- Dication
-
- Distinguish from dictation.
A dication is any cation, of general formula 2+, formed by the removal of two electrons from a neutral species.
Diatomic dications corresponding to stable neutral species (e.g. H22+ formed by removal of two electrons from H2) often decay quickly into two singly charged particles (H+), due to the loss of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals. Energy levels of diatomic dications can be studied with good resolution by measuring the yield of pairs of zero-kinetic-energy electrons from double photoionization of a molecule as a function of the photoionizing wavelength (threshold photoelectrons coincidence spectroscopy - TPEsCO). The He22+ dication is kinetically stable.
An example of a stable diatomic dication which is not formed by oxidation of a neutral diatomic molecule is the dimercury dication Hg22+. An example of a polyatomic dication is S82+, formed by oxidation of S8 and unstable with respect to further oxidisation over time to form SO2.
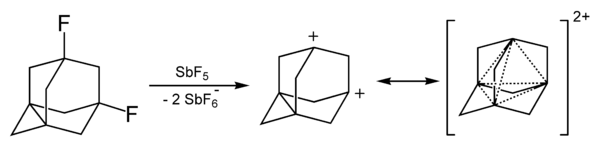
Many organic dications can be detected in mass spectrometry for example CH42+ (a CH22+ , H2 complex) and the acetylene dication C2H22+.[1] The adamantyl dication has been synthesized.
References
- ^ Lammertsma, K., von Ragué Schleyer, P. and Schwarz, H. (1989), Organic Dications: Gas Phase Experiments and Theory in Concert. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 28: 1321–1341. doi:10.1002/anie.198913211
Categories:- Ions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.