity) and each group is then presented to an independent Kohonen network. The independent Kohonen networks provide output independently and in parallel with the other independent networks in the system.[3] Once presented to the independent Kohonen networks, the groups are then combined for a final time and sent to a final Kohonen network. After being sent to the final Kohnen network, the system will suggest the preliminary classifications that will be sent on to the next and final phase. By the end of the neural network phase, all of the input data will have been analyzed, grouped, and classified into patterns that will become the basis for which the final results depend on.
Heuristics System Phase
The heuristics system phase is the final phase of the CSSCP application and is the stage at which the output data is refined. During this phase, the preliminary classifications that were developed in the previous phase are enhanced in order to improve classifications or to eliminate deficiencies. In CSSCP, heuristics are used for two main purposes:
-
- Adding records to a class
- Extracting records from a class
CSSCP uses heuristics to add records to a class that have been left out by the neural network. In CSSCP in particular, crimes that occur before midnight and after midnight would not be grouped together during the neural network phase regardless of how many similarities exists between them. The use of heuristics corrects this problem by adding an appropriate group for both crimes to be grouped together.[3]
CSSCP also uses heuristics to extract or remove records from a class in two ways. One way is in instances where the neural network has grouped two or more specific crimes together that cannot be related to each other. The second way is in instances when classifications have been created that are irrelevant to the user; such as when a group is created to compare characteristics of multiple criminals involved in the same crime as opposed to a group that compares the characteristics of the crime itself.
Applications
The first use of CSSCP was during a trial study in which statistics from three years of armed robbery cases were analyzed. Professor Muscarello decided to demonstrate with armed robbery cases not only because they were some of the most frequent cases dealt with by police, but also because they tend to demonstrate common patterns that would highlight the abilities of CSSCP.[3] During the trial, CSSCP demonstrated how it could correctly classify patterns at a much higher rate than the suggested one percent that a Rand Corporation study reported as the common rate.[5] Because of CSSCP's success during the trial studies, the Chicago Police Department decided to conduct live trials of CSSCP on their networks in 2006. However,due to upper management changes within the Chicago Police Department and the retirement of the Deputy Superintendent who sponsored the project, CSSCP was never actually put into use by the department (Thomas Muscarello, personal communication, October, 2011).
The CSSCP program is designed to assist law enforcement officials who constantly deal with large volumes of criminal cases beyond what their departments can effectively handle by providing them with an inexpensive tool that can reduce investigation costs and department man-power.[5] However, the application of CSSCP does not intend to entirely replace human detectives with a computer program, but instead intends to assist detectives by making their jobs easier and their workloads lighter.[6]
Through its ability to continuously operate accurately at a rate of ten times faster than a team of detectives doing the same type of work, CSSCP has begun to draw interest from law enforcement agencies all over the world that are looking for tools that can enhance security.[6]
References
- ^ The Crime Report, (2005). "Super Computer Program To Track Chicago Crime Patterns". www.thecrimereport.org. Retrieved on 2011-10-16. Available @ http://www.thecrimereport.org/archive/super-computer-program-to-track-chicago-crime-patterns.
- ^ Patrice M. Jones, (2005). "The cyber sleuth". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved on 2011-10-17. Available @ http://articles.chicagotribune.com/2005-11-29/features/0511290268_1_computer-system-cyber-sleuth-violent-crimes.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Kamal Dahbur and Thomas Muscarello, (2004). "Classification system for serial criminal patterns". Artificial Intelligence and Law 11: 251–269.
- ^ Kohonen, T. (1990). The Self-Organizing Map, Proceedings of IEEE, 78 (9).
- ^ a b DePaul University, (2004). "DePaul Researchers Develop Computer Program to Assist Police in Identifying Patterns of Criminal Activity". DePaul University. Retrieved on 2011-10-18. Available @ https://newsroom.depaul.edu/NewsReleases/showNewsPrint.aspx?NID=1258.
- ^ a b The Age, (2005). "Tech comes to the aid of crimefighters". www.theage.com.au. Retrieved on 2011-10-22. Available @ http://www.theage.com.au/news/technology/tech-comes-to-the-aid-of-crimefighters/2005/12/12/1134235994179.html.
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.