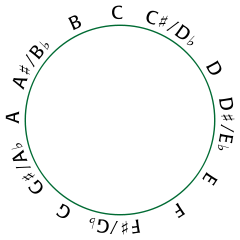
- Chromatic circle
-
The chromatic circle is a geometrical space that shows relationships among the 12 equal-tempered pitch classes making up the familiar chromatic scale. If one starts on any equal-tempered pitch and repeatedly ascends by the musical interval of a semitone, one will eventually land on a pitch with the same pitch class as the initial one, passing through all the other equal-tempered chromatic pitch classes in between.
Since the space is circular, it is also possible to descend by semitone. The chromatic circle is useful because it represents melodic distance, which is often correlated with physical distance on musical instruments. For instance, to move from any C on a piano keyboard to the nearest E, one must move up four semitones, corresponding to four clockwise steps on the chromatic circle. One can also move down by eight semitones, corresponding to eight counterclockwise steps on the pitch class circle. Larger motions on the piano (or in pitch space) can be represented in pitch class space by paths that "wrap around" the chromatic circle one or more times.
A key difference between the chromatic circle and the circle of fifths is that the former is truly a continuous space: every point on the circle corresponds to a conceivable pitch class, and every conceivable pitch class corresponds to a point on the circle. By contrast, the circle of fifths is fundamentally a discrete structure, and there is no obvious way to assign pitch classes to each of its points. A mathematician would say that the circle of fifths and the chromatic circle are not homeomorphic.
However, one can represent the twelve equal-tempered pitch classes by the cyclic group of order twelve, or equivalently, the residue classes modulo twelve, Z/12Z. The group Z12 has four generators, which can be identified with the ascending and descending semitones and the ascending and descending perfect fifths. The semitonal generator gives rise to the chromatic circle while the perfect fifth gives rise to the circle of fifths.
Notes
- ^ "Prelude to Musical Geometry", p.364, Brian J. McCartin, The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 29, No. 5 (Nov., 1998), pp. 354-370. (abstract) (JSTOR)
References
- Brower, Candace (2000), "A Cognitive Theory of Musical Meaning", Journal of Music Theory (Duke University Press) 44 (2): 323–379, doi:10.2307/3090681, JSTOR 3090681.
- Kučinskas, Darius (2005), "Symmetry in creative work of Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis", Menotyra 38 (1): 42–46, http://images.katalogas.lt/maleidykla/Men51/Men_042_046.pdf.
Categories:- Post-tonal music theory
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.