- Désert de Retz
-
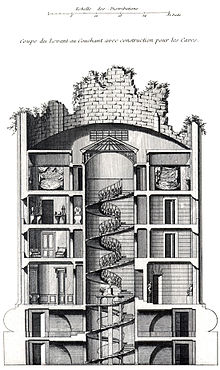
The Désert de Retz is an Anglo-Chinois or French landscape garden - created on the edge of the forêt de Marly in the commune of Chambourcy, in north-central France. It was built at the end of the 18th century by the aristocrat François Racine de Monville on his 40-hectare (99-acre) estate. It is notable for the construction of 17 (or 20) buildings, of which only 10 still survive, referring to classical antiquity or in an exotic style. Those buildings include: a summer house (the "colonne brisée", or ruined column), in the form of the base of a shattered column from an imaginary gigantic temple, an ice house in the form of an Egyptian pyramid, an obelisk, a temple dedicated to Pan, and a (now-lost) Chinese pavilion.
Contents
History
In 1774, Monville bought the house, its service quarters and an estate of about 13 hectares (32 acres) from Antoine Joseph Basire, and then extended the estate to 90 arpents (31 ha) by 1785. In July 1792, Monville sold the Désert and his two hôtels in Paris to the Englishman Lewis Disney Ffytche and as the property of an English subject these were seized and sold in 1793 on the outbreak of the War of the First Coalition. En 1811, Lebigre Beaurepaire bought the Désert, but he did not honour his debts, and the estate was again seized and in 1816 sold back to Disney Ffytche after the Bourbon Restoration. Ffytche's grandson Auguste Guilaume Hilary took possession in 1824 and sold it in 1827 to a notary of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Maître Alexandre Marie Denis. Denis sold it in 1839 to Jean-François Bayard, a nephew of Eugène Scribe.
In 1856, Jean-François Bayard's widow ceded it to Frédéric Passy (1822-1912) and his son Pierre (born on the estate) added a hen farm but in 1936 was forced to sell the estate due to financial difficulties, with the buyer being Georges Courtois. Courtois bought into via par a société named Neueberg. When he realised how much work was needed to restore the Désert (now nearly in ruins), the new owner decided not to do so, though the architect Jean-Charles Moreux bemoaned its ruined state. It was decided to list the estate and its buildings on 9 December 1938, resulting in a decree signed on 30 August 1939, and published 25 November 1939. However, the société owning it changed the statutes, forcing the authorities to resume the procedure to have the Désert finally classed as a monument historique, which came with a decree of 9 April 1941, against the owners' wishes. On 8 December 1966, André Malraux, then minister of culture, strongly evoked the estate's state before the Assemblée Nationale l’état du domaine and had them vote for the law of 30 December 1966, which allowed the Désert to be saved. The main effect of this law was to force a building's owner to pay 50% of the cost of the work. On the 31 December 1981, the Worms group bought the Désert and gave it to the Société Civile du Désert de Retz.
Part of the former estate has since 1992 been occupied by the Joyenval golf course.
Structures
The 1785 plan in Monville's hand mentions:
- The ruined column
- Rock at the entrance to the garden
- Temple to the God Pan
- Ruined Gothic church
- Chinese house
- Dairy
- a "Métairie arrangée"
- Hermitage
- Orangery
- "Isle du Bonheur" (Isle of Happiness)
- Greenhouses
- a "Chaumière" or thatched cottage
- Tomb
- Pyramid icehouse
- Obelisk
- "Communs"
- open-air theatre.
To this list may be added:
- Tartar tent
- Temple of repose
- Little Altar.
Famous visitors
The garden was visited around the time of its creation by Gustav III of Sweden (to whom Monville offered some drawings) as well as the prince de Ligne, the duc de Chartres and Thomas Jefferson (who inspired the ruined column). Later visitors included Colette and André Breton.
Bibliography
- Louis-Eugène Lefevre, Le Jardin anglais et la singulière habitation du Désert de Retz près de Marly, Paris éd. Jean Schemit, 1917, tiré à part du Bulletin de la Commission des Antiquités et des Arts de Seine-et-Oise.
- Pierre-Émile Renard, Chambourcy, son passé, 1980
- Pierre-Émile Renard, Chambourcy et le Désert de Retz, 1984
- Michel Dach, Le Désert de Retz à la lumière d’un angle particulier, 1995
- Le Désert de Retz, texte anonyme publié en avril 1988 par la Société Civile du Désert de Retz, Croissy sur Seine.
- Julien Cendres, Chloé Radiguet, Le Désert de Retz, paysage choisi, éditions de l'éclat, septembre 2009, nouvelle édition revue et augmentée
External links
- Désert de Retz on Flickr
- Fascinating article on the Broken column, with beautiful black-and-white photos.
- Association d’Histoire de Chambourcy de Retz et d’Aigremont (HISCREA)
- The désert de Retz.
- Photos of the Désert de Retz
- The Racine de Monville Home Page (English-language website about the Désert de Retz and François Racine de Monville, created in 1996 and continually updated. Numerous exclusive color photographs; detailed, hyperlinked chronology of the life of François Racine de Monville; extensive bibliography and list of sources and references.)
Categories:- Gardens in Yvelines
- French architecture
- Folly buildings
- Yvelines
- Visitor attractions in France
- English Landscape Garden style
- Landscape design history of France
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.