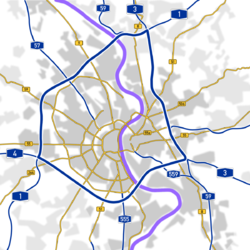
- Cologne Beltway
-
This article is about the Cologne Outer Ring. For the Cologne Inner Ring, see Cologne Ring.
Basic data Total length 50km (31 miles) Bundesland North Rhine-Westphalia Autobahns A 1, A 3, A 4 Exit list Eastring (14 km)

(23) Leverkusen 4-way interchange A 1 E 37 
(24) Leverkusen 
(25) Köln-Mülheim 
(26) Köln-Dellbrück 
(27) Köln-Ost 4-way interchange A 4 E 40 
(28) Heumar 3-way interchange A 4 E 40, A 59 Southring (22 km)

(16) Köln-Ost 4-way interchange A 3 E 35 
(15) Heumar 3-way interchange A 3 E 35, A 59 
(14) Gremberg 4-way interchange A 559 
(13) Köln-Poll 
Rodenkirchener Brücke 
(12) Köln-Süd 4-way interchange A 555 
(—) Containerbahnhof Köln-Eifeltor 
(11) Köln-Klettenberg 
(10) Köln-West 4-way interchange A 1 E 31 North-westring (18 km)
(104) Köln-West 4-way interchange A 4 E 40 
(103) Köln-Lövenich 
(102) Köln-Bocklemünd 
(101) Köln-Nord 4-way interchange A 57 E 31 
(100) Köln-Niehl 
Leverkusener Brücke 
(99) Leverkusen-West 4-way interchange A 59 
(98) Leverkusen 4-way interchange A 3 E 35 The Cologne Beltway (German:Kölner Autobahnring) is the generic term for the Autobahns encircling Cologne. It consists of the Bundesautobahn 3, the Bundesautobahn 4 and the Bundesautobahn 1. The beltway handles one of the highest traffic volumes in Germany.
The Autobahns on the beltway cross Bundesautobahn 559, Bundesautobahn 555 and Bundesautobahn 57. The Bundesautobahn 59 is tied to the beltway at the interchange Leverkusen-West in the north and to Dreieck Heumar in the south.
Contents
History
The beltway was constructed in a clockwise fashion beginning at Leverkusen. In 1936 the section between Leverkusen and Cologne-Mülheim was built as a component of the Autobahn Oberhausen-Wiesbaden and in 1937 the section to Siegburg was finished. Thus today's Ostring (East-Ring) was drivable at that time. In 1941, the Rodenkirchener Autobahnbrücke was completed and the connection between the A 3 and the Autobahn to Bonn (today A 555) was established.
From 1957 to 1960 the Autobahn Cologne-Aachen was finished and the section from Kreuz Köln-Süd to the later Kreuz Köln-West was put into service in 1958. Construction of a second Autobahn-bridge across the Rhine in the north of Cologne began in 1961. At its completion, the beltway could be used along its entire length.
In 1971, the A 1 was extended to the south beyond the Köln-West interchange and in 1974 the A 4 was connected to the A 3 from the east at the Köln-Ost interchange. Since then, the section between interchanges Kreuz Köln-Ost and Dreieck Heumar consists of two Autobahns, the A 3 and the A 4.
Current state
Traffic volume on the Cologne Beltway has been increasing continuously since the 1950s. All sections have since been expanded to three lanes in each direction, but since more than 180,000 cars use at least part of the Autobahnring every day, traffic jams are a frequent occurrence. The section between the interchanges Kreuz Köln-Ost and Dreieck Heumar was expanded to four lanes in each direction in 2005, a first for North Rhine-Westphalia.
In preparation for the 2006 FIFA World Cup the A 3 was outfitted with a traffic management system which is able to route traffic around congestion and construction sites.
"Second Beltway"
In the 1970s, a second beltway around Cologne was considered, incorporating existing Autobahns, instead of expanding the first one to more lanes. An expansion of the old beltway was considered as too expensive because of the large number of bridges. It was planned to incorporate some of Cologne's other Autobahns into this second Autobahnring. These plans were however never implemented.
See also
- List of streets in Cologne
- Transport in Cologne
External links
Categories:- Transport in Cologne
- Roads in North Rhine-Westphalia
- Autobahns in Germany
- Orbital roads in Germany
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.