- Peabody Trust
-
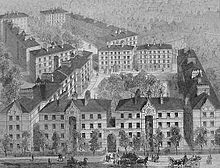 Peabody Square on Blackfriars Road, Southwark, is a typical example of an early Peabody estate, and of pre-World War I social housing in London in general.
Peabody Square on Blackfriars Road, Southwark, is a typical example of an early Peabody estate, and of pre-World War I social housing in London in general.
 Peabody Trust housing on Marshalsea Road in Southwark.
Peabody Trust housing on Marshalsea Road in Southwark.
Peabody Trust (Peabody), founded in 1862, is one of London's oldest and largest housing associations with over 19,000 properties. It also a charity and urban regeneration agency. The organisation was originally named the Peabody Donation Fund, and now brands itself simply as “Peabody”.[1]
Contents
History
The Trust was founded in 1862 by London-based American banker George Peabody, who in the 1850s had developed a great affection for London, and determined to make a charitable gift to benefit it. His initial ideas included a system of drinking fountains (comparable to the Metropolitan Drinking Fountain and Cattle Trough Association scheme actually set up by Samuel Gurney and Edward Thomas Wakefield in 1859), or a contribution to the "ragged schools" of the Earl of Shaftesbury. In March 1859, however, he settled on establishing a model dwellings company. Three years later, in a letter to The Times on 26 March 1862, he launched the Peabody Donation Fund, with an initial gift of £150,000. The aim of the organisation, he said, would be to "ameliorate the condition of the poor and needy of this great metropolis, and to promote their comfort and happiness". The paper reported, "We have today to announce an act of beneficence unexampled in its largeness and in the time and manner of the gift".[2] Shortly before his death in 1869, Peabody increased his gift to a munificent £500,000.[3]
The Peabody Trust was later constituted by Act of Parliament, stipulating its objectives to work solely within London for the relief of poverty. This was to be expressed through the provision of model dwellings for the capital's poor.
 The first block of Peabody dwellings in Commercial Street, Spitalfields. A wood-engraving published in the Illustrated London News in 1863, shortly before the building opened.
The first block of Peabody dwellings in Commercial Street, Spitalfields. A wood-engraving published in the Illustrated London News in 1863, shortly before the building opened.
The first block, designed by H.A. Darbishire in a red-brick Jacobethan style, opened in Commercial Street, Spitalfields, on 29 February 1864.[4] It cost £22,000 to build, and contained 57 "dwellings" (i.e. flats) for the poor, nine shops with accommodation for the shopkeepers, and baths and laundry facilities on the upper floor.[5][6]. It was followed by blocks in Chelsea, Bermondsey, Islington and Shadwell. By 1882 the Trust housed more than 14,600 people in 3,500 dwellings. By 1939 it owned more than 8,000 dwellings.
In its early days, the Trust imposed strict rules to ensure that its tenants were of good moral character. Rents were to be paid weekly and punctually; there was a night-time curfew and a set of moral standards to be adhered to; and the dwellings could not be used for certain trades.
Current Mission
Peabody's current mission is to make London a city of opportunity for all by ensuring as many people as possible have a good home, a real sense of purpose and a strong feeling of belonging.[7]
Peabody defines "a good home" as "a place that is safe, warm, clean, light, well maintained and evokes personal pride"; "a real sense of purpose" as "regular endeavour through work, learning, caring for others, personal development or volunteering"; and "a strong feeling of belonging" as "active involvement in the neighbrouhood and the spirit of togetherness and friendliness that goes with it".[1]
21st Century Peabody
In December 2009, Peabody launched its new vision for social housing communities in the 21st century. The vision was announced alongside regeneration plans for Peabody's estate near Clapham Junction.[8]
Areas of activity
Peabody has four areas of activity:
- The provision of rented housing for people who are unable to afford to rent or buy in the open market;
- The provision of supported housing and care for those who need additional support;
- The provision of low cost home ownership, particularly shared ownership;
- The delivery of community regeneration activities such as the provision of learning opportunities and access to training and accreditation.[1]
Activate London
Peabody leads Activate London, funded by the Big Lottery Fund, in partnership with Broomleigh Housing, Circle Anglia, Family Mosaic, Metropolitan Housing, Southern Housing and CBHA.
Activate London promotes mental well-being, physical activity and healthy eating. Over 80 community projects developed to suit a wide range of interests will be launched across London over the course of Activate London programme (2008–2012).
Peabody's Activate London projects include Cockney Sparrow, an initiative to create wildlife havens on Peabody estates, and Elvis' Kitchen, a healthy eating campaign fronted by charismatic Peabody caretaker Elvis Campbell.[9][10]
Well-being Wagon
As part of Activate London, Peabody operates the Well-being Wagon, a large green van that visits Peabody estates across London offering free health checks and healthy living advice.
Peabody Group
The Peabody Group comprises two housing associations, Peabody and CBHA, and a number of trading companies.[1]
Community-based Housing Association
Community-based Housing Association (CBHA) is a community-based housing association serving the London Borough of Waltham Forest and surrounding areas. It is the successor landlord to Waltham Forest Housing Action Trust. The organisation owns around 1,600 homes in six areas:
- Cambridge Road estate, Oatland Rise and Gosport Road estate, Walthamstow
- Cathall, Leytonstone
- Chingford Hall estate, Chingford
- Oliver Close, Leyton
Funding
Housing associations borrow money to pay for new homes and improvements. In March 2011, Peabody raised £200 million on a corporate bond, at a rate among the best secured by a housing association borrowing in its own name.[11]
See also
- List of existing model dwellings
References
- ^ a b c d Peabody report and financial statements 2009, Peabody, UK.
- ^ "Unprecedented Munificence" and untitled leader article, The Times, 26 Mar. 1862, p. 9.
- ^ News story, Peabody website
- ^ The block was sold by the Trust in the late 1970s, being considerably smaller than most of the later estates and outdated in its facilities. However, it still stands, and is now a private residential block named The Cloisters.
- ^ "Mr. Peabody's Gift", The Times, 1 Feb. 1864, p. 5.
- ^ Illustrated London News (1863).
- ^ About us, Peabody, UK.
- ^ 21st Century Peabody report, UK.
- ^ Cockney Sparrow, Blogspot.
- ^ Elvis' Kitchen.
- ^ Peabody issues £200m bond, Inside Housing, UK, 11 March 2011.
Further Reading
- Parker, Franklin (1995). George Peabody: a biography (2nd ed.). Nashville & London.
External links
- peabody.org.uk, official website
- Peabody on Flickr
- peabodytenants.co.uk, unofficial Peabody tenants' website & forum
Housing associations in London G15 A2 Dominion · Affinity Sutton · Amicus Horizon · Catalyst · Circle · East Thames · Family Mosaic · Genesis · Hyde · L&Q · Metropolitan · Notting Hill · Network · Peabody · SouthernNational associations in London Local associations Housing cooperatives Categories:- Organizations established in 1862
- 1862 establishments in the United Kingdom
- Housing associations
- Housing in London
- Charities based in London
- Model dwellings
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
