- USS Lindsey (DM-32)
-
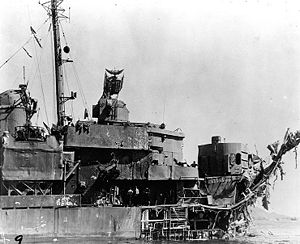
View of extensive damage to the ship's forward hull and superstructure, received when she was struck by two Kamikaze planes off Okinawa on 12 April 1945.Career 
Builder: Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation, San Pedro, California Laid down: 12 September 1943 Launched: 5 March 1944 Commissioned: 20 August 1944 Decommissioned: 25 May 1946 Struck: 1 October 1970 General characteristics Class and type: Robert H. Smith-class destroyer Displacement: 2,380 tons Length: 376 ft 6 in (114.76 m) Beam: 40 ft 10 in (12.45 m) Draught: 18 ft 10 in (5.74 m) Speed: 34 kts Complement: 363 officers and enlisted Armament: 6 5", 12 40 mm. USS Lindsey (DD-771/DM-32/MMD-32) was a Robert H. Smith-class destroyer minelayer in the United States Navy during World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War. She was named for Eugene E. Lindsey.
Lindsey was laid down as DD-771 12 September 1943 by Bethlehem Steel Company, San Pedro, California; launched 5 March 1944; sponsored by Mrs. Eugene E. Lindsey, widow of Lt. Comdr. Lindsey; reclassified DM-32 19 July 1944; and commissioned 20 August 1944, Commander T. E. Chambers in command.
After shakedown off southern California, the new destroyer minelayer sailed from San Francisco 25 November 1944 via Pearl Harbor for Ulithi, arriving 3 February 1945. Underway from Ulithi the morning of 8 February, Lindsey steamed toward Iwo Jima. Operating off Iwo 17 to 19 February, Lindsey knocked out six guns ashore and provided covering fire as minesweepers cleared the harbor. On the 23d she returned to Ulithi to prepare for landings on Okinawa.
Underway 19 March, Lindsey arrived off Okinawa 24 March and swept the harbor for the inbound transports. Then as the marines gained a foothold, the ship bombarded Japanese gun installations and transferred wounded soldiers to hospital ships. On the afternoon of 12 April, Lindsey experienced a mass kamikaze attack. Her gunners scored repeated hits on seven onrushing dive bombers, but two “Vals”, damaged and out of control, crashed Lindsey killing 57 sailors and wounding 57 more. The explosion from the second Val ripped some 60 feet off her bow. Only the “all back full” ordered by Commander Chambers prevented the pressure of inrushing water from collapsing the fireroom bulkhead and sinking the ship.
Towed to Kerama Retto the same night, Lindsey remained in the lagoon for 2 weeks repairing battle damage. On 28 April she departed under tow for Guam, where, after arrival 6 May, she received a temporary bow. She sailed under her own power 8 July for the east coast via Pearl Harbor and the Panama Canal, arriving Norfolk, Virginia 19 August 1945.
After extensive repairs at the Norfolk Naval Shipyard, Lindsey steamed 6 March 1946 for Charleston, South Carolina, and arrived the next day. Lindsey decommissioned 25 May 1946 and entered the Atlantic Reserve Fleet. She was struck from the Naval Vessel Register on 1 October 1970.
Lindsey received two battle stars for World War II.
As of 2006, no other ship in the United States Navy has been named Lindsey.
References
This article includes text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships.
External links
- Photo gallery at Navsource.org
- Photo gallery at Naval Historical Center
Robert H. Smith · Thomas E. Fraser · Shannon · Harry F. Bauer · Adams · Tolman · Henry A. Wiley · Shea · J. William Ditter · Lindsey · Gwin · Aaron Ward
List of destroyers of the United States Navy · List of destroyer classes of the United States NavyCategories:- Robert H. Smith class destroyers
- Ships built in Los Angeles, California
- 1944 ships
- Ships damaged by kamikaze attack
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
