- Greek letters used in mathematics, science, and engineering
-

Greek alphabet Αα Alpha Νν Nu Ββ Beta Ξξ Xi Γγ Gamma Οο Omicron Δδ Delta Ππ Pi Εε Epsilon Ρρ Rho Ζζ Zeta Σσς Sigma Ηη Eta Ττ Tau Θθ Theta Υυ Upsilon Ιι Iota Φφ Phi Κκ Kappa Χχ Chi Λλ Lambda Ψψ Psi Μμ Mu Ωω Omega History Archaic local variants
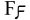 ·
·  ·
·  ·
·  ·
·  ·
· 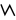
Ligatures (ϛ, ȣ, ϗ) · Diacritics Numerals: 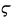 (6) ·
(6) · 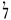 (90) ·
(90) · 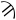 (900)
(900)In other languages Bactrian · Coptic · Albanian Scientific symbols
 Book ·
Book ·  Category ·
Category ·  Commons
Commons
Greek letters are used in mathematics, science, engineering, and other areas where mathematical notation is used as symbols for constants, special functions, and also conventionally for variables representing certain quantities. In these contexts, the capital letters and the small letters represent distinct and unrelated entities. Those Greek letters which have the same form as Latin letters are usually not used: capital A, B, E, H, I, K, M, N, O, P, T, X, Y, Z. Small ι (iota), ο (omicron) and υ (upsilon) are also rarely used, since they closely resemble the Latin letters i, o and u. Sometimes font variants of Greek letters are used as distinct symbols in mathematics, in particular for φ (phi) and π (pi).
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the variables denoted by Greek letters used to describe the risk of certain investments.
English-speaking mathematicians use neither the modern nor the historical Greek pronunciations of the names of the letters, but the traditional English pronunciation, e.g. /ˈθeɪtə/ for θ, cf. ancient [tʰɛ̂ːta] and modern [ˈθita].
Typography
The Greek letter forms used in maths are often different from those used in Greek-language text: they are designed to be used in isolation, not connected to other letters, and some use variant forms which are not normally used in current Greek typography.
The OpenType font format has the feature tag 'mgrk' "Mathematical Greek" to identify a glyph as representing a Greek letter to be used in mathematical (as opposed to Greek language) contexts.
The table below shows a comparison of Greek letters rendered in TeX and HTML. The font used in the TeX rendering is an italic style. This is in line with the convention that variables should be italicized. As Greek letters are more often than not used as variables in mathematical formulas, a Greek letter appearing similar to the TeX rendering is more likely to be encountered in works involving mathematics.
Greek letters Name TeX HTML Name TeX HTML Name TeX HTML Name TeX HTML Name TeX HTML Alpha 
Αα Digamma 
Ϝϝ Kappa 
Κκ Omicron 
Οο Upsilon 
Υυ Beta 
Ββ Zeta 
Ζζ Lambda 
Λλ Pi 
Ππϖ Phi 
Φϕφ Gamma 
Γγ Eta 
Ηη Mu 
Μμ Rho 
Ρρϱ Chi 
Χχ Delta 
Δδ Theta 
Θθϑ Nu 
Νν Sigma 
Σσς Psi 
Ψψ Epsilon 
Εϵε Iota 
Ιι Xi 
Ξξ Tau 
Ττ Omega 
Ωω Concepts represented by a Greek letter
Αα (alpha)
- α represents:
- the first angle in a triangle, opposite the side A
- one root of a quadratic equation, where β represents the other
- the ratio of collector current to emitter current in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) in electronics
- the statistical significance of a result
- the false positive rate in statistics
- the reciprocal of the sacrifice ratio
- the fine structure constant in physics
- the angle of attack of an airplane
- an alpha particle (He2+)
- angular acceleration in physics
- the linear thermal expansion coefficient
- the thermal diffusivity
- the alpha carbon is the first carbon after the carbon that attaches to a functional group in organic chemistry
- the α-carbon is the backbone carbon next to the carbonyl carbon in amino acids
- right ascension in astrometry
Ββ (beta)
- Β represents the beta function
- β represents:
- the second angle in a triangle, opposite the side B
- one root of a quadratic equation, where α represents the other
- the ratio of collector current to base current in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) in electronics (current gain)
- the false negative rate in statistics
- the beta coefficient, the non-diversifiable risk, of an asset in mathematical finance
- the sideslip angle of an airplane
- the first-order effects of variations in Coriolis force with latitude in planetary dynamics
- a beta particle (e-)
- sound intensity
- velocity divided by the speed of light in special relativity
- the beta brain wave in brain or cognitive sciences
- ecliptic latitude in astrometry
Γγ (gamma)
- Γ represents:
- the reflection coefficient of a transmission or telecommunication line.
- the confinement factor of an optical mode in a waveguide
- the gamma function, a generalization of the factorial
- the upper incomplete gamma function
- the modular group, the group of fractional linear transformations
- the gamma distribution, a continuous probability distribution defined using the gamma function
- second-order sensitivity to price in mathematical finance
- the Christoffel symbols of the second kind
- γ represents:
- the partial safety factors applied to loads and materials in structural engineering
- the specific weight of substances
- the lower incomplete gamma function
- the third angle in a triangle, opposite the side C
- the Euler-Mascheroni constant in mathematics
- gamma rays and the photon
- the heat capacity ratio in thermodynamics
- the Lorentz factor in special relativity
- the damping constant (kg/s)
Δδ (delta)
- Δ represents:
- a finite difference
- a difference operator
- a symmetric difference
- the Laplace operator
- the angle that subtends the arc of a circular curve in surveying
- the determinant of an inverse matrix[1]
- the maximum degree of any vertex in a given graph
- the difference or change in a given variable, e.g. ∆v means a difference or change in velocity
- sensitivity to price in mathematical finance
- distance to Earth, measured in astronomical units
- heat in a chemical formula
- the discriminant in the quadratic formula which determines the nature of the roots
- the degrees of freedom in a non-pooled statistical hypothesis test of two population means
- δ represents:
- a variation in the calculus of variations
- the Kronecker delta function
- the force of interest in mathematical finance
- the Dirac delta function
- the Skorokhod integral in Malliavin calculus, a subfield of stochastic analysis
- the minimum degree of any vertex in a given graph
- a partial charge. δ- represents a negative partial charge, and δ+ represents a positive partial charge chemistry (See also: Solvation)
- declination in astrometry
- the Turner Function in computational material science
- noncentrality measure in statistics[2]
Εε (epsilon)
- ε represents:
- a small positive quantity; see limit
- a random error in regression analysis
- in set theory, the limit ordinal of the sequence

- in computer science, the empty string
- the Levi-Civita symbol
- in electromagnetics, dielectric permittivity
- emissivity
- strain in continuum mechanics
- permittivity
- the Earth's axial tilt in astrometry
- elasticity in economics
- expected value in probability theory and statistics
- electromotive force
- set membership symbol ∈ is based on ε
Ϝϝ (digamma)
- Ϝ is sometimes used to represent the digamma function, though the Latin letter F (which is nearly identical) is usually substituted.
Ζζ (zeta)
- ζ represents:
- the Riemann zeta function and other zeta functions in mathematics
- the coefficient of viscous friction in polymer dynamics
- the damping ratio
- relative vertical vorticity in fluid dynamics
Ηη (eta)
- η represents:
- the intrinsic impedance of medium (usually free space)
- the partial regression coefficient in statistics
- elasticities in economics
- the absolute vertical vorticity (relative vertical vorticity + Coriolis effect) in fluid dynamics
- an index of refraction
- a type of meson
- viscosity
- efficiency
- the Minkowski metric tensor in relativity
- noise in communication system models
Θθ (theta)
- Θ represents:
- an asymptotically tight bound related to big O notation.
- sensitivity to the passage of time in mathematical finance
- Θ (set theory), a certain ordinal number
- θ represents:
- a plane angle in geometry
- the angle to the x axis in the xy-plane in spherical or cylindrical coordinates
- potential temperature in thermodynamics
- the mean time between failure in reliability engineering
- soil water contents in soil science
- Debye temperature
- theta functions
- sometimes also ϑ ("script theta"), cursive form of theta, often used in handwriting
- the first Chebyshev function in number theory
Ιι (iota)
- ι represents:
- the index generator function in APL (in the form ⍳)
Κκ (kappa)
- κ represents:
- the Von Kármán constant
- the kappa curve
- the condition number of a matrix in numerical analysis
- the connectivity of a graph in graph theory
- curvature
- dielectric constant (ε / ε0)
- thermal conductivity (usually a lowercase Latin k)
- thermal diffusivity
- a spring constant (usually a lowercase Latin k)
- the heat capacity ratio in thermodynamics (usually γ)
Λλ (lambda)
- Λ represents:
- the von Mangoldt function in number theory
- the set of logical axioms in the axiomatic method of logical deduction in first-order logic
- the cosmological constant
- a type of baryon
- a diagonal matrix of eigenvalues in linear algebra
- the permeance of a material in electromagnetism
- λ represents:
- one wavelength of electromagnetic radiation
- the decay constant in radioactivity
- function expressions in the lambda calculus
- a general eigenvalue in linear algebra
- the expected number of occurrences in a Poisson distribution in probability
- the arrival rate in queueing theory
- the average lifetime or rate parameter in an exponential distribution (commonly used across statistics, physics, and engineering)
- the failure rate in reliability engineering
- the mean or average value (probability and statistics)
- the latent heat of fusion
- the lagrange multiplier in the mathematical optimization method, known as the shadow price in economics
- the Lebesgue measure denotes the volume or measure of a Lebesgue measurable set
- longitude in geodesy
- linear density
- ecliptic longitude in astrometry
- the Liouville function in number theory
- the Carmichael function in number theory
- a unit of measure of volume equal to one microlitre (1 μL) or one cubic millimetre (1 mm³)
- the empty string in formal grammar
Μμ (mu)
- μ represents:
- the Möbius function in number theory
- the ring representation of a representation module
- the population mean or expected value in probability and statistics
- a measure in measure theory
- micro-, an SI prefix denoting 10−6 (one millionth)
- the coefficient of friction in physics
- the service rate in queueing theory
- the dynamic viscosity in physics
- magnetic permeability in electromagnetics
- a muon
- reduced mass
- chemical potential in condensed matter physics
Νν (nu)
- ν represents:
- frequency in physics in hertz (Hz)
- Poisson's ratio in material science
- a neutrino
- kinematic viscosity of liquids
- stoichiometric coefficient in chemistry
- dimension of nullspace in maths
Ξξ (xi)
- Ξ represents:
- the grand canonical ensemble found in statistical mechanics
- a type of baryon
- ξ represents:
- a random variable.
- the extent of a chemical reaction
- coherence length
- the damping ratio
- universal set
Οο (omicron)
- Ο represents:
- big O notation (may be represented by an uppercase Latin O as well)
Ππ (pi)
- Π represents:
- the product operator in mathematics
- a plane
- π represents:
- Archimedes' constant, the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter
- the prime-counting function
- profit in microeconomics and game theory
- inflation in macroeconomics, expressed as a constant with respect to time
- the state distribution of a Markov chain
- a type of covalent bond in chemistry (pi bond)
- a pion (pi meson) in particle physics
- in electronics, a special type of small signal model is referred to as a hybrid-pi model
- ϖ (a graphic variant, see pomega) represents:
- angular frequency of a wave, in fluid dynamics (angular frequency is usually represented by ω but this may be confused with vorticity in a fluid dynamics context)
- longitude of pericenter, in celestial mechanics[3]
- comoving distance, in cosmology[4]
Ρρ (rho)
- ρ represents:
- the radius in a polar, cylindrical, or spherical coordinate system
- the correlation coefficient in statistics
- the sensitivity to interest rate in mathematical finance
- density (mass or charge per unit volume)
- resistivity
- the shape and reshape operators in APL (in the form ⍴)
- the utilization in queueing theory
- the rank of a matrix
Σσ (sigma)
- Σ represents:
- the summation operator
- the covariance matrix
- the set of terminal symbols in a formal grammar
- σ represents:
- Stefan's constant in blackbody radiation
- the divisor function in number theory
- the real part of the complex variable s = σ + i t in analytic number theory
- the sign of a permutation in the theory of finite groups
- the population standard deviation or spread in probability and statistics
- a type of covalent bond in chemistry (sigma bond)
- the selection operator in relational algebra
- stress in mechanics
- electrical conductivity
- area density
- nuclear cross section
- uncertainty
- utilization in operations management
- surface charge density for microparticles
Ττ (tau)
- τ (lower-case) represents:
- an interval of time
- a mean lifetime
- torque, the rotational force in mechanics
- the elementary tau lepton in particle physics
- the lifetime of a spontaneous emission process
- the time constant of any device, such as an RC circuit
- proper time in relativity
- a correlation coefficient — see Kendall's tau
- the golden ratio 1.618... (although φ (phi) is more common)
- Ramanujan's tau function in number theory
- in astronomy, a measure of opacity, or how much sunlight cannot penetrate the atmosphere
- the intertwining operator in representation theory
- the tau in biochemistry, a protein associated to microtubules
- shear stress in continuum mechanics
- the number of divisors of highly composite numbers (sequence A000005 in OEIS)
- the prefix of many stars, via the Bayer stellar designation system
- an internal system step in transition systems
- a type variable in type theories, such as the simply typed lambda calculus
- τ has been suggested as a circle constant to replace pi and has a value of 6.283..., or 2×π
Υυ (upsilon)
- Υ represents:
- an elementary particle
Φφ (phi)
- Φ represents:
- the work function in physics; the energy required by a photon to remove an electron from the surface of a metal
- magnetic flux
- the cumulative distribution function of the normal distribution in statistics
- phenyl functional group
- the reciprocal of the golden ratio (represented by φ, below), also represented as 1/φ
- note: a symbol for the empty set,
 , resembles Φ but is not Φ
, resembles Φ but is not Φ
- φ represents:
- the golden ratio 1.618... in mathematics, art, and architecture
- Euler's totient function in number theory
- a holomorphic map on an analytic space
- the argument of a complex number in mathematics
- the value of a plane angle in physics and mathematics
- the angle to the z axis in spherical coordinates
- latitude in geodesy
- a scalar field
- radiant flux
- electric potential
- the probability density function of the normal distribution in statistics
- a feature of a syntactic node giving that node characteristics such as gender, number and person in syntax
Χχ (chi)
- χ represents:
- the chi distribution in statistics (χ2 is the more frequently encountered chi-square distribution)
- the chromatic number of a graph in graph theory
- the Euler characteristic in algebraic topology
- a variable in algebraic equations
- electronegativity in the periodic table
- the Rabi frequency
- the spinor of a fundamental particle
- the Fourier transform of a linear response function (see susceptibility)
- a character in mathematics; especially a Dirichlet character in number theory
- the Sigma vectors in the unscented transform used in the unscented Kalman filter
- sometimes the mole fraction
- a characteristic or indicator function in mathematics
Ψψ (psi)
- Ψ represents:
- water potential
- a quaternary combinator in combinatory logic
- ψ represents:
- the wave function in the Schrödinger equation of quantum mechanics
- the stream function in fluid dynamics
- yaw angle in vehicle dynamics
- the angle between the x-axis and the tangent to the curve in the intrinsic coordinates system
- the second Chebyshev function in number theory
Ωω (omega)
- Ω represents:
- the Omega constant
- an asymptotic lower bound related to big O notation
- in probability theory and statistical mechanics, the set of possible distinct system states
- the SI unit measure of electric resistance, the ohm
- the rotation rate of an object, particularly a planet, in dynamics
- a solid angle
- a baryon
- the arithmetic function counting a number's prime factors
- the right ascension of the ascending node in celestial mechanics
- the density parameter in cosmology
- ω represents:
- the first infinite ordinal
- the set of natural numbers in set theory (although
 or N is more common in other areas of mathematics)
or N is more common in other areas of mathematics) - an asymptotically dominant quantity related to big O notation
- in probability theory, a possible outcome of an experiment
- angular velocity / radian frequency
- a complex cube root of unity — the other is ω² — (used to describe various ways of calculating the discrete Fourier transform)
- vertical velocity in pressure-based coordinate systems (commonly used in atmospheric dynamics)
- a meson
- the arithmetic function counting a number's distinct prime factors
- a differential form (esp. on an analytic space)
- the argument of periapsis in celestial mechanics
- the symbol ϖ, a graphic variant of π, is sometimes construed as omega with a bar over it; see π
See also
- Greek alphabet
- English pronunciation of Greek letters
- A pronunciation guide with audio
- Latin letters used in mathematics
- Mathematical alphanumeric symbols
- Table of mathematical symbols
- Typographical conventions in mathematical formulae
- The Greeks (Greek letters used in mathematical finance)
References
- ^ http://www.maths.abdn.ac.uk/~igc/tch/eg1006/notes/node119.html
- ^ Applied Linear Statistical Models (5th ed.). Michael H. Kutner, Christopher J. Nachtsheim, John Neter, & William Li. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005. ISBN 0-07-310874-X. xxviii + 1396 pp.
- ^ Pomega - from Eric Weisstein's World of Physics
- ^ Outline for Weeks 14&15, Astronomy 225 Spring 2008
Categories:- Mathematical notation
- Greek letters
- α represents:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
