- Giraffe
Taxobox
name = Giraffe
status = LR/cd | status_system = IUCN2.3
trend = stable
status_ref = [IUCN2006|assessors=Antelope Specialist Group|year=1996|id=9194|title=Giraffa camelopardalis|downloaded=5 May 2006 ]

image_width = 230px
regnum =Animal ia
phylum =Chordata
classis =Mammal ia
ordo =Artiodactyla
familia =Giraffidae
genus = "Giraffa"
range_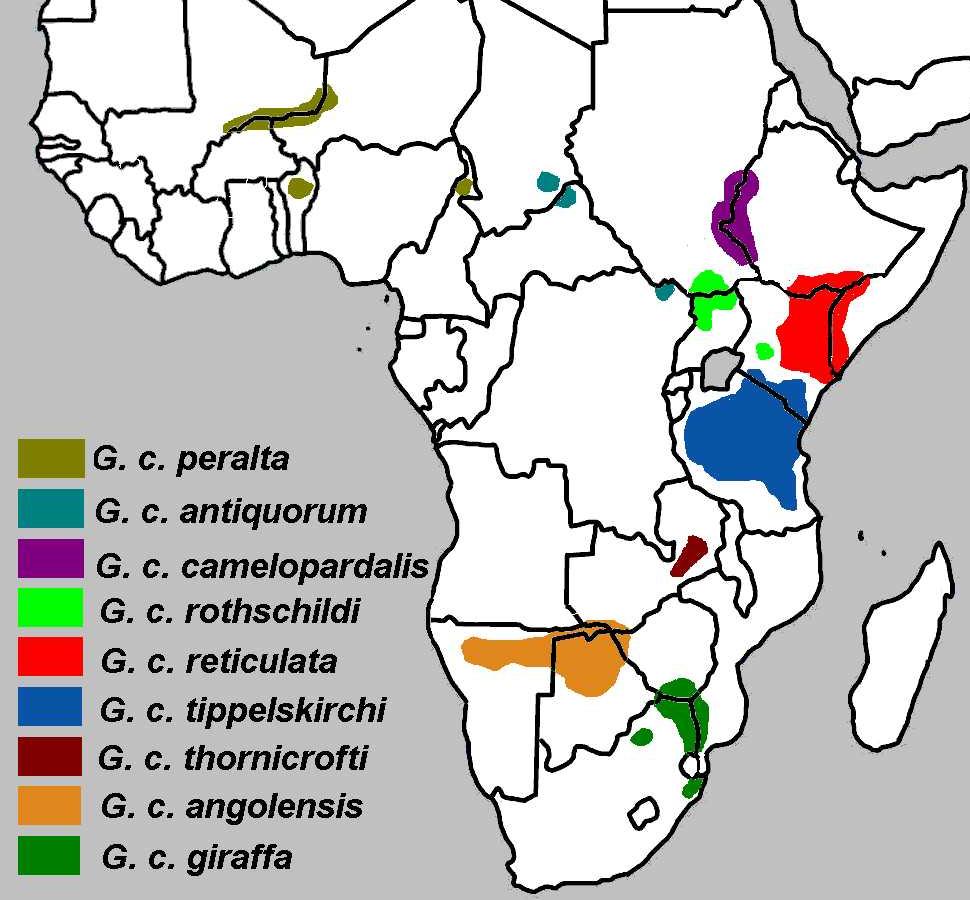
range_map_caption=Range map
range_map_width = 230px
species = "G. camelopardalis"
binomial = "Giraffa camelopardalis"
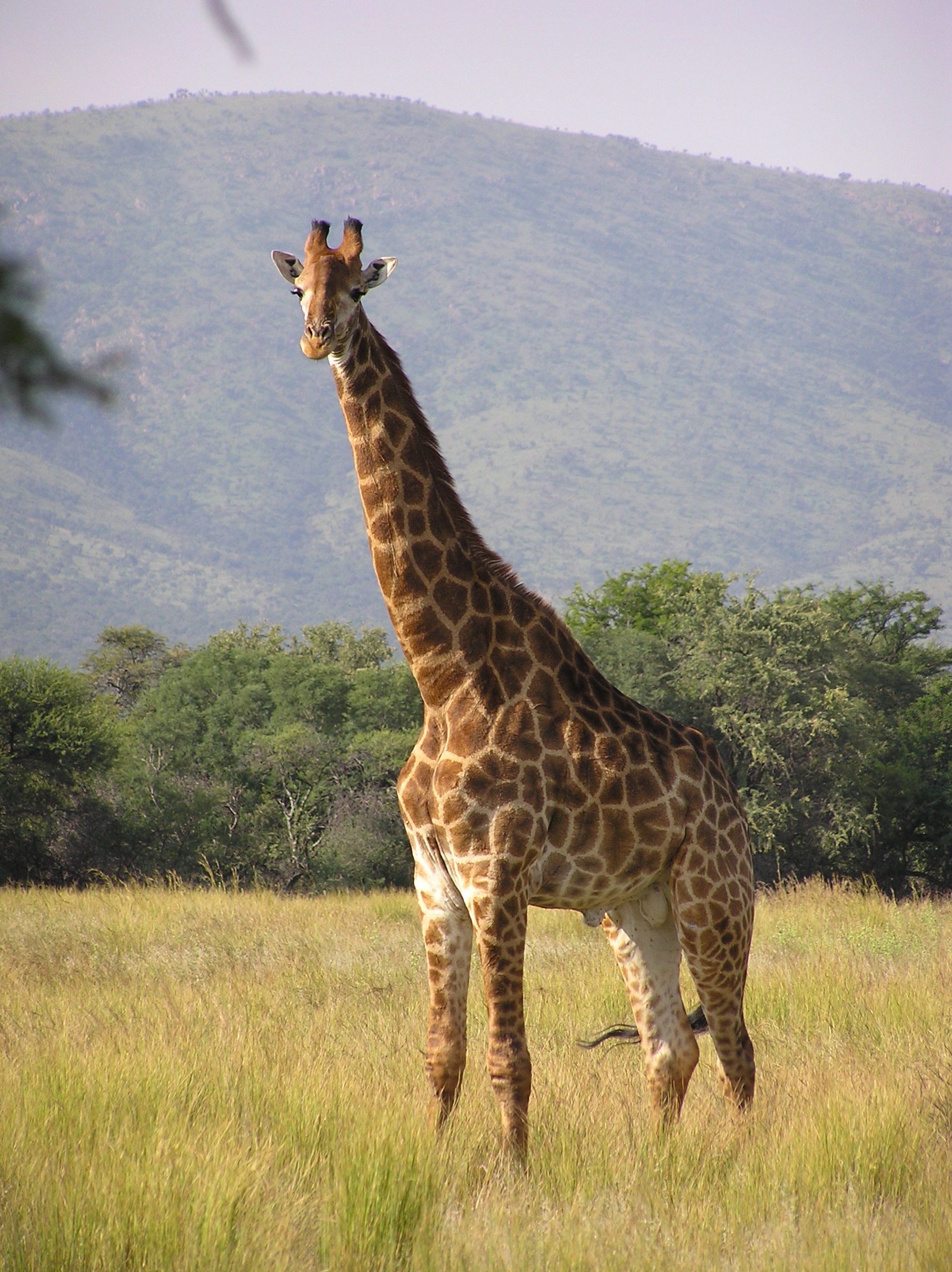
binomial_authority = Linnaeus, 1758The giraffe ("Giraffa camelopardalis") is anAfrica neven-toed ungulate mammal , the tallest of all land-livinganimal species , and the largestruminant . Males can be 4.8 to 5.5 metres (16 to 18 feet) tall and weigh up to 1,700 kilograms (3,800 pounds). The record-sized bull, shot inKenya in 1934, was 5.87 m (19.2 ft) tall and weighed approximately 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). [ [http://www.sandiegozoo.org/animalbytes/t-giraffe.html San Diego Zoo giraffe fact sheet] Retrieved 14 August 2006.] Females are generally slightly shorter, and weigh less than the males do.The giraffe is related to
deer andcattle , but is placed in a separatefamily , theGiraffidae , consisting only of the giraffe and its closest relative, theokapi . Its range extends fromChad toSouth Africa .Giraffes can inhabit
savanna s, grasslands, or open woodlands. They prefer areas enriched withacacia growth. They drink large quantities of water and, as a result, they can spend long periods of time in dry, arid areas. When searching for more food they will venture into areas with denser foliage.Etymology
The species name "camelopardalis" (camelopard) is derived from its early Roman name, where it was described as having characteristics of both a
camel and aleopard . [ [http://www.eaudrey.com/myth/camelopard.htm Camelopard ] ] The English word "camelopard" first appeared in the 14th century and survived in common usage well into the 19th century. TheAfrikaans language retained it. The Arabic word الزرافة "ziraafa" or "zurapha", meaning "assemblage" (of animals), or just "tall", was used in English from the sixteenth century on, often in the Italianate form "giraffa".Taxonomy and evolution
. The modern long-necked giraffe, "Giraffa camelopardalis", appeared 1 million years ago.
Classification
There are nine generally accepted
subspecies , differentiated by colour and pattern variations and range:
* Reticulated orSomali Giraffe ("G.c. reticulata") — large, polygonal liver-coloured spots outlined by a network of bright white lines. The blocks may sometimes appear deep red and may also cover the legs. Range: northeasternKenya ,Ethiopia ,Somalia .
* Angolan orSmoky Giraffe ("G.c. angolensis") — large spots and some notches around the edges, extending down the entire lower leg. Range:Angola ,Zambia .
*Kordofan Giraffe ("G.c. antiquorum") — smaller, more irregular spots that cover the inner legs. Range: western and southwesternSudan .
* Masai or Kilimanjaro Giraffe ("G.c. tippelskirchi") — jagged-edged, vine-leaf shaped spots of dark chocolate on a yellowish background. Range: central and southernKenya ,Tanzania .
* Nubian Giraffe ("G.c. camelopardalis") — large, four-sided spots of chestnut brown on an off-white background and no spots on inner sides of the legs or below the hocks. Range: easternSudan , northeast Congo.
*Rothschild Giraffe or Baringo Giraffe or Ugandan Giraffe ("G.c. rothschildi") — deep brown, blotched or rectangular spots with poorly defined cream lines. Hocks may be spotted. Range:Uganda , north-centralKenya .
*South African Giraffe ("G.c. giraffa") — rounded or blotched spots, some with star-like extensions on a light tan background, running down to the hooves. Range:South Africa ,Namibia ,Botswana ,Zimbabwe ,Mozambique .
* Thornicroft orRhodesian Giraffe ("G.c. thornicrofti") — star-shaped or leafy spots extend to the lower leg. Range: easternZambia .
* West African orNigerian Giraffe ("G.c. peralta") — numerous pale, yellowish red spots. Range:Niger ,Cameroon .Some scientists regard Kordofan and West African Giraffes as a single subspecies; similarly with Nubian and Rothschild's Giraffes, and with Angolan and South African Giraffes. Further, some scientists regard all populations except the Masai Giraffes as a single subspecies. By contrast, scientists have proposed four other subspecies — Cape Giraffe ("G.c. capensis"), Lado Giraffe ("G.c. cottoni"), Congo Giraffe ("G.c. congoensis"), and Transvaal Giraffe ("G.c. wardi") — but none of these is widely accepted.Though giraffes of these populations interbreed freely under conditions of captivity, suggesting that they are subspecific populations, genetic testing published in 2007 [David Brown, Rick A Brenneman, "et al.", "Extensive Population Genetic Structure in the Giraffe", "BioMedCentral Biology". Reported in [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7156146.stm BBC News, "Not one but 'six giraffe species'", 21 December 2007] and in [http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2007/12/071221094911.htm ScienceDaily, "Giraffes And Frogs Provide More Evidence Of New Species Hidden In Plain Sight"] , 21 December 2007] has been interpreted to show that there may be at least six species of giraffe that are reproductively isolated and not interbreeding, even though no natural obstacles, like mountain ranges or impassable rivers block their mutual access. In fact, the study found that the two giraffe populations that live closest to each other— the reticulated giraffe ("G. camelopardalis reticulata") of north Kenya, and the Masai giraffe ("G. c. tippelskirchi") in south Kenya— separated genetically between 0.13 and 1.62 million years BP, judging from
genetic drift in nuclear andmitochondrial DNA .The implications for conservation of as many as eleven such
cryptic species and sub-species were summarised by David Brown forBBC News : "Lumping all giraffes into one species obscures the reality that some kinds of giraffe are on the brink. Some of these populations number only a few hundred individuals and need immediate protection."Anatomy and morphology
Male giraffes are around 4.8-5.5 m (16-19 ft) tall at the horn tips, and normally weigh 1300-1700 kg (2900-3800 lb) Females are 30-60 cm (1-2 ft) shorter and weigh about 200-400 kg (400-800 lb) less than males. Giraffes have spots covering their entire bodies, except their underbellies, with each giraffe having a unique pattern of spots.
Horns
Both sexes have horns, although the horns of a female are smaller. The prominent horns are formed from ossified cartilage and are called
ossicone s. The appearance of horns is a reliable method of identifying the sex of giraffes, with the females displaying tufts of hair on the top of the horns, where as males' horns tend to be bald on top — an effect of necking in combat. Males sometimes develop calcium deposits which form bumps on their skull as they age, which can give the appearance of up to three further horns. [ [http://www.sandiegozoo.org/animalbytes/t-giraffe.html San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes: Giraffe ] ]Neck
Giraffes have long necks, which they use to browse the leaves of trees. They possess seven vertebrae in the neck (the usual number for a mammal) that are elongated. The vertebrae are separated by highly flexible joints. The base of the neck has spines which project upward and form a hump over the shoulders. They have anchor muscles that hold the neck upright.
Legs and pacing
Giraffes also have slightly elongated forelegs, about 10% longer than their hind legs. The pace of the giraffe is an amble, though when pursued it can run extremely fast. It can not sustain a lengthy chase. Its leg length compels an unusual gait with the left legs moving together followed by right (similar to
pacing ) at low speed, and the back legs crossing outside the front at high speed. When hunting adult giraffes,lion s try to knock the lanky animal off its feet and pull it down. Giraffes are difficult and dangerous prey though, and when attacked the giraffe defends itself by kicking with great force. A single well-placed kick from an adult giraffe can shatter a lion's skull or break its spine. Lions are the only predators which pose a serious threat to an adult giraffe.Circulatory system
Modifications to the giraffe's structure have evolved, particularly to the
circulatory system . A giraffe's heart, which can weigh up to 10 kg (22 lb) and measure about 60 cm (2 ft) long, has to generate around double the normal blood pressure for an average large mammal in order to maintain blood flow to the brain against gravity. In the upper neck, a complex pressure-regulation system called therete mirabile prevents excess blood flow to the brain when the giraffe lowers its head to drink. Conversely, the blood vessels in the lower legs are under great pressure (because of the weight of fluid pressing down on them). In other animals such pressure would force the blood out through the capillary walls; giraffes, however, have a very tight sheath of thick skin over their lower limbs which maintains high extravascular pressure in exactly the same way as a pilot'sg-suit .Behaviour
ocial structure and breeding habits
Female giraffes associate in groups of a dozen or so members, occasionally including a few younger males. Younger males tend to live in "bachelor" herds, with older males often leading solitary lives. Reproduction is polygamous, with a few older males impregnating all the fertile females in a herd. Male giraffes determine female fertility by tasting the female's urine in order to detect estrus, in a multi-step process known as the
Flehmen response .Giraffes will mingle with the other herbivores in the African bush. They are beneficial to be around because of their height. A giraffe is tall enough to have a much wider scope of an area and will watch out for predators.
Reproduction
Giraffe
gestation lasts between 14 and 15 months, after which a single calf is born. The mother gives birth standing up and theembryo nic sack usually bursts when the baby falls to the ground. Newborn giraffes are about 1.8 m (6 ft) tall. Within a few hours of being born, calves can run around and are indistinguishable from a week-old calf; however, for the first two weeks, they spend most of their time lying down, guarded by the mother. The young can fall prey to lions,leopard s,spotted hyena s, and wild dogs. It has been speculated that their characteristic spotted pattern provides a certain degree ofcamouflage . Only 25 to 50% of giraffe calves reach adulthood; the life expectancy is between 20 and 25 years in the wild and 28 years in captivity ("Encyclopedia of Animals").Necking
As noted above, males often engage in necking, which has been described as having various functions. One of these is combat. Battles can be fatal, but are more often less severe. The longer the neck, and the heavier the head at the end of the neck, the greater the force a giraffe is able to deliver in a blow. It has also been observed that males that are successful in necking have greater access to estrous females, so the length of the neck may be a product of
sexual selection . [Robert E. Simmons and Lue Scheepers: [http://bill.srnr.arizona.edu/classes/182/Giraffe/WinningByANeck.pdf Winning by a neck: Sexual selection in the evolution of giraffe.] "The American Naturalist", 148 (1996): pp. 771-786.]After a necking duel, a giraffe can land a powerful blow with his head — occasionally knocking a male opponent to the ground. These fights rarely last more than a few minutes or end in physical harm.
Another function of necking is affectionate and sexual, in which two males will caress and court each other, leading up to mounting and climax. Same sex relations are more frequent than heterosexual behaviour. In one area 94% of mounting incidents were of a homosexual nature. The proportion of same sex courtships varies between 30 and 75%, and at any given time one in twenty males will be engaged in affectionate necking behaviour with another male. Females, on the other hand, only appear to have same sex relations in 1% of mounting incidents. [Bruce Bagemihl, Biological Exuberance: Animal Homosexuality and Natural Diversity, St. Martin's Press, 1999; pp.391-393]
tereotypic behavior
Many animals when kept in captivity, such as in
zoo s, display abnormal behaviours. Such unnatural behaviours are known asstereotypic behaviour s. [Jentz, D.C. & A.B. Gull 1978. Towards a definition of abnormal activity: stereotypic behaviours in captive primates. "Mamm. Ecol." 12: 145–154.] In particular, giraffes show distinct patterns of stereotypic behaviours when removed from their natural environment. Due to a subconscious response to suckle milk from their mother, something which many human-reared giraffes and other captive animals do not experience, giraffes resort instead to excessive tongue use on inanimate objects. [Harrison, J.C, Q.F. George & C.C. Cronk 2001. Stereotypic behaviour in zoo animals. "J. Zoo Sc." 23: 71–86.]Due to the obvious social and cultural discomfort associated with the addition of milk delivery devices, animal enclosures are often enriched with other stimuli, such as food and mental distractions (toys, scent markings etc.). This operates as a distraction, removing the giraffe’s focus from its instinctual tendencies towards suckling, resulting in tongue lolling and licking of objects in close proximity.
Foraging and cleaning
The giraffe browses on the twigs of trees, preferring trees of the
genus "Mimosa "; but it appears that it can live without inconvenience on other vegetable food. A giraffe can eat 63 kg (140 lb) of leaves and twigs daily. As ruminants, they first chew their food, swallow for processing and then visibly regurgitate the semi-digested cud up their necks and back into the mouth, in order to chew again. This process is usually repeated several times for each mouthful.A giraffe will clean off any bugs that appear on its face with its extremely long tongue (about 45 cm/18 in). The tongue is tough on account of the giraffe's diet, which can include thorns from the trees that they eat. InSouthern Africa , giraffes feed on allacacia s, especially "Acacia erioloba ", and possess a specially-adapted tongue and lips that are tough enough to withstand, or even ignore, the vicious thorns of this plant.leeping
The giraffe has one of the shortest sleep requirements of any mammal, which is between 10 minutes and two hours in a 24-hour period, averaging 1.9 hours per day. [ [http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/sleep/articles/whatissleep.shtml BBC - Science & Nature - Human Body and Mind - What is sleep ] ]
Communication
Although generally quiet and not vocal, giraffes have been heard to make various sounds. Courting males will emit loud coughs. Females will call their young by whistling or bellowing. Calves will bleat, moo, or make mewing sounds. In addition, giraffes will grunt, snort, hiss, or make strange flute-like sounds. Recent research has shown evidence that the animal communicates at an
infrasound level. [ [http://www.animalvoice.com/Giraffe.htm Infrasound From the Giraffe ] ]Human interactions
Conservation
Giraffes are hunted for their hides, hair, and meat. In addition, habitat destruction also hurts the giraffe. In the
Sahel trees are cut down for firewood and to make way for livestock. Normally, giraffes are able to cope with livestock since they feed in the trees above their heads. The giraffe population is shrinking in West Africa. However, the populations in eastern and southern Africa are stable and, due to the popularity of privately-owned game ranches and sanctuaries (i.e.Bour-Algi Giraffe Sanctuary ), are expanding. The giraffe is a protected species in most of its range. The total African giraffe population has been estimated to range from 110,000 to 150,000. Kenya (45,000), Tanzania (30,000), and Botswana (12,000), have the largest national populations. [East, R. 1998, in: African Antelope Database 1998. IUCN/SSC Antelope Specialist Group Report.]An unexpected danger to giraffes in captivity is that, as they are typically the tallest objects in a zoo, giraffes are at increased risk of being struck by
lightning . In the wild, this hazard is reduced by the presence of trees; as well, the giraffe's natural habitat range has an extremely low occurrence of lightning -- NASA's satellite lightning detection system indicates that the area receives an average of less than one cloud-to-ground flash per square kilometre per year. [ [http://www.weatherquesting.com/giraffe-contrail.htm Lightning strikes giraffes] ]In art and culture
Giraffes can be seen in paintings, including the famous painting of a giraffe which was taken from Africa to
China in 1414. The giraffe was placed in aMing Dynasty zoo.The
Medici giraffe was a giraffe presented toLorenzo de' Medici in 1486. It caused a great stir on its arrival inFlorence , being reputedly the first living giraffe to be seen inItaly since the days ofAncient Rome . Another famous giraffe, called Zarafa, was brought fromAfrica toParis in the early 1800s and kept in amenagerie for 18 years."Giraffe" is a novel by the author
J. M. Ledgard . The work concerns a true incident in which 49 giraffes were slaughtered in the Czech Republic (then Czechoslovakia) in 1975 following the suspected outbreak of disease amongst the group. The novel contains extensive information about the species, including the long history of European fascination with the beast and its captivity in zoos.Notable fictional giraffes include:
*
Toys "R" Us mascot Geoffrey the Giraffe. He was originally portrayed as a cartoon giraffe but in the 2001 commercials he was portrayed as a real-life giraffe who talks; an animatronic version of Geoffrey the Giraffe (created by Stan Winston Studios), was voiced byJim Hanks in commercials for radio and television.*
Longrack of the Transformers universe
* Girafarig from thePokémon franchise
* Melman from "MadagascarGiraffes have also appeared as background characters in various other animated works such as "
Dumbo " and "The Lion King ".References
External links
* [http://youtube.com/watch?v=XrX9NBMUOzw Video - Giraffe birth at the San Francisco Zoo]
* [http://www.awf.org/wildlives/118 Giraffes: Wildlife summary from the African Wildlife Foundation]
*ARKive - [http://www.arkive.org/species/GES/mammals/Giraffa_camelopardalis/ images and movies of the giraffe "(Giraffa camelopardalis)"] .
* [http://www.girafes.net/girafes Introduction to the history of the Giraffe in Middle Ages (French)]
* [http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Giraffa_camelopardalis.html Animal Diversity Web - "Giraffa camelopardalis"]
* [http://www.isidore-of-seville.com/giraffe/ Giraffe Central web directory]
* [http://www.iucnredlist.org/search/details.php?species=9194 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species]
* [http://www.pbs.org/wnet/nature/tallblondes/index.html PBS Nature: Tall Blondes (Giraffes)]
* [http://www.wickedgiraffe.com Matt's World of Wicked Giraffes]
* [http://www.bio.davidson.edu/people/vecase/Behavior/Spring2004/breedlove/matingsystem.html Mating System]
* [http://www.learnanimals.com/giraffe/ Giraffe Info Sheet]
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=16423382&dopt=Abstract Long-term suppression of fertility in female giraffe using the GnRH agonist deslorelin as a long-acting implant]
*cite web|url=http://www.archive.org/download/ErikRingmaraudienceForAGiraffeEuropeanExceptionalismAndTheQuest_744/ErikRingmarAudienceForAGiraffe.pdf |title=Audience for a Giraffe: European Expansionism and the Quest for the Exotic|author=Erik Ringmar|publisher="Journal of World History", 17:4, December, 2006. pp. 353-97
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
