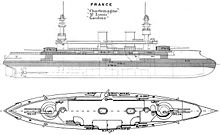
- Charlemagne class battleship
-

The St Louis in April 1903Class overview Name: Charlemagne Builders: Brest and Lorient shipyards Operators: French Navy Preceded by: Battleship Displacement: 11,300 tonnes Length: 117.5 metres (385 ft) Beam: 20.5 metres (67 ft) Draught: 8.40 metres (27.6 ft) Propulsion: 2 steam engines, 3 shafts, 14,500 horsepower (10,800 kW) Speed: 18 knots (33 km/h; 21 mph) Complement: 725 men Armament: 2 × 2 - 305 mm Mle 1893/96 guns
4 × 450mm torpedo tubes
10 × 1 - 138mm/45 Modèle 1893 guns
8 × 1 - 100 mm/10Armour: Belt: 250–400 millimetres (9.8–16 in)
Bunker: 75 millimetres (3.0 in)
Decks: 90 and 40 millimetres (3.5 and 1.6 in)
Barbettes: 400 millimetres (16 in)Notes: Ships in class include: Charlemagne, St Louis, Gaulois The Charlemagne class was a class of pre-dreadnought battleships of the French Navy. It consisted of three ships, the Charlemagne, the St Louis and the Gaulois. Several other single ship classes were based on the Charlemagne class. The class participated in World War I.
Contents
Design
The ships had a displacement of 11,300 tonnes, were 117.5 metres (385 ft) long, had a beam of 20.5 metres (67 ft), and a draught of 8.40 metres (27.6 ft). Propulsion machinery consisted of two steam engines which supplied 14,500 horsepower (10,800 kW) to the three propeller shafts. Maximum speed was 18 knots (33 km/h; 21 mph). The ship's company was 725 strong.
Each ship's main armament consisted of four 305 mm Mle 1893/96 guns in two twin turrets. The Charlemagne design was the first French ship to use twin turrets instead of the French trademark of a single-gun turret at each end of the upper deck. The main guns were supplemented by ten 138mm/45 Modèle 1893 guns in single mountings, plus eight 100 mm/10 guns in single mounts. Four 450mm torpedo tubes were also fitted.
The ships' main belt armour varied from 250 to 400 millimetres (9.8 to 16 in) in thickness, and ran the entire length of the hull. Deck armour was either 90 or 40 millimetres (3.5 or 1.6 in). The barbettes were 400 millimetres (16 in) thick, while the bunker was protected by 75 millimetres (3.0 in) of armour.
Opertional history
At the outbreak of the First World War, these ships were considered to be second-rate battleships, fit for areas of low danger. On 18 March 1915 the Charlemagne and Gaulois, along with the Bouvet and Suffren, took part in the Battle of Gallipoli, under Admiral Guépratte. The Gaulois was damaged in a minefield but survived the battle.
Gaulois was sunk on 27 December 1916 by the German U-boat UB-47 was to Cergio in the Aegean Sea, despite the battleship being protected by an escort screen of light cruisers and naval trawlers.[1][2] Two of Gaulois' crew members were killed in the initial torpedo explosion, while another two died during the battleship's sinking.[3] UB-47 was able to escape the scene unharmed and continued her patrol.[1]
References
- ^ a b Gibson and Prendergast, p. 134.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Ships hit during WWI: Gaulois". U-Boat War in World War I. Uboat.net. http://uboat.net/wwi/ships_hit/2386.html. Retrieved 9 February 2009.
- ^ "Big French cruiser torpedoed and sunk". The Washington Post: p. 1. 31 December 1916. According to this article, Gaulois had been re-classed as a cruiser before the start of World War I.
External links
 Media related to Classe Charlemagne at Wikimedia CommonsFrench naval ship classes of World War I
Media related to Classe Charlemagne at Wikimedia CommonsFrench naval ship classes of World War IDreadnought battleships Pre-dreadnought battleships BrennusS · Charles MartelS · CarnotS · JauréguiberryS · MassénaS · BouvetS · Charlemagne · Henri IVS · SuffrenS · République · Liberté · Danton
Armoured cruisers Dupuy de LômeS · Amiral Charner · PothuauS · Jeanne d'ArcS · Gueydon · Dupleix · Gloire · Léon Gambetta · Jules MicheletS · Ernest RenanS · Edgar Quinet
Protected cruisers Amiral CécilleS · Destroyers
Durandal · Framée · Rochefortais · Arquebuse · Claymore · Branlebas · Spahi · Voltigeur · Chasseur · Bouclier · Bisson · Enseigne Roux · Enseigne GaboldeS · Aventurier · Arabe
Submarines Seaplane carriers
S - Single ship of class · C - Completed after the war · X - Cancelled Categories:- Battleship classes
- Charlemagne class battleships
- World War I battleships of France
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.