- Filesystem in Userspace
-
Filesystem in Userspace 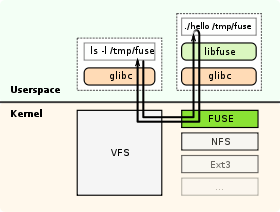
A flow-chart diagram which shows how FUSE worksStable release 2.8.6 / September 13, 2011 Written in C Operating system Unix-like Type File system driver License The kernel part GPL and Libfuse under LGPL. Website http://fuse.sourceforge.net/ Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) is a loadable kernel module for Unix-like computer operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a "bridge" to the actual kernel interfaces.
Released under the terms of the GNU General Public License and the GNU Lesser General Public License, FUSE is free software. The FUSE system was originally part of A Virtual Filesystem (AVFS), but has since split off into its own project on SourceForge.net.
FUSE is available for Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD (as puffs), OpenSolaris, and Mac OS X. It was officially merged into the mainstream Linux kernel tree in kernel version 2.6.14.[1]
Contents
Virtual file system
FUSE is particularly useful for writing virtual file systems. Unlike traditional file systems that essentially save data to and retrieve data from disk, virtual filesystems do not actually store data themselves. They act as a view or translation of an existing file system or storage device.
In principle, any resource available to a FUSE implementation can be exported as a file system.
Examples
- Wuala: A multi-platform, Java-based fully OS integrated distributed file system. Using FUSE, MacFUSE and Callback File System respectively for file system integration, in addition to a Java-based app accessible from any Java-enabled web browser.
- MyVDrive: Fully OS integrated Internet file system using FUSE
- WebDrive: A commercial filesystem implementing WebDAV, SFTP, FTP, FTPS and Amazon S3
- Transmit: A commercial FTP client that also adds the ability to mount WebDAV, SFTP, FTP and Amazon S3 servers as disks in Finder, via MacFUSE.
- ExpanDrive: A commercial filesystem implementing SFTP/FTP/FTPS using FUSE
- GlusterFS: Clustered Distributed Filesystem having capability to scale up to several petabytes.
- SSHFS: Provides access to a remote filesystem through SSH
- FTPFS
- GmailFS: Filesystem which stores data as mail in Gmail
- GAEDrive: A Network Storage based on Google App Engine
- gae-filestore: Virtual File System library on Google App Engine
- GVFS: The virtual filesystem for the GNOME desktop
- EncFS: Encrypted virtual filesystem
- NTFS-3G and Captive NTFS, allowing access to NTFS filesystems
- WikipediaFS: View and edit Wikipedia articles as if they were real files
- Sun Microsystems's Lustre cluster filesystem will use FUSE to allow it to run in userspace, so that a FreeBSD port is possible.[2] However, the ZFS-Linux port of Lustre will be running ZFS's DMU (Data Management Unit) in userspace.[3]
- archivemount
- LoggedFS [1]: Logging of file system access
- HDFS: FUSE bindings exist for the open source Hadoop distributed filesystem.
- mtpfs: mounting MTP devices like Creative Zen music players
- Sector File System: Sector is a distributed file system designed for large amount of commodity computers. Sector uses FUSE to provide a mountable local file system interface.
- CurlFtpFS Filesystem to access FTP/SFTP locations.
- fuse-ext2 An open source ext2/ext3 file system. (Supports Mac OS X 10.4 and later (Universal Binary), using MacFuse)
- Lessfs: inline data de-duplicating filesystem for Linux that includes support for lzo or QuickLZ compression and encryption.
- CloudStore (formerly, Kosmos filesystem): By mounting via FUSE, existing Linux utilities can interface with CloudStore.
- MooseFS: An open source distributed fault-tolerant file system available on every OS with FUSE implementation (Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenSolaris, MacOS X), capable of storing petabytes of data spread over several servers visible as one resource.
- NagusFS: Filesystem representation of Nagios services.
- NagiosFS (http://sourceforge.net/apps/mediawiki/fuse/index.php?title=NetworkFileSystems#NagiosFS): Filesystem representation of remote monitoring values.
- CassandraFS (https://code.launchpad.net/cassandrafs): Filesystem over Cassandra (cassandra.apache.org).
- ZFS: ZFS-Fuse-Linux implementation
- fuse-zip: Allows to use zip files as a filesystem (supports writing)
- OWFS [2] One-Wire File System giving access to 1-Wire devices via a file system directory structure.
- TrueCrypt: a software application used for on-the-fly encryption (OTFE). It can create a virtual encrypted disk within a file as well as encrypt a partition or entire storage device.
- s3fs-FuseOverAmazonS3: A FUSE-based file system backed by Amazon S3. Mount a bucket as a local file system read/write. Store files/folders natively and transparently on AWS: Simple Storage Service.
- s3fs-c: A file system backed by Amazon S3. Forked from s3fs and rewritten to be compatible with some other S3 clients such as AWS Management Console.
- LR|FS [3]: An Mac OS X file system for Adobe Lightroom catalogs. Requires MacFuse.
See also
- 9P the Plan9 operating system file protocol that preceded FUSE that provides many of the same features.
- Installable File System
References
- ^ http://www.linux.com/archive/feature/47839[dead link]
- ^ "Lustre FreeBSD". http://lustre.sev.net.ua/. Retrieved 2008-03-02.
- ^ "Architecture ZFS for Lustre". Sun Microsystems. http://arch.lustre.org/index.php?title=Architecture_ZFS_for_Lustre. Retrieved 2008-03-02.
External links
- FUSE Home Page
- Develop your own filesystem with FUSE by Sumit Singh
- List of FUSE filesystems
- Callback File System - SDK that lets developers create virtual file systems for Windows in user mode
- Fuse for FreeBSD
- MacFUSE
- Dokan Windows user mode file system library
- Documentation/filesystems/fuse.txt documentation in Linux source tree
Categories:- Free special purpose file systems
- Linux kernel features
- User space file systems
- Unix file system-related software
- Free software programmed in C
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
