- Adeno-associated virus
Taxobox
color = violet
name = Adeno-associated virus
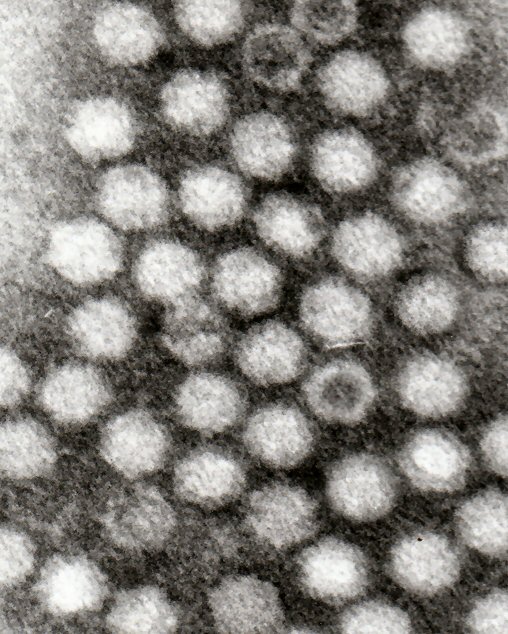
image_width = 180px
image_caption = Adeno-Associated Viruses
virus_group = II
familia = "Parvoviridae "
subfamilia = "Parvovirinae "
genus = "Dependovirus "
species = "adeno-associated virus"Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a small
virus which infects humans and some other primate species. AAV is not currently known to causedisease and consequently the virus causes a very mildimmune response . AAV can infect both dividing and non-dividing cells and may incorporate itsgenome into that of the host cell. These features make AAV a very attractive candidate for creating viral vectors forgene therapy .Harvard reference
Surname1=Grieger
Given1=JC
Surname2=Samulski
Given2=RJ
Title=Adeno-associated virus as a gene therapy vector: vector development, production and clinical applications.
Journal=Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology
Id=PMID 16568890
Issue=99
Pages=119-145
Year=2005
Place=Berlin ,Germany ]AAV belongs to the
genus "Dependovirus ", which in turn belongs to the family "Parvoviridae ". The virus is a small (20 nm) replication-defective, nonenveloped virus.Gene Therapy Vector
Advantages and drawbacks
Wild-type AAV has attracted considerable interest from gene therapy researchers due to a number of features. Chief amongst these is the viruses' apparent lack of pathogenicity. It can also infect non-dividing cells and has the ability to stably integrate into the host cell genome at a specific site (designated AAVS1) in the human 19th
chromosome . Harvard reference
Surname1=Surosky
Given1=RT
Surname2=Urabe
Given2=M
Surname3=Godwin
Given3=SG "et al"
Volume
Title=Adeno-associated virus Rep proteins target DNA sequences to a unique locus in the human genome
Journal=Journal of virology
Issue=10
Volume=71
ID=PMID 9311886
Year=1997] The feature makes it somewhat more predictable than retroviruses, which present threat of a random insertion and of mutagenesis, which is sometimes followed by development of acancer . The AAV genome integrates most frequently into the site mentioned, while random incorporations into the genome take place with a negligible frequency. AAVs also present very lowimmunogenicity , seemingly restricted to generation of neutralizingantibodies , while they induce no clearly-defined cytotoxic response.Harvard reference
Surname1=Chirmule
Given1=N
Surname2=Propert
Given2=K
Surname3=Magosin
Given3=S "et al"
Title=Immune responses to adenovirus and adeno-associated virus in humans
Journal=Gene therapy
Issue=September
Pages=1574-83
Year=1999
ID=PMID 10490767] Harvard reference
Surname1=Hernandez
Given1=YJ
Surname2=Wang
Given2=J
Surname3=Kearns
Given3=WG "et al"
Title=Latent adeno-associated virus infection elicits humoral but not cell-mediated immune responses in a nonhuman primate model
Journal=Journal of virology
Issue=October
Pages=8549-58
Year=1999
ID=PMID 10482608] Harvard reference
Surname1=Ponnazhagan
Given1=S
Surname2=Mukherjee
Given2=P
Surname3=Yoder
Given3=MC "et al"
Title=Adeno-associated virus 2-mediated gene transfer "in vivo": organ-tropism and expression of transduced sequences in mice
Journal=Gene
Issue=Apr 29
Pages=203-10
Year=1997
ID=PMID 9185868] This feature, along with the ability to infect quiescent cells present their dominance over adenoviruses as vectors for the humangene therapy .Use of the virus does present some disadvantages. The cloning capacity of the vector is relatively limited and most therapeutic genes require the complete replacement of the virus's 4.8 kilobase genome. It is accordingly unclear if the site-specific integration can be preserved in a usable vector since it appears to be partially dependent on products of the Rep open reading frame. The humoral immunity instigated by infection with the wild type is thought to be a very common event. The associated neutralising activity limits the usefulness of the most commonly used serotype AAV2 in certain applications.
Clinical trials
To date, AAV vectors have been used for first- and second-phase clinical trials for treatment of
cystic fibrosis and first-phase trials forhemophilia . Promising results have been obtained from phase I trials forParkinson's disease , showing good tolerance of an AAV2 vector in the central nervous system. Other trials have begun, concerning AAV safety for treatment ofCanavan disease ,muscular dystrophy and late infantileneuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis .Trials for the treatment of
prostate cancer have reached phase IIIHarvard reference
Surname1=Carter
Given1=BJ
Surname2=
Given2=
Surname3=
Given3=
Surname4=
Year=2005
Title=Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors in Clinical Trials
Journal=Human Gene Therapy
Volume=16
Issue=
Pages=541-50
ID=PMID 15916479] , however these ex vivo studies do not involve direct administration of AAV to patients.Pathology
AAV is not considered to have any known role in disease. It has been suggested to have a role in male
infertility cite journal
author=Erles K, Rohde V, Thaele M, Roth S, Edler L, Schlehofer JR
title=DNA of adeno-associated virus (AAV) in testicular tissue and in abnormal semen samples
journal=Hum. Reprod.
volume=16
issue=11
pages=2333–7
year=2001
month=November
pmid=11679515
doi=
url=http://humrep.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11679515] , as AAV DNA is more commonly found in semen samples from men with abnormal semen. However, no causal link has been found between AAV infection and male infertility.AAV structure
AAV genome, transcriptome and proteome
The AAV genome is built of single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (ss
DNA ), either positive- or negative-sensed, which is about 4.7 kilobase long. The genome comprises inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) at both ends of the DNA strand, and twoopen reading frame s (ORFs): "rep" and "cap". The former is composed of four overlapping genes encoding Rep proteins required for the AAV life cycle, and the latter contains overlapping nucleotide sequences ofcapsid proteins: VP1, VP2 and VP3, which interact together to form a capsid of an icosahedral symmetry.Harvard reference
Surname1=Carter
Given1=BJ
Year=2000
Editor=DD Lassic & N Smyth Templeton
ID=ISBN 0-585-39515-2
Chapter=Adeno-associated virus and adeno-associated virus vectors for gene delivery
Title=Gene Therapy: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Strategies
Publisher=Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Place=New York City
Pages=41-59]ITR sequences
The Inverted Terminal Repeat (ITR) sequences comprise 145 bases each. They were named so because of their symmetry, which was shown to be required for efficient multiplication of the AAV genome.Harvard reference
Surname1=Bohenzky
Given1=RA
Surname2=LeFebvre
Given2=RB
Surname3=Berns
Given3=KI
Title=Sequence and symmetry requirements within the internal palindromic sequences of the adeno-associated virus terminal repeat
Journal=Virology
Year=1988
Issue=2
Volume=166
Place=San Diego
Publisher=Academic Press
ID=PMID 2845646] Another property of these sequences is their ability to form a hairpin, which contributes to so-called self-priming that allowsprimase -independent synthesis of the second DNA strand. The ITRs were also shown to be required for both integration of the AAV DNA into the host cell genome (19th chromosome in humans) and rescue from it,Harvard reference
Surname1=Wang|Given1=X.S.|Surname2=Ponnazhagan|Given2=S.|Surname3=Srivastava|Given3=A|Year=1995|Journal=Journal of Molecular Biology|Volume=250|Issue=5|Pages=573-80|Title=Rescue and replication signals of the adeno-associated virus 2 genome|ID=PMID 7623375] Harvard reference
Surname1=Weitzman
Given1=MD
Surname2=Kyostio
Given2=SR
Surname3=Kotin
Given3=RM
Surname4=Owens
Given4=RA
Year=1994
ID=PMID 8016070
Title=Adeno-associated virus (AAV) Rep proteins mediate complex formation between AAV DNA and its integration site in human DNA
Journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Volume=91
Issue=13
Pages=5808-12] as well as for efficient encapsidation of the AAV DNA combined with generation of a fully-assembled,deoxyribonuclease -resistant AAV particles.Harvard reference
Surname1=Zhou
Given1=X
Surname2=Muzyczka
Given2=N
Title=In vitro packaging of adeno-associated virus DNA
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=72
Issue=4
Year=1998
Pages=3241-7
ID=PMID 9525651]With regard to gene therapy, ITRs seem to be the only sequences required "in cis" next to the therapeutic gene: structural ("cap") and packaging ("rep") genes can be delivered "in trans". With this assumption many methods were established for efficient production of recombinant AAV (rAAV) vectors containing a reporter or therapeutic gene. However, it was also published that the ITRs are not the only elements required "in cis" for the effective replication and encapsidation. A few research groups have identified a sequence designated "cis-acting Rep-dependent element" (CARE) inside the coding sequence of the "rep" gene. CARE was shown to augment the replication and encapsidation when present "in cis".Harvard reference
ID=PMID 11559833
Surname1=Nony
Given1=P
Surname2=Tessier
Given2=J
Surname3=Chadeuf
Given3=G
Surname4=Ward
Given4=P "et al"
Year=2001
Title=Novel cis-acting replication element in the adeno-associated virus type 2 genome is involved in amplification of integrated rep-cap sequences
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=75
Issue=20
Pages=9991-4] Harvard reference
ID=PMID 12477885
Surname1=Nony
Given1=P
Surname2=Chadeuf
Given2=G
Surname3=Tessier
Given3=J
Surname4=Moullier
Given4=P "et al"
Year=2003
Title=Evidence for packaging of rep-cap sequences into adeno-associated virus (AAV) type 2 capsids in the absence of inverted terminal repeats: a model for generation of rep-positive AAV particles
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=77
Issue=1] Harvard reference
ID=PMID 11991970
Surname1=Philpott
Given1=NJ
Surname2=Giraud-Wali
Given2=C
Surname3=Dupuis
Given3=C
Surname4=Gomos
Given4=J "et al"
Title=Efficient integration of recombinant adeno-associated virus DNA vectors requires a p5-rep sequence in cis
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=76
Issue=11
Year=2002] Harvard reference
ID=PMID 11090148
Surname1=Tullis
Given1=GE
Surname2=Shenk
Given2=T
Year=2000
Title=Efficient replication of adeno-associated virus type 2 vectors: a cis-acting element outside of the terminal repeats and a minimal size
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=74
Issue=24]"rep" genes and Rep proteins
On the "left side" of the genome there are two
promoter s called p5 and p19, from which two overlapping messenger ribonucleic acids (mRNA s) of different length can be produced. Each of these contains anintron which can be either spliced out or not. Given these possibilities, four various mRNAs, and consequently four various Rep proteins with overlapping sequence can be synthesized. Their names depict their sizes in kilodaltons (kDa): Rep78, Rep68, Rep52 and Rep40.Harvard reference
Surname1=Kyostio
Given1=SR
Surname2=Owens
Given2=RA
Surname3=Weitzman
Given3=MD
Surname4=Antoni
Given4=BA "et al"
Title=Analysis of adeno-associated virus (AAV) wild-type and mutant Rep proteins for their abilities to negatively regulate AAV p5 and p19 mRNA levels
Journal=Journal of virology
Year=1994
Volume=68
Issue=5
Pages=2947-57
ID=PMID 8151765] Rep78 and 68 can specifically bind thehairpin formed by the ITR in the self-priming act and cleave at a specific region, designated terminal resolution site, within the hairpin. They were also shown to be necessary for the AAVS1-specific integration of the AAV genome. All four Rep proteins were shown to bind ATP and to possesshelicase activity. It was also shown that they upregulate the transcription from the p40 promoter (mentioned below), but downregulate both p5 and p19 promoters.Harvard reference
Surname1=Im
Given1=DS
Surname2=Muzyczka
Given2=N
Year=1990
Title=The AAV origin binding protein Rep68 is an ATP-dependent site-specific endonuclease with DNA helicase activity.
Journal=Cell
Volume=61
Issue=3
Pages=447-57
ID=PMID 2159383] Harvard reference
Surname1=Im
Given1=DS
Surname2=Muzyczka
Given2=N
Year=1992
Title=Partial purification of adeno-associated virus Rep78, Rep52, and Rep40 and their biochemical characterization
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=66
Issue=2
Pages=1119-28
ID=PMID 1309894] Harvard reference
Surname1=Samulski
Given1=RJ
Year=2003
ID=PMID 12894449
Journal=Ernst Schering Research Foundation workshop
Title=AAV vectors, the future workhorse of human gene therapy
Issue=43
Pages=25-40] Harvard reference
Surname1=Trempe
Given1=JP
Surname2=Carter
Given2=BJ
Year=1988a
ID=PMID 2824856
Title=Regulation of adeno-associated virus gene expression in 293 cells: control of mRNA abundance and translation
Journal=Journal of virology
Vol=62
Issue=1
Pages=68-74]"cap" genes and VP proteins
The right side of a positive-sensed AAV genome encodes overlapping sequences of three capsid proteins, VP1, VP2 and VP3, which start from one promoter, designated p40. The molecular weights of these proteins are 87, 72 and 62 kiloDaltons, respectively.Harvard reference
Surname1=Jay
Given1=FT
Surname2=Laughlin
Given2=CA
Surname3=Carter
Given3=BJ
Year=1981
Title=Eukaryotic translational control: adeno-associated virus protein synthesis is affected by a mutation in the adenovirus DNA-binding protein
Journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Volume=78
Issue=5
Pages=2927-31
ID=PMID 6265925] All three of them are translated from one mRNA. After this mRNA is synthesized, it can be spliced in two different manners: either longer or shorterintron can be excised, which results in formation of two pools of mRNAs: 2.3 kb-, and 2.6 kb-long. Usually, especially in the presence ofadenovirus , the longer intron is preferred, so the 2.3-kb-long mRNA represents so-called major splice. In this form the first AUG codon, from which the synthesis of VP1 protein starts, is cut out, resulting in a reduced overall level of VP1 protein synthesis. The first AUG codon, which remains in the major splice, is the initiation codon for VP3 protein. However, upstream of that codon in the same open reading frame lies the ACG sequence, which endcodes threonine, but is surrounded by the optimal Kozak context, that contributes to a low level of synthesis of VP2 protein, which is actually VP3 protein with additional N terminal residues, as is VP1.Harvard reference
Surname1=Becerra
Given1=SP
Surname2=Rose
Given2=JA
Surname3=Hardy
Given3=M
Surname4=other
Year=1985
Title=Direct mapping of adeno-associated virus capsid proteins B and C: a possible ACG initiation codon
Journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Volume=82
Issue=23
Pages=7919-23
ID=PMID 2999784] Harvard reference
Surname1=Cassinotti
Given1=P
Surname2=Weitz
Given2=M
Surname3=Tratschin
Given3=JD
Year=1988
Title=Organization of the adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid gene: mapping of a minor spliced mRNA coding for virus capsid protein 1
Journal=Virology
Volume=167
Issue=1
Pages=176-84
ID=PMID 2847413] Harvard reference
Surname1=Muralidhar
Given1=S
Surname2=Becerra
Given2=SP
Surname3=Rose
Given3=JA
Year=1994
ID=PMID 8254726
Title=Site-directed mutagenesis of adeno-associated virus type 2 structural protein initiation codons: effects on regulation of synthesis and biological activity
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=68
Issue=1
Pages=170-6] Harvard reference
Surname1=Trempe
Given1=JP
Surname2=Carter
Given2=BJ
Year=1988b
Title=Alternate mRNA splicing is required for synthesis of adeno-associated virus VP1 capsid protein
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=62
Issue=9
Pages=3356-63
ID=PMID 2841488]Since the bigger intron is preferred to be spliced out, and since in the major splice the ACG codon is a much weaker
translation initiation signal, the ratio at which the AAV structural proteins are synthesized "in vivo" is about 1:1:20, which is the same as in the mature virus particle.Harvard reference
Surname1=Rabinowitz
Given1=JE
Surname2=Samulski
Given2=RJ
Year=2000
Title=Building a better vector: the manipulation of AAV virions
Journal=Virology
Volume=278
Issue=2
Pages=301-8
ID=PMID 11118354] The unique fragment at the N terminus of VP1 protein was shown to possess thephospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity, which is probably required for the releasing of AAV particles from lateendosome s.Harvard reference
Surname1=Girod
Given1=A
Surname2=Wobus
Given2=CE
Surname3=Zádori
Given3=Z
Surname4=others
Year=2002
Title=The VP1 capsid protein of adeno-associated virus type 2 is carrying a phospholipase A2 domain required for virus infectivity
Journal=The Journal of general virology
Volume=83
Issue=5
Pages=973-8
ID=PMID 11961250] Muralidhar "et al." reported that VP2 and VP3 are crucial for correct virion assembly. More recently, however, Warrington "et al" showed VP2 to be unnecessary for the complete virus particle formation and an efficient infectivity, and also presented that VP2 can tolerate large insertions in its N terminus, while VP1 can not, probably because of the PLA2 domain presence.Harvard reference
Surname1=Warrington
Given1=KH,Jr
Surname2=Gorbatyuk
Given2=OS
Surname3=Harrison
Given3=JK
Surname4=others
Year=2004
Title=Adeno-associated virus type 2 VP2 capsid protein is nonessential and can tolerate large peptide insertions at its N terminus
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=78
Issue=12
Pages=6595-609
ID=PMID 15163751]The
crystal structure of the VP3 protein was determined by Xie, Bue, "et al".Harvard reference
Surname1=Xie
Given1=Q
Surname2=Bu
Given2=W
Surname3=Bhatia
Given3=S
Surname4=others
Year=2002
Title=The atomic structure of adeno-associated virus (AAV-2), a vector for human gene therapy
Journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Volume=99
Issue=16
Pages=10405-10
ID=PMID 12136130]AAV serotypes, receptors and native tropism
As of 2006 there have been 11 AAV
serotype s described, the 11th in 2004.Harvard reference
Surname1=Mori
Given1=S
Surname2=Wang
Given2=L
Surname3=Takeuchi
Given3=T
Surname4=Kanda
Given4=T
Year=2004
Title=Two novel adeno-associated viruses from cynomolgus monkey: pseudotyping characterization of capsid protein
Journal=Virology
Volume=330
Issue=2
Pages=375-83
ID=PMID 15567432] All of the known serotypes can infect cells from multiple diverse tissue types. Tissue specificity is determined by the capsid serotype and pseudotyping of AAV vectors to alter their tropism range will likely be important to their use in therapy.Serotype 2
Serotype 2 (AAV2) has been the most extensively examined so far.Harvard reference
Surname1=Bartlett
Given1=JS
Surname2=Samulski
Given2=RJ
Surname3=McCown
Given3=TJ
Surname4=others
Year=1998
Title=Selective and rapid uptake of adeno-associated virus type 2 in brain
Journal=Human gene therapy
Volume=9
Issue=8
Pages=1181-6
ID=PMID 9625257] Harvard reference
Surname1=Fischer
Given1=AC
Surname2=Beck
Given2=SE
Surname3=Smith
Given3=CI
Surname4=others
Year=2003
Title=Successful transgene expression with serial doses of aerosolized rAAV2 vectors in rhesus macaques
Journal=Molecular therapy : the journal of theAmerican Society of Gene Therapy
Volume=8
Issue=6
Pages=918-26
ID=PMID 14664794] Harvard reference
Surname1=Nicklin
Given1=SA
Surname2=Buening
Given2=H
Surname3=Dishart
Given3=KL
Surname4=others
Year=2001
Title=Efficient and selective AAV2-mediated gene transfer directed to human vascular endothelial cells
Journal=Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy
Volume=4
Issue=3
Pages=174-81
ID=PMID 11545607] Harvard reference
Surname1=Rabinowitz
Given1=JE
Surname2=Xiao
Given2=W
Surname3=Samulski
Given3=RJ
Year=1999
Title=Insertional mutagenesis of AAV2 capsid and the production of recombinant virus
Journal=Virology
Volume=265
Issue=2
Pages=274-85
ID=PMID 10600599] Harvard reference
Surname1=Shi
Given1=W
Surname2=Bartlett
Given2=JS
Year=2003
Title=RGD inclusion in VP3 provides adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2)-based vectors with a heparan sulfate-independent cell entry mechanism
Journal=Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy
Volume=7
Issue=4
Pages=515-25
ID=PMID 12727115] Harvard reference
Surname1=Wu
Given1=P
Surname2=Xiao
Given2=W
Surname3=Conlon
Given3=T
Surname4=others
Year=2000
Title=Mutational analysis of the adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) capsid gene and construction of AAV2 vectors with altered tropism
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=74
Issue=18
Pages=8635-47
ID=PMID 10954565] AAV2 presents natural tropism towards e.g.skeletal muscle s,Harvard reference
Surname1=Manno
Given1=CS
Surname2=Chew
Given2=AJ
Surname3=Hutchison
Given3=S
Surname4=others
Year=2003
Title=AAV-mediated factor IX gene transfer to skeletal muscle in patients with severe hemophilia B
Journal=Blood
Volume=101
Issue=8
Pages=2963-72
ID=PMID 12515715]neuron s,vascular smooth muscle cellsHarvard reference
Surname1=Richter
Given1=M
Surname2=Iwata
Given2=A
Surname3=Nyhuis
Given3=J
Surname4=others
Year=2000
Title=Adeno-associated virus vector transduction of vascular smooth muscle cells "in vivo"
Journal=Physiological genomics
Volume=2
Issue=3
Pages=117-27
ID=PMID 11015590] andhepatocyte s.Harvard reference
Surname1=Koeberl
Given1=DD
Surname2=Alexander
Given2=IE
Surname3=Halbert
Given3=CL
Surname4=others
Year=1997
Title=Persistent expression of human clotting factor IX from mouse liver after intravenous injection of adeno-associated virus vectors
Journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Volume=94
Issue=4
Pages=1426-31
ID=PMID 9037069]Three cell receptors have been described for AAV2: heparan sulfate proteoglican (HSPG), aVβ5
integrin andfibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR-1). The first functions as a primary receptor, while the latter two have a co-receptor activity and enable AAV to enter the cell by receptor-mediatedendocytosis .Harvard reference
Surname1=Qing
Given1=K
Surname2=Mah
Given2=C
Surname3=Hansen
Given3=J
Surname4=other
Year=1999
Title=Human fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is a co-receptor for infection by adeno-associated virus 2
Journal=Nature medicine
Volume=5
Issue=1
Pages=71-7
ID=PMID 9883842] Harvard reference
Surname1=Summerford
Given1=C
Surname2=Samulski
Given2=RJ
Surname3=
Given3=
Surname4=
Year=1998
Title=Membrane-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 virions
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=72
Issue=2
Pages=1438-45
ID=PMID 9445046] Harvard reference
Surname1=Summerford
Given1=C
Surname2=Bartlett
Given2=JS
Surname3=Samulski
Given3=RJ
Year=1999
Title=AlphaVbeta5 integrin: a co-receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 infection
Journal=Nature medicine
Volume=5
Issue=1
Pages=78-82
ID=PMID 9883843] ) These study results have been disputed by Qiu, Handa, "et al".Harvard reference
Surname1=Qiu
Given1=J
Surname2=Handa
Given2=A
Surname3=Kirby
Given3=M
Surname4=Brown
Given4=KE
Year=2000
Title=The interaction of heparin sulfate and adeno-associated virus 2
Journal=Virology
Volume=269
Issue=1
Pages=137-47
ID=PMID 10725206] HSPG functions as the primary receptor, though its abundance in theextracellular matrix can scavenge AAV particles and impair the infection efficiency.Harvard reference
Surname1=Pajusola
Given1=K
Surname2=Gruchala
Given2=M
Surname3=Joch
Given3=H
Surname4=other
Year=2002
Title=Cell-type-specific characteristics modulate the transduction efficiency of adeno-associated virus type 2 and restrain infection of endothelial cells
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=76
Issue=22
Pages=11530-40
ID=PMID 12388714]erotype 2 and cancer
Studies have shown that serotype 2 of the virus (AAV-2) apparently kills cancer cells without harming healthy ones. "Our results suggest that adeno-associated virus type 2, which infects the majority of the population but has no known ill effects, kills multiple types of cancer cells yet has no effect on healthy cells," said [http://www.fred.psu.edu/ds/retrieve/fred/investigator/cmm10 Craig Meyers] , a professor of
immunology andmicrobiology at thePenn State College of Medicine inPennsylvania .Harvard reference
Surname1=CNN.com
First=
Year=2005
Title=Common virus 'kills cancer'
Access-date=August 23, 2006
URL=http://www.cnn.com/2005/HEALTH/06/22/cancer.virus/index.html] This could lead to a new anti-cancer agent.Other Serotypes
Although AAV2 is the most popular serotype in various AAV-based research, it has been shown that other serotypes can be more effective as gene delivery vectors. For instance AAV6 appears much better in infecting airway epithelial cells, AAV7 presents very high transduction rate of murine skeletal muscle cells (similarly to AAV1 and AAV5), AAV8 is superb in transducing hepatocytesHarvard reference
Surname1=Gao
Given1=GP
Surname2=Alvira
Given2=MR
Surname3=Wang
Given3=L
Surname4=other
Year=2002
Title=
Journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Volume= 99
Issue=18
Pages=11854-9
ID=PMID 12192090] Harvard reference
Surname1=Halbert
Given1=CL
Surname2=Allen
Given2=JM
Surname3=Miller
Given3=AD
Year=2001
Title=Adeno-associated virus type 6 (AAV6) vectors mediate efficient transduction of airway epithelial cells in mouse lungs compared to that of AAV2 vectors
Journal=Journal of virology. (J Virol) Jul; ():
Volume=75
Issue=14
Pages=6615-24
ID=PMID 11413329] Harvard reference
Surname1=Rabinowitz
Given1=JE
Surname2=Bowles
Given2=DE
Surname3=Faust
Given3=SM
Surname4=other
Year=2004
Title=Cross-dressing the virion: the transcapsidation of adeno-associated virus serotypes functionally defines subgroups
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=78
Issue=9
Pages=4421-32
ID=PMID 15078923] and AAV1 and 5 were shown to be very efficient in gene delivery to vascular endothelial cells.Harvard reference
Surname1=Chen
Given1=S
Surname2=Kapturczak
Given2=M
Surname3=Loiler
Given3=SA
Surname4=others
Year=2005
Title=Efficient transduction of vascular endothelial cells with recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 1 and 5 vectors
Journal=Human gene therapy
Volume=16
Issue=2
Pages=235-47
ID=PMID 15761263] AAV6, a hybrid of AAV1 and AAV2, also shows lower immunogenicity than AAV2.Serotypes can differ with the respect to the receptors they are bound to. For example AAV4 and AAV5 transduction can be inhibited by soluble
sialic acid s (of different form for each of these serotypes),Harvard reference
Surname1=Kaludov
Given1=N
Surname2=Brown
Given2=KE
Surname3=Walters
Given3=RW
Surname4=others
Year=2001
Title=Adeno-associated virus serotype 4 (AAV4) and AAV5 both require sialic acid binding for hemagglutination and efficient transduction but differ in sialic acid linkage specificity
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=75
Issue=15
Pages=6884-93
ID=PMID 11435568] and AAV5 was shown to enter cells via theplatelet-derived growth factor receptor.Harvard reference
Surname1=Di Pasquale
Given1=G
Surname2=Davidson
Given2=BL
Surname3=Stein
Given3=CS
Surname4=others
Year=
Title=Identification of PDGFR as a receptor for AAV-5 transduction
Journal=Nature medicine
Volume=9
Issue=10
Pages=1306-12
ID=PMID 14502277]AAV immunology
AAV is of particular interest to gene therapists due to its apparent limited capacity to induce immune responses in humans, a factor which should positively influence vector transduction efficiency while reducing the risk of any immune-associated
pathology .Innate
The innate immune response to the AAV vectors has been characterised in animal models. Intravenous administration in mice causes transient production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and some infiltration of neutrophils and other leukocytes into the liver, which seems to sequester a large percentage of the injected viral particles. Both soluble factor levels and cell infiltration appear to return to baseline within six hours. By contrast, more aggressive viruses produce innate responses lasting 24 hours or longer.Harvard reference
Surname1=Zaiss
Given1=AK
Surname2=Liu
Given2=Q
Surname3=Bowen
Given3=GP
Surname4=others
Year=2002
Title=Differential Activation of Innate Immune Responses by Adenovirus and Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors
Journal=Journal of Virology
Volume=76
Issue=9
Pages=4580-90
ID=PMID 11932423]Humoral
The virus is known to instigate robust humoral immunity in animal models and in the human population where up to 80% of individuals are thought to be seropositive for AAV2. Antibodies are known to be neutralising and do impact on vector transduction efficiency via some routes of administration. As well as persistent AAV specific antibody levels, it appears from both prime-boost studies in animals and from clinical trials that the B-cell memory is also strong.Harvard reference
Surname1=Zaiss
Given1=AK
Surname2=Muruve
Given2=DA
Surname3=
Given3=
Surname4=
Year=2005
Title= Immune responses to adeno-associated virus vectors
Journal=Current Gene Therapy
Volume=5
Issue=3
Pages=323-31
ID=PMID 15975009]Cell-mediated
The cell-mediated response to the virus and to vectors is poorly characterised and has been largely ignored in the literature as recently as 2005.Harvard reference
Surname1=Zaiss
Given1=AK
Surname2=Muruve
Given2=DA
Surname3=
Given3=
Surname4=
Year=2005
Title= Immune responses to adeno-associated virus vectors
Journal=Current Gene Therapy
Volume=5
Issue=3
Pages=323-31
ID=PMID 15975009] Clinical trials using an AAV2-based vector to treat haemophilia B seem to indicate that targeted destruction of transduced cells may be occurring.Harvard reference
Surname1=High
Given1=KA
Surname2=Mannos
Given2=CS
Surname3=Pierce
Given3=GF
Surname4=Others
Year=2006
Title=Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response
Journal=Nature Medicine
Volume=12
Issue=3
Pages=342-47
ID=PMID 16474400] Combined with data that shows that CD8+ T-cells can recognise elements of the AAV capsid in vitroHarvard reference
Surname1=High
Given1=KA
Surname2=Sabatino
Given2=DE
Surname3=Mingozzi
Given3=F
Surname4=Others
Year=2005
Title=Identification of Mouse AAV Capsid-Specific CD8+ T Cell Epitopes
Journal=Molecular Therapy
Volume=12
Issue=6
Pages=1023-33
ID=PMID 16263332] , it appears that there may be a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to AAV vectors. However, the data is incomplete as the role of T-helper cells and evidence of targeted cytoxicity has not been fully explored.AAV infection cycle
There are several steps in the AAV infection cycle, from infecting a cell to producing new infectious particles:
# attachment to thecell membrane
#endocytosis
# endosomal trafficking
# escape from the lateendosome orlysosome
# translocation to the nucleus
# formation of double-stranded DNA replicative form of the AAV genome
# "rep" genes expression
# genome replication
# "cap" genes expression, synthesis of progeny ssDNA particles
# assembly of completevirion s, and
# release from the infected cell.Some of these steps may look different in various types of cells, which, in part, contributes to the defined and quite limited native tropism of AAV. Replication of the virus can also vary in one cell type, depending on the cell's current
cell cycle phase.Harvard reference
Surname1=Rohr
Given1=UP
Surname2=Kronenwett
Given2=R
Surname3=Grimm
Given3=D
Surname4=others
Year=2002
Title=Primary human cells differ in their susceptibility to rAAV-2-mediated gene transfer and duration of reporter gene expression
Journal=Journal of virological methods
Volume=105
Issue=2
Pages=265-75
ID=PMID 12270659]The characteristic feature of the adeno-associated virus is a deficiency in replication and thus its inability to multiply in unaffected cells. The first factor that was described as providing successful generation of new AAV particles, was the
adenovirus , from which the AAV name originated. It was then shown that AAV replication can be facilitated by selected proteins derived from the adenovirus genome,Harvard reference
Surname1=Matsushita
Given1=T
Surname2=Elliger
Given2=S
Surname3=Elliger
Given3=C
Surname4=others
Year=1998
Title=Adeno-associated virus vectors can be efficiently produced without helper virus
Journal=Gene therapy
Volume=5
Issue=7
Pages=938-45
ID=PMID 9813665] Harvard reference
Surname1=Myers
Given1=MW
Surname2=Laughlin
Given2=CA
Surname3=Jay
Given3=FT
Surname4=other
Year=1980
Title=Adenovirus helper function for growth of adeno-associated virus: effect of temperature-sensitive mutations in adenovirus early gene region 2
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=35
Issue=1
Pages=65-75
ID=PMID 6251278] by other viruses such as HSV,Harvard reference
Surname1=Handa
Given1=H
Surname2=Carter
Given2=BJ
Year=1979
Title=Adeno-associated virus DNA replication complexes in herpes simplex virus or adenovirus-infected cells
Journal=The Journal of biological chemistry
Volume=254
Issue=14
Pages=6603-10
ID=PMID 221504] or by genotoxic agents, such asUV irradiation orhydroxyurea .Harvard reference
Surname1=Yalkinoglu
Given1=AO
Surname2=Heilbronn
Given2=R
Surname3=Bürkle
Given3=A
Surname4=other
Year=1988
Title=DNA amplification of adeno-associated virus as a response to cellular genotoxic stress
Journal=Cancer research
Volume=48
Issue=11
Pages=3123-9
ID=PMID 2835153] Harvard reference
Surname1=Yakobson
Given1=B
Surname2=Koch
Given2=T
Surname3=Winocour
Given3=E
Year=1987
Title=Replication of adeno-associated virus in synchronized cells without the addition of a helper virus
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=61
Issue=4
Pages=972-81
ID=PMID 3029431] Harvard reference
Surname1=Yakobson
Given1=B
Surname2=Hrynko
Given2=TA
Surname3=Peak
Given3=MJ
Surname4=Winocour
Given4=E
Year=1989
Title=Replication of adeno-associated virus in cells irradiated with UV light at 254 nm
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=63
Issue=3
Pages=1023-30
ID=PMID 2536816]The minimal set of the adenoviral genes required for efficient generation of progeny AAV particles, was discovered by Matsushita, Ellinger "et al". This discovery allowed for new production methods of recombinant AAV, which do not require adenoviral co-infection of the AAV-producing cells. In the absence of helper virus or genotoxic factors, AAV DNA can either integrate into the host genome or persist in episomal form. In the former case integration is mediated by Rep78 and Rep68 proteins and requires the presence of ITRs flanking the region being integrated. In mice, the AAV genome has been observed persisting for long periods of time in quiescent tissues, such as skeletal muscles, in episomal form (a circular head-to-tail conformation).Harvard reference
Surname1=Duan
Given1=D
Surname2=Sharma
Given2=P
Surname3=Yang
Given3=J
Surname4=others
Year=1998
Title=Circular intermediates of recombinant adeno-associated virus have defined structural characteristics responsible for long-term episomal persistence in muscle tissue
Journal=Journal of virology
Volume=72
Issue=11
Pages=8568-77
ID=PMID 9765395]Notes
External links
*http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/G/GeneTherapy2.html
* [http://www.genetherapynet.com Gene Therapy Net]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
