- Norumbega
-
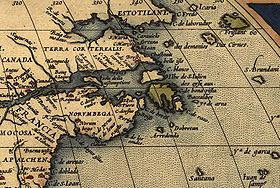 Part of Abraham Ortelius atlas from 1570, showing "Norvmbega" among other more or less mythical names for various areas (as well as several phantom islands).
Part of Abraham Ortelius atlas from 1570, showing "Norvmbega" among other more or less mythical names for various areas (as well as several phantom islands).
Norumbega (or Norumbègue, Nurumbega, etc) was a legendary settlement in northeastern North America, inextricably connected with attempts to demonstrate Viking incursions in New England.[1][2][3] Like Cathay, it was a semi-legendary place name used to fill a gap in existing geographical knowledge.
An early reference was that of the French navigator Jean Allefonsce (1542) who reported that he had coasted south from Newfoundland and had discovered a great river. "The river is more than 40 leagues wide at its entrance and retains its width some thirty or forty leagues. It is full of Islands, which stretch some ten or twelve leagues into the sea. ... Fifteen leagues within this river there is a town called Norombega, with clever inhabitants, who trade in furs of all sorts; the town folk are dressed in furs, wearing sable. ... The people use many words which sound like Latin. They worship the sun. They are tall and handsome in form. The land of Norombega lie high and is well situated."[4]
It often appeared on subsequent European maps of North America, lying south of Acadia somewhere in what is now New England. Norumbega was thought to be a large, rich Native city, and by extension the river it was on, and the region surrounding it.
Samuel de Champlain searched for Norumbega in 1604 and believed he had found Allefonsce's river in the form of the Penobscot, which he called "the great river of Norumbega". He sailed at far as the rapids at what is now Bangor, Maine, but finding only villages, his and subsequent maps deleted reference to Norumbega as a town, region, or even river. [5] Most historians have subsequently accepted the Penobscot region as Allefonsce's source for Norumbega, though the matter was hotly contested by nineteenth century antiquarians, who argued that the name should be identified with their own river or region.[6]
The city of Bangor embraced the Norumbega legend in the nineteenth century, naming their Greek Revival style municipal hall "Norumbega Hall", a venue for public meetings and lectures. The building stood in the center of the city until destroyed in the Great Fire of 1911. A park named "Norumbega Mall" now occupies the site, and an adjacent building housing the University of Maine Art Gallery is now named "Norumbega Hall". There was also a Norumbega Bank in nineteenth century Bangor. In 1886 Joseph Stearns, the inventor of the duplex telegraphy system, built a mansion named "Norumbega Castle", which still stands on US Route 1 in Camden, Maine, overlooking Penobscot Bay.
In the late 19th century, Eben Norton Horsford linked the name and legend of Norumbega to sites in the Cambridge, Massachusetts area, and built the Norumbega Tower at the confluence of Stony Brook and the Charles River in Weston, Massachusetts, where he believed Fort Norumbega was located (see the Horsford article for more on his claims). In honor of Horsford's generous donations to Wellesley College, a building named Norumbega Hall was dedicated in 1886 and celebrated by a poem by John Greenleaf Whittier.[7]
The word "Norumbega" was originally spelled Oranbega in Girolamo da Verrazzano's 1529 map of America, and the word is believed to derive from one of the Algonquian languages spoken in New England. It is often cited as meaning "quiet place between the rapids" or "quiet stretch of water".
Contents
See also
- Norumbega Park, a park in Newton, Massachusetts established opposite Horsford's Norumbega Tower.
Further reading
- DeCosta, B.F. 1890. Ancient Norumbega, or the voyages of Simon Ferdinando and John Walker to the Penobscot River, 1579-1580. Joel Munsell's Sons, Albany, NY
- R. H. Ramsay, 1972. No Longer on the Map'
- Baker, Emerson W., Churchill, Edwin A., D'Abate, Richard S., Jones, Kristine L., Konrad, Victor A. and Prins, Harald E.L., editors, 1994. American beginnings: Exploration, culture, and cartography in the land of Norumbega (University of Nebraska Press)
- Diamond, Sigmund. (April 1951). "Norumbega: New England Xanadu" in The American Neptune vol. 11. pp. 95–107.
- 1941 edition of the Columbia Encyclopedia
References and notes
- ^ "Did Leif Erikson once live in Cambridge, Massachusetts?". The Straight Dope. http://www.straightdope.com/mailbag/mleifinma.html. Retrieved 2008-08-09.
- ^ Horsford, Eben Norton (1892). The Landfall of Leif Erikson, A.D. 1000: And the Site of His Houses in Vineland. Damrell and Upham. http://books.google.com/books?id=5wNCAAAACAAJ&dq=The+Landfall+of+Leif+Erikson:+A.D.+1000.
- ^ Horsford, Eben Norton (1890). The Discovery of the Ancient City of Norumbega. Houghton, Mifflin. http://books.google.com/books?id=c2ETAAAAYAAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+Discovery+of+the+Ancient+City+of+Norumbega.
- ^ DeCosta, 1890, p. 99.
- ^ Susan Danforth, The Land of Norumbega: Maine in the Age of Exploration and Settlement (Portland, Me.: Portland Museum of Art, 1988), p. 54
- ^ John Fiske, The Dutch and Quaker Colonies in America (NY: 1899) p. 70: “the most common opinion is that the Penobscot was the River of Norumbega, with a village on its bank somewhere up country, where European skippers traded with the natives for furs”. Fiske argued for the Hudson being Norumbega.
- ^ Greenleaf, John (1894). The writings of John Greenleaf Whittier. 4. Houghton, Mifflin and company. http://books.google.com/books?id=Ly0AAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA222&lpg=PA222.
External links
- davistownmuseum.org: The Davistown Museum, special-topic bibliographies: Bibliography of Pre-Columbian visitors to North America: The Ancient Dominions of Maine Norumbega Reconsidered and the Wawenoc Diaspora....The Myths of Norumbega Quote: "...The European Discovery of America: The Northern Voyages debunks the 19th century assertion of Norumbega as a Viking name and is the foremost among many historians who assert it is entirely a myth. "Norumbega, apart from the name, which means 'quiet place between two rapids' in Algonkin, was wholly created by European imagination." (pg. 464)..."
- nsexplore.ca: The Defences of Norumbega. Professor Dr Eben Norton Horsford. 1891 Quote: "...was written to advance the view of the author that Norse emigrants from the Greenland colony had founded a settlement near Boston, Massachusetts, dating from the beginning of the 11th century...The book itself has been scanned and made available as a sequence of images..."
- 30-Apr-2002, The Straight Dope: Did Leif Erikson once live in Cambridge, Massachusetts? Quote: "...Around the intersection of Memorial Drive and Mt. Auburn St. there is a granite plaque in the ground, with the following: "On this spot in the year 1000 Lief Erikson built his house in Vinland."...Horsford did a little digging (literally) and found some buried artifacts that he claimed were Norse. On the spot he built the memorial you saw. He didn't stop there..."
- "Vikings on the Charles" Needham Historical Society
Categories:- Mythical lost cities and towns
- Pseudohistory
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
