- Mers El Kébir
-
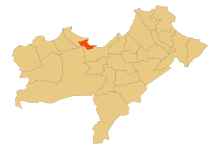
Mers El Kébir
بلدية المرسى الكبير— Municipality — Commune of Mers El Kébir Location of Mers El Kébir within Oran Province Location of Mers El Kébir within Algeria Coordinates: 35°44′N 0°43′W / 35.733°N 0.717°WCoordinates: 35°44′N 0°43′W / 35.733°N 0.717°W Country  Algeria
AlgeriaProvince Oran District Aïn El Turk Government - PMA Seats 9 Area - Total 10.98 km2 (4.2 sq mi) Elevation 0 m (0 ft) Population (2006) - Total 16,950 - Density 1,543.7/km2 (3,998.2/sq mi) Time zone CET (UTC+01) Postal code 31310 ONS code 3115 Mers-el-Kébir (Arabic: المرسى الكبير, “the Great Harbor”) is a port town in northwestern Algeria, located by the Mediterranean Sea near Oran, in the Oran Province.
Contents
History
Originally a Roman port, Mers-el-Kébir became an Almohad naval arsenal in the 12th century, fell under the rulers of Tlemcen in the 15th century, and eventually became a center of pirate activity around 1492. It was occupied variously by the Ottoman Turks, Portuguese and Spanish, with the Spanish (which named it Mazalquivir) capturing it in 1505 under Cardinal Cisneros. Mazalquivir was the base used to capture neighbouring Oran in 1509. The Spanish held both cities until 1708, when they were driven out by Turkish Bey Mustapha Ben Youssef (also known as Bouchelaghem). The Spanish returned in 1732 when the armada of the Duke of Montemar was victorious in the Battle of Aïn-el-Turk and again took Oran and Mazalquivir. Both cities were held until 1792, when they were sold by King Charles IV to the Bey of Algiers.
The French occupied it in 1830, and renamed it Saint André de Mers-el-Kébir, enhancing the port in 1868 with an eponymous lighthouse,[1] the latter was destroyed during World War II.
World War II
Main article: Attack on Mers-el-KébirFollowing the German defeat of France in 1940, part of the French fleet holed up in the port. On July 3, 1940, Force H of the British Royal Navy, led by Vice-Admiral Sir James Somerville, attacked the French fleet at Mers-el-Kébir to stop it falling into German hands.
Post World War II
After World War II, France used its naval base at Mers-el-Kébir to assist in atomic tests. The Évian Accords of March 18, 1962, which recognized Algerian independence, allowed France to maintain its base for 15 years; however, France withdrew within five years.
See also
References
External links
- A plan of the Mers-el-Kébir anchorage is available at http://www.hmshood.org.uk/reference/official/adm234/adm234-317.html
- (French) Accueil Kébir
- (French) MERS EL KEBIR 1940
- Mers-el-Kebir – A Battle Between Friends by Irwin J. Kappes
 Oran Province
Oran ProvinceOran District 
Aïn El Turk District Aïn El Turk · Mers El Kébir · Bousfer · El Ançor Arzew District Arzew · Sidi Ben Yebka Bethioua District Bethioua · Mers El Hadjadj · Aïn Bya Es Sénia District Es Sénia · El Kerma · Sidi Chami Bir El Djir District Bir El Djir · Hassi Bounif · Hassi Ben Okba Boutlélis District Boutlélis · Aïn El Kerma · Misserghin Oued Tlélat District Oued Tlélat · El Braya · Boufatis · Tafraoui Gdyel District Gdyel · Hassi Mefsoukh · Ben Freha Categories:- Oran Province
- Aïn El Turk District
- Populated places in Oran Province
- Communes of Algeria
- Former Spanish colonies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.