- Gummarp Runestone
-
Runestone 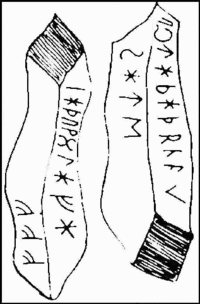
Name Gummarp Runestone Rundata ID DR 358 Country Sweden Region Blekinge City/Village Gummarp Produced 500-700AD Runemaster Unknown
Text - NativeProto-Norse : HaþuwulfR/HaþuwulfaR satte staba þria fff. Text - English Haþuwulfar placed three staves fff. Other resources Runestones - Runic alphabet
Runology - Runestone stylesThe Gummarp Runestone, designated as DR 358, was a runestone from the Vendel era and which was located in the former village of Gummarp in the province of Blekinge, Sweden.
Contents
Description
The Gummarp Runestone was removed and taken to Copenhagen, where it was destroyed in the Copenhagen Fire of 1728.[1] The runic inscription was recorded on reproductions of the runestone. It is classified as being in runestone style RAK.
The runes read: [(h)AþuwolAfA] [sAte] [(s)tA(b)A þr(i)a] [fff]
There are two interpretations of the text. One of them reads "Haþuwulfar placed three staves fff," and the other one assumes that the word apt meaning "after" was originally placed before the name Haþuwulfar which would change the meaning into "In memory of Haþuwulfar [...] placed [these] three staves fff." The three f-runes have been interpreted as being abbreviated charm words for "wealth, wealth, wealth."[1]
The Gummarp, Istaby Runestone and Stentoften Runestone inscriptions can be identified with the same clan through the names that are mentioned on them, and the names are typical for chieftains. The Björketorp Runestone lacks names and is raised some tens of kilometers from the others. However, it is beyond doubt that the Björketorp runestone is connected to them, because in addition to the special runic forms, the same message is given on the Stentoften Runestone.
The name Haþuwulfar has the common Viking Age name element of wulafa meaning "wolf"[2] and heru, which when combined in personal names, means a "host" or "magnitude."[3] It has been suggested that the assignment of such a name is related to ritualistic practices and religious wolf-symbolism used in the initiation of young warriors.[4]
Inscription
A transliteration of the runes into roman letters is:
- §QA [... (h)AþuwolAfA]
- §QB [... sAte]
- §QC [... (s)tA(b)A þr(i)a]
- §QD [fff][5]
See also
References
- ^ a b MacLeod, Mindy; Mees, Bernard (2006). Runic Amulets and Magic Objects. Boydell Press. pp. 112. ISBN 1-84383-205-4. http://books.google.com/books?id=hx7UigqsTKoC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_navlinks_s#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- ^ Looijenga, Tineke (2003). Texts & Contexts of the Oldest Runic Inscriptions. Leiden: Koninklijke Brill NV. pp. 181. ISBN 90-04-12396-2. http://books.google.com/books?id=-edm1fMPbXwC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_navlinks_s#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- ^ Cleasby, Richard; Vigfússon, Guðbrandur (1878). An Icelandic-English Dictionary. Clarendon Press. p. 258. http://books.google.com/books?id=RnEJAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_navlinks_s#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- ^ Gräslund, Anne-Sofie (2006). "Wolves, Serpents and Birds: Their Symbolic Meaning in Old Norse Belief". In Andrén, Anders; Jennbert, Kristina et al. Old Norse Religion in Long-Term Perspectives: Origins, Changes, and Interactions. Lund: Nordic Academic Press. pp. 124–129. ISBN 91-89116-81-X. http://books.google.com/books?id=gjq6rvoIRpAC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_navlinks_s#v=onepage&q=&f=false. p. 125.
- ^ Project Samnordisk Runtextdatabas Svensk - Rundata.
Categories:- Haþuwulf's runestones
- Proto-Norse
- Runestones in Blekinge
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
