- Chlorophyll d
-
Chlorophyll d 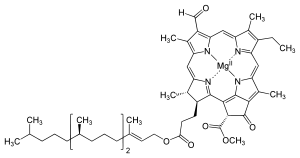
Identifiers CAS number 519-63-1 
PubChem 16070025 ChemSpider 16736116 
ChEBI CHEBI:38199 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)CCC[C@@H](C)CCC[C@@H](C)CCCC(\C)=C\COC(=O)CC[C@H]6[C@H](C)C=5/C=C/2\N\1[Mg]n4c(\C=C\3/N=C(/C=C/1C(\C=O)=C\2\C)C(/C)=C/3/CC)c(C)c7c4\C(=C6/N=5)[C@@H](C(=O)OC)C7=O
- InChI=1S/C54H71N4O6.Mg/c1-12-38-34(7)42-27-46-40(29-59)36(9)41(56-46)26-43-35(8)39(51(57-43)49-50(54(62)63-11)53(61)48-37(10)44(58-52(48)49)28-45(38)55-42)22-23-47(60)64-25-24-33(6)21-15-20-32(5)19-14-18-31(4)17-13-16-30(2)3;/h24,26-32,35,39,50H,12-23,25H2,1-11H3,(H-,55,56,57,58,59,61);/q-1;+2/p-1/b33-24+;/t31-,32-,35+,39+,50-;/m1./s1

Key: QXWRYZIMSXOOPY-SKHCYZARSA-M
InChI=InChI=1S/C54H71N4O6.Mg/c1-12-38-34(7)42-27-46-40(29-59)36(9)41(56-46)26-43-35(8)39(51(57-43)49-50(54(62)63-11)53(61)48-37(10)44(58-52(48)49)28-45(38)55-42)22-23-47(60)64-25-24-33(6)21-15-20-32(5)19-14-18-31(4)17-13-16-30(2)3;/h24,26-32,35,39,50H,12-23,25H2,1-11H3,(H-,55,56,57,58,59,61);/q-1;+2/p-1/b33-24+;/t31-,32-,35+,39+,50-;/m1./s1
Properties Molecular formula C54H70MgO6N4  d (verify) (what is:
d (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references
Chlorophyll d is a form of chlorophyll, identified in 1996. It absorbs far-red light, at 710 nm wavelength, just outside the optical range.[1] Acaryochloris marina, a bacterium, uses it for photosynthesis.[2]References
- ^ http://www.physorg.com/news201502581.html
- ^ "Researchers decode genetics of rare photosynthetic bacterium" (Press release). EurekAlert!. 7-Feb-2008. http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2008-02/asu-rdg020708.php. Retrieved 9 July 2010.
Types of Plant pigments Flavonoids Betalains Betacyanins • BetaxanthinsCarotenoids Xanthophylls • Carotenes • RetinoidsOther Chlorophyll (a, b, c1, c2, d, f) • Allophycocyanin • Phycocyanin • Phycoerythrin • Phycoerythrocyanin • Quinones • XanthonoidsCategories:- Biochemistry stubs
- Tetrapyrroles
- Photosynthetic pigments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
