- Orionids
-
 An Orionid meteor streaking across the sky below the Milky Way and to the right of Venus. The zodiacal light can also be seen in the image.
An Orionid meteor streaking across the sky below the Milky Way and to the right of Venus. The zodiacal light can also be seen in the image.
The Orionid meteor shower, usually shortened to the Orionids, is the most prolific meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet. The Orionids are so-called because the point they appear to come from, called the radiant, lies in the constellation Orion. Orionids are an annual meteor shower which last approximately one week in late-October. In some years, meteors may occur at rates of 50-70 per hour.[1][2]
Contents
History
Meteor showers first designated "shooting stars" were connected to comets in the 1800s.[3] E.C. Herrick made an observation in 1839 and 1840 about the activity present in the October night skies. However A.S. Herschel produced the first documented record which produced accurate forecasts for the next meteor shower.[4] The Orionid meteor shower is produced by the well-known Halley's Comet, which was named after the astronomer Edmund Halley and last passed through the inner solar system in 1986 on its 75-to-76-year orbit.[5] When the comet passes through the solar system, the sun melts some of the ice which allows rock particles to break away from the comet. These particles continue on the comet's trajectory and appear as meteors or "falling stars" when they pass through Earth's upper atmosphere.[3][6] Halley's comet is also responsible for creating the Eta Aquariids which occur annually in May.[6]
Year Activity Date Range Peak Date 1839 October 8–15[4] 1864 October 18–20[4] 1981 October 18–21[4] October 23 (ZHRmax 20) 1984 October 21–24[4] October 21–24 (flat maximum) 2006 October 2 – November 7[7][4] October 21–24 (ZHRmax 23 with peaks at 67)[7][8] 2007 October 20–24[9] October 21 (predicted)[9] 2008 October 15–29[6] October 20–22 (predicted)[6] 2009 October 18–25 [4] October 22[10][11][12] * This meteor shower may give double peaks as well as plateaus, and time periods of flat maximums lasting several days.[4]
Meteor shower and location
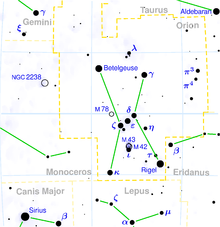
The radiant of the Orionids is located between the constellations Orion and Gemini (in the south-eastern sky before dawn, as viewed from mid-northern latitudes.[13][14] The most active time of the meteor shower was stated by Telegraph.uk.co to be in the early morning of October 21, 2009 6 a.m. Eastern Standard Time in the United States or 11 a.m. in the United Kingdom. Tweets and user news articles were shared on Social networking and micro-blogging services such as Twitter and Yahoo! Buzz. Photos and videos of the event were posted on photo and video sharing websites such as YouTube and Flickr.[15] Universe Today reported that the meteor shower arrived at 140,000 miles (230,000 km) per hour on the morning of the 21 when showing was predicted to be at its height, however compared to previous showers in years past, the trail of 2009 appeared narrower without branching out.[16] Cooke, found that the originating points of 30 meteors were from within a very small area of the Orion constellation even though observers observing the small meteor "Halleyids" at Alabama's Space Flight Center saw streaks radiating in all directions with the naked eye.[17]
Gallery
-
Two Orionids and the Milky Way.
See also
External links
- Worldwide viewing times for the 2011 Orionids meteor shower
- Spaceweather.com: 2009 Orionid Meteor Shower photo gallery: Page 1
- realclearwx.com: 2009 Orionid Meteor Shower Photos and Video
References
- ^ "IMO Meteor Shower Calendar 2009". The International Meteor Organization. 1997–2009. http://www.imo.net/calendar/2009#ori. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- ^ "Orionids Meteor Shower Lights Up the Sky". PhysOrg.com. 2003–2009. http://www.physorg.com/news175364339.html. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
- ^ a b Jaggard, Victoria (1996–2009). "Orionids Meteor Shower Starts This Weekend". National Geographic News. National Geographic Society. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2009/10/091016-orionids-meteor-shower-halleys-comet.html. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Orionid". Observing the Orionids. Meteor Showers Online. http://meteorshowersonline.com/orionids.html. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
- ^ Phillips, Dr. Tony (2009-10-19). "NASA – The 2009 Orionid Meteor Shower". NASA. http://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2009/19oct_orionids.htm. Retrieved 2009-10-19.
- ^ a b c d "Orionids Meteor Shower 2008 of October". Meteor. October 15, 2008. http://www.meteorblog.com/2008/10/meteor-shower-2008-orionids-october/. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
- ^ a b "October to December 2006". The International Meteor Organization -. 1997–2007. http://www.imo.net/calendar/2006/fall. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- ^ Stone, Wes. "2006 Orionid Meteor Shower Surprise!". Sky tour. http://skytour.homestead.com/files/ORI2006.pdf. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- ^ a b Handwerk, Brian (October 17, 2009). ""Old Faithful" Orionid Meteor Shower Peaks This Weekend". r National Geographic News. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2007/10/071016-orionid-meteor.html. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- ^ Orionids 2009
- ^ Jaggard, Victoria (October 20, 2009). "2009 Orionid Meteor Shower Peak Begins". National Geographic News. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2009/10/091020-2009-orionids-meteor-shower-peak.html. Retrieved 2009-10-20.
- ^ French, John. "Abrams Planetarium Night Sky Notes". http://www.pa.msu.edu/abrams/nightskynotes/index.php. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
- ^ "Observing the Orionids". Meteor Showers Online. http://meteorshowersonline.com/orionids.html. Retrieved 2009-10-19.
- ^ "Okanagan Observatory's Notes". Okanagan Observatory. 2009. http://www.facebook.com/notes.php?id=104026432182. Retrieved 2009-10-021.
- ^ Collins, Nick (October 21, 2009). "Meteor shower: Orionids reach peak The Orionid meteor shower, a trail of debris left in space by Halley's Comet, was at its most intense in the early hours of Wednesday.". Telegraph.co.uk. Telegraph Media Group Limited. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/space/6396173/Meteor-shower-Orionids-reach-peak.html. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
- ^ Piotner, Tammy (2009-10-21). "The Orionid Meteor Shower – What Did You See?". Universe Today. http://www.universetoday.com/2009/10/21/the-orionid-meteor-shower-what-did-you-see/. Retrieved 2009-10-21.[dead link]
- ^ "SpaceWeather.com – News and information about meteor showers, solar flares, auroras, and near-Earth asteroids". Meteor Shower Update: The Orionid meteor shower is subsiding. Spaceweather.com. http://spaceweather.com/. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
Categories:- Meteor showers
- October
- Halley's Comet
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.