- Chlamydia (bacterium)
Taxobox
color = lightgrey
name = "Chlamydia trachomatis"
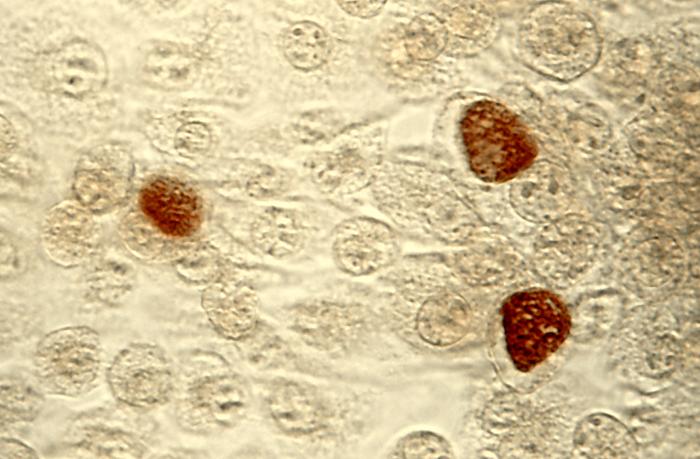
image_width = 200px
image_caption = "C. trachomatis" inclusion bodies (brown) in a McCoy cell culture.
regnum = Bacteria
phylum =Chlamydiae
ordo = Chlamydiales
familia =Chlamydiaceae
genus = "Chlamydia"
subdivision_ranks = Species
subdivision ="
Chlamydia muridarum " "Chlamydia suis " "Chlamydia trachomatis ""Chlamydia" is a
genus ofbacteria in the familyChlamydiaceae , orderChlamydiales , class and phylumChlamydiae .cite book | author = Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) | title = Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th ed. | pages=pp. 463-70| publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | isbn = 0838585299]The three
species in this genus are "Chlamydia trachomatis " (affects onlyhuman s), "Chlamydia suis " (affects only swine), and "Chlamydia muridarum " (affects only mice andhamster s). [cite web |url= http://www.chlamydiae.com/docs/Chlamydiales/diagram/taxondiag.htm|title= www.chlamydiae.com (professional) - Taxonomy diagram|accessdate=2007-10-27 |format= |work=]At one time, this genus also included the species that are presently in the genus, "
Chlamydophila ". In 1999, two clinically relevant species, "Chlamydophila pneumoniae " and "Chlamydophila psittaci " were moved to theChlamydophila genus.Chlamydia infection is the most common bacterialsexually transmitted disease and the leading cause of infectious blindness in the world.Life cycle
"Chlamydiae" are obligate intracellular bacterial pathogens, which means they are unable to replicate outside of a host cell. However, to disseminate effectively, these pathogens have evolved a unique biphasic life cycle wherein they alternate between two functionally and morphologically distinct forms.cite book | author = Becker Y | chapter = Chlamydia | title=Baron's Medical Microbiology (Baron S "et al", eds.)| edition = 4th ed. | publisher = Univ of Texas Medical Branch | year = 1996 | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=mmed.section.2173 | isbn = 0-9631172-1-1 ]
* The elementary body (EB) is infectious, but metabolically inert (much like a spore), and can survive for limited amounts of time in the extracellular milieu. Once the EB attaches to a susceptible host cell, it mediates its own internalization through pathogen-specified mechanisms (via
type III secretion system) that allows for the recruitment ofactin with subsequent engulfment of the bacterium.* The internalized EB, within a membrane-bound compartment, immediately begins differentiation into the "reticulate body (RB)". RBs are metabolically active but non-infectious, and in many regards, resemble normal replicating bacteria. The intracellular bacteria rapidly modifies its membrane-bound compartment into the so-called chlamydial inclusion so as to prevent phagosome-lysosome fusion. According to published data, the inclusion has no interactions with the endocytic pathway and apparently inserts itself into the exocytic pathway as it retains the ability to intercept sphingomyelin-containing vesicles.
To date, no one has been able to detect a host cell protein that is trafficked to the inclusion through the exocytic pathway. As the RBs replicate, the inclusion grows as well to accommodate the increasing numbers of organisms. Through unknown mechanisms, RBs begin a differentiation program back to the infectious EBs, which are released from the host cell to initiate a new round of infection. Because of their obligate intracellular nature, "Chlamydiae" have no tractable genetic system, unlike "
E. coli ", which makes "Chlamydiae" and related organisms difficult to investigate.References
Sources
* [http://www.chlamydiae.com/ Chlamydiae.com]
* [http://knol.google.com/k/hunter-handsfield/chlamydia "Chlamydia" by Hunter Handsfield.]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
