- Worldwide Governance Indicators
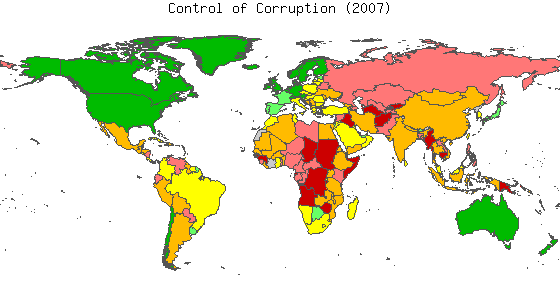
thumb|450px|_2007_World_Map_of_the_Control_of_Corruption_Index,_which_measures_the_degree_to_which_corruption_is_perceived_to_exist_among_businesses,_public_officials_and_politicians.Colors_range_from_dark_green_(90th-100th_percentile ) to light green (75th-90th percentile), yellow (50th-75th percentile), orange (25th-50th percentile), pink (10th-25th percentile) and red (0th-10th percentile). Percentile rank indicates the percentage of countries worldwide that rate below the selected country. Higher values indicate better governance ratings.]Based on a long-standing research program of the
World Bank , the Kaufmann-Kraay-Mastruzzi [http://www.govindicators.org Worldwide Governance Indicators] capture six key dimensions ofgovernance (Voice & Accountability, Political Stability and Lack of Violence,Government Effectiveness, Regulatory Quality, Rule of Law, and Control of Corruption) between 1996 and present. Sometimes referred to as the "KK", "KKZ" or "KKM"indicator s, they measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries, based on close to 40 data sources produced by over 30 different organizations worldwide and are updated on an annual basis since 2002.The governance indicators contribute to the growing empirical research of governance which have provided activists and reformers worldwide with
advocacy tools for policy reform and monitoring. The indicators, and the underlying data behind them, are part of the current research and opinions that have reinforced the experiences and observations of reform-minded individuals in government,civil society , and the private sector, thatgood governance is key for development. [Kaufmann, Daniel and Kraay, Aart, [http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=316861 "Growth Without Governance"] (November 2002). World Bank Policy Research Working Paper No. 2928.] Their growing recognition of the link between good governance and successful development has stimulated demand for monitoring the quality of governance across countries and within individual countries over time. Virtually all of the individual data sources underlying the aggregate indicators are, along with the aggregate indicators themselves, publicly available.The Worldwide Governance Indicators are a compilation of the perceptions of a very diverse group of respondents, collected in large number of
surveys and other cross-countryassessment s of governance. Some of these instruments capture the views of firms, individuals, and public officials in the countries being assessed. Others reflect the views ofNGO s and aid donors with considerable experience in the countries being assessed, while others are based on the assessments of commercial risk-rating agencies.A complementary vision of the macro-level Worldwide Governance Indicators are the
World Bank Governance Surveys , which are country level governance assessment tools developed by theWorld Bank Institute .Countries with governance indicators
The countries presented in the table have a Country Data Report with the summary of the six aggregate governance indicators trends over the last decade, together with all of the publicly-available disaggregated data on which the aggregate indicators are based. Additional information is available at [http://govindicators.org Worldwide Governance Indicators] .
References
External links
* [http://www.govindicators.org Worldwide Governance Indicators] :Worldwide ratings of country performances on six governance dimensions from 1996 to present
* [http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/WBI/EXTWBIGOVANTCOR/0,,contentMDK:21407860%7EpagePK:64168445%7EpiPK:64168309%7EtheSitePK:1740530,00.html Press Releases and Media Coverage]
* [http://info.worldbank.org/governance/wgi2007/resources.htm Relevant Documentation]
* [http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1148386 Governance Matters VII: Aggregate and Individual Governance Indicators for 1996-2007]
* [http://go.worldbank.org/QNX8GPF9T0 Governance Indicators: Where Are We, Where Should We Be Going?] .
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.