- Xylyl bromide
-
Xylyl bromide, also known as methylbenzyl bromide or T-stoff, is a poisonous organic chemical compound with the formula C8H9Br, formerly used as a tear gas. Physically it is a colourless liquid (melting point 21°C) with a pleasant aromatic odour.
Contents
Use as a weapon
Xylyl bromide is highly toxic, irritant and lachrymatory, and has been incorporated in chemical weapons since the early months of World War I. Some commentators say the first use was in August 1914, when the French attacked German soldiers with tear gas grenades,[1][2] but the agent used in that incident was more likely to be ethyl bromoacetate, which the French had tested before the war.[3]
The first extensive use of xylyl bromide was the firing by German forces of 18,000 "T-shells" at Russian positions in the Battle of Bolimów in January 1915. The shells were modified 15 cm (6 inch) artillery shells containing an explosive charge and c. 3 kg (7 lb) xylyl bromide. The attack was a complete failure because the winter weather was too cold to permit an effective aerosol, and the agent was either blown back towards the German lines, fell harmlessly to the ground, or was insufficiently concentrated to cause damage. A similar attack at Nieuwpoort in March 1915 was also unsuccessful.[3] Nevertheless, because of its ease of manufacture xylyl bromide was widely used in World War I, in particular as a component of the Germans' Weisskreuz (white cross) mixture.
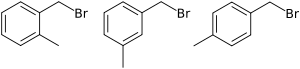
Structural isomers
The three isomers, collectively referred to by CAS registry number [], are:
- CAS RN[]: o-xylyl bromide (2-methylbenzyl bromide, systematic name 1-(Bromomethyl)-2-methyl-benzene) (NIST record)
- CAS RN[]: m-xylyl bromide (3-methylbenzyl bromide, systematic name 1-(Bromomethyl)-3-methyl-benzene) (NIST record)
- CAS RN[]: p-xylyl bromide (4-methylbenzyl bromide, systematic name 1-(Bromomethyl)-4-methyl-benzene) (NIST record)
See also
- Use of poison gas in World War I
References
- ^ Chris Trueman. "Poison Gas and World war One". History Learning Site. http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/poison_gas_and_world_war_one.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-26.
- ^ Michael Duffy (August 22, 2009). "Weapons of War - Poison Gas". firstworldwar.com. http://www.firstworldwar.com/weaponry/gas.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-26.
- ^ a b Corey J Hilmas, Jeffery K Smart, Benjamin A Hill (2008). "Chapter 2: History of Chemical Warfare (pdf)". Medical Aspects of Chemical Warfare. Borden Institute. pp. 12–14. http://www.bordeninstitute.army.mil/published_volumes/chemwarfare/CHAP2_Pg_09-76.pdf.
External links
Categories:- Organobromides
- Lachrymatory agents
- World War I chemical weapons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.