- Mons Hadley
-
For other uses, see Hadley (disambiguation).See also: Hadley–Apennine (lunar region)
Mons Hadley 
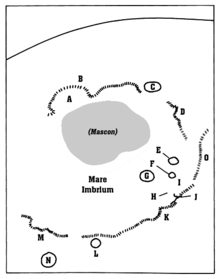
Jim Irwin and the LRV from Apollo 15, with Mons Hadley in the backgroundElevation 4.6 km Listing Lunar mountains Location Location the Moon Coordinates 26°30′N 4°42′E / 26.5°N 4.7°E Mons Hadley is a massif in the northern portion of the Montes Apenninus, a range in the northern hemisphere of the Moon. The selenographic coordinates of this peak are 26.5° N, 4.7° E. It has a height of 4.6 km and a maximum diameter of 25 km at the base.
To the southwest of this mountain is a valley that served as the landing site for the Apollo 15 expedition. To the southwest of this same valley is the slightly smaller Mons Hadley Delta (δ) peak with a height of about 3.5 km. The coordinates of this peak are 25.8° N, 3.8° E. To the west of these peaks is the sinuous Rima Hadley rille where the Fallen Astronaut memorial has been placed in memory of those astronauts who died in the advancement of space exploration.
These features were named after John Hadley.
Contents
Rima Hadley
This sinuous lunar rille follows a course generally to the northeast, toward the Mons Hadley peak, for which it is named. This feature is centered at selenographic coordinates 25.0° N, 3.0° E, and lies within a diameter of 80 km. It begins at the crater Béla, an elongated formation with the long axis oriented to the northwest.
Nearby craters
Four small craters near this rille have been assigned names by the IAU. These are listed in the table below.
Crater Coordinates Diameter Name source Béla 24°42′N 2°18′E / 24.7°N 2.3°E 11 × 2 km Hungarian masculine name Carlos 24°54′N 2°18′E / 24.9°N 2.3°E 4 km Spanish masculine name Jomo 24°24′N 2°24′E / 24.4°N 2.4°E 7 km African masculine name Taizo 24°42′N 2°12′E / 24.7°N 2.2°E 6 km Japanese masculine name Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater mid-point that is closest to Mons Hadley.
Hadley Latitude Longitude Diameter C 25.5° N 2.8° E 6 km See also
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A., (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-81528-2.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 0-936389-27-3.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. http://host.planet4589.org/astro/lunar/. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode 1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 0-304-35469-4.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-33500-0.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 0-913135-17-8.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revision ed.). Dover. ISBN 0-486-20917-2.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-62248-4.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 1-85233-193-3.
External links
- LTO-41B4 Hadley — L&PI Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap
Categories:- LQ12 quadrangle
- Mountains on the Moon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.