- Endocerid
Taxobox
name = Endocerid
fossil_range =Ordovician - ?Silurian
regnum =Animal ia
phylum =Mollusca
classis =Cephalopod a
subclassis =Nautiloid ea
ordo = Endocerida
subdivision_ranks = families
subdivision = †Proterocameroceratidae
†Piloceratidae
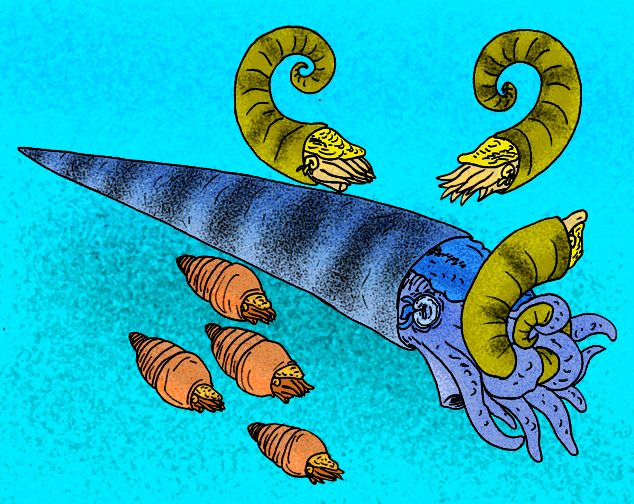
†Endoceratidae The endocerids were a diverse group of
cephalopod s that lived from the EarlyOrdovician possibly to the LateSilurian . Their shells varied in form. Some were straight (orthoconic) others curved (cyrtoconic); some were long (longiconic), others short (breviconic). Some long-shelled forms like "Endoceras" attained lengths as much as 3.5 m (11 ft 8 in). The related "Cameroceras " is anecdotally reported to have reached lengths approaching 9 m (30 feet), but these claims are not unproblematic (Teichert and Kümmel 1960). The overwhelming majority of endocerids and nautiloids in general are much smaller, usually less than a meter long fully grown.Morphology
Endocerids have a relatively small living chamber and a generally large
siphuncle that suggests much of the visceral mass of the animal may have been housed within the siphuncle itself, unlike other nautiloids in which the body is restricted to the body chamber. Endocerids are primarily distinguished however by the presence of calcareous deposits, known as endocones, formed in the more apical portion of the siphuncle and thought to counterweight the animal’s body. The chambers (camerae) of endocerids are always free of organic deposits, unlike other orders such as the Michelinocerida andActinocerida .Extent
Endocerids were among some half a dozen cephalopod orders that appeared in the Lower Ordovician. They reached their greatest diversity during the Lower to Mid-Ordovician, but were already in decline by the middle of this period with most genera becoming extinct by the end of the Ordovician, while some rare hangers on lasted into the Silurian. In any case, the endocerid lineage became completely extinct relatively early on in cephalopod history.
Derivation and Evolution
Endocerids are derived from the earlier ellesmerocerids, most likely from "Pachendoceras" or a similar genus. This ellesmerocerid gave rise to "Proendoceras", the earliest representative of the Proterocameroceratidae and hence of the Endocerida. Endocerids evolved from ellesmerocerids by reduction of siphuncle
diaphragm s and the development of endocones. From that time, in the early middle Lower Ordovician, the Endocerida quickly diversified into different families. Two general evolutionary trends can be recognized. In one lineage, the siphuncle grew more complex, resulting in genera such as "Chihlioceras" and "Allotrioceras ". In the other lineage, over size increased, resulting in such genera as "Endoceras" and "Cameroceras".Taxonomy, Classification
Citing its diversity, Curt Teichert placed the Endocerida in its own cephalopod subclass called Endoceroidea or Endoceratoidea. (Some Russian paleontologists ranked it as a superorder instead). Rousseau Flower rejected this separation on the grounds that endocerids were no more diverse or complex than any other order and considered them simply another order within the Nautiloidea.
The Endocerida have been divided (Flower 1958) into two suborders, the Proterocamerocerina and the Endocerina, which respectively follow the two primary evolutionary trends described above. The Proterocamerocerina includes the Proterocameroceratidae, Manchurocheratidae, and Allotrioceratidae. The Endocerina includes the Piloceratidae and Endoceratidae.
Ecology
Endocerids may have included the superpredators of the Ordovician, probably living close to the sea bottom where they could easily snatch an unwary trilobite or crustacean . They were probably not active nektonic swimmers, but rather crawled over the sea floor or lay there in ambush. They probably filled a different ecological niche than that filled by such as sharks and squid today.
See also
*
Cameroceras
*Nautilus
*Nautiloidea References
Flower, R. H. 1955, Status of Endoceroid Classification; Jour. Paleon. V 29. n.3 May 1955,pp 327-370; figs,plates.
— — — 1958, Some Chazyan and Mohawkian Endoceratida, Jour Paleon V 32,n 2,May 1858, pp 433-458;figs,plates.
— — — 1976, Ordovician Cephalopod Faunas and Their Role in Correlation,in Bassett,M.C.(Ed);The Ordovician System: Proceedings of a Paleontological Association Symposium; Birmingham,Eng.1974;Univ of Wales and Welsh Nat’l Mus Press.
Teichert, C. 1964, Endoceratoidea, in the Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, VolK(Nautiloidea; Geol Soc of America and University of Kansas Press;pp K160–K188; figs.
Teichert, C., and B. Kümmel 1960, Size of Endocerid Cephalopods; Breviora Mus. Comp. Zool. No. 128, 1–7.
* Monks, Neale and Palmer, Philip. "Ammonites". Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington D.C. 2002.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
