- Decade (log scale)
-
One decade is a factor of 10 difference between two numbers (an order of magnitude difference) measured on a logarithmic scale. It is especially useful when referring to frequencies and when describing frequency response of electronic systems, such as audio amplifiers and filters.
Calculations
The factor-of-ten in a decade can be in either direction: so one decade up from 100 Hz is 1000 Hz, and one decade down is 10 Hz. The factor-of-ten is what is important, not the unit used, so 3.14 rad/s is one decade down from 31.4 rad/s.
To determine the number of decades between two frequencies, use the logarithm of the ratio of the two values:
- How many decades is it from 15 rad/s to 150,000 rad/s?
- log 10(150000 / 15) = 4 decades
- How many decades is it from 3.2 GHz to 4.7 MHz?
 decades
decades
- How many decades is one octave?
- One octave is a factor of 2, so log 10(2) = 0.301 decades per octave
To find out what frequency is a certain number of decades from the original frequency, multiply by appropriate powers of 10:
- What is 3 decades down from 220 Hz?
 Hz
Hz
- What is 1.5 decades up from 10?
To find out the size of a step for a certain number of frequencies per decade, raise 10 to the power of the inverse of the number of steps:
- What is the step size for 30 steps per decade?
- 101 / 30 = 1.079775 - or each step is 7.9775% larger than the last.
 Bode plot showing the concept of a decade: each major division on the horizontal axis is one decade
Bode plot showing the concept of a decade: each major division on the horizontal axis is one decade
Graphical representation and analysis
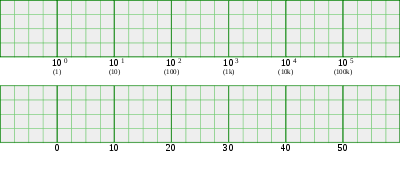
Decades on a logarithmic scale, rather than unit steps (steps of 1) or other linear scale, are commonly used on the horizontal axis when representing the frequency response of electronic circuits in graphical form, such as in Bode plots, since depicting large frequency ranges on a linear scale is often not practical. For example, an audio amplifier will usually have a frequency band ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz and representing the entire band using a decade log scale is very convenient. Typically the graph for such a representation would begin at 1 Hz (100) and go up to perhaps 100 kHz (105), to comfortably include the full audio band in a standard-sized graph paper, as shown below. Whereas in the same distance on a linear scale, with 10 as the major step-size, you might only get from 0 to 50.
Electronic frequency responses are often described in terms of "per decade". The example Bode plot shows a slope of -20 dB/decade in the stopband, which means that for every factor-of-ten increase in frequency (going from 10 rad/s to 100 rad/s in the figure), the gain decreases by 20 dB.
See also
Categories:- Charts
- Scales
- Electronics terms
- How many decades is it from 15 rad/s to 150,000 rad/s?
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.