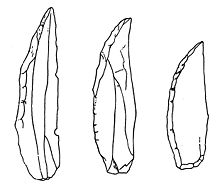
- Châtelperronian
-
Subdivisions of the Quaternary Period System Series Stage Age (Ma) Quaternary Holocene 0–0.0117 Pleistocene Tarantian (Upper) 0.0117–0.126 Ionian (Middle) 0.126–0.781 Calabrian (Lower) 0.781–1.806 Gelasian (Lower) 1.806–2.588 Neogene Pliocene Piacenzian older In Europe and North America, the Holocene is subdivided into Preboreal, Boreal, Atlantic, Subboreal, and Subatlantic stages of the Blytt-Sernander time scale. There are many regional subdivisions for the Upper or Late Pleistocene, usually these represent locally recognized cold (glacial) and warm (interglacial) periods. The last glacial period ends with the cold Younger Dryas substage. Châtelperronian was the earliest industry of the Upper Palaeolithic in central and south western France, extending also into Northern Spain. It derives its name from the site of la Grotte des Fées, in Châtelperron, Allier, France.
It arose from the earlier, Mousterian industry. It made use of the Levallois technique of lithic reduction (stone-knapping) and lasted from between c. 35,000 and c. 29,000 BP. The industry produced denticulate, or toothed, stone tools and also a distinctive flint knife with a single cutting edge and a blunt, curved back. The use of ivory at Châtelperronian sites tends to be more frequent than that of the later Aurignacian,[1] while antler tools appear to be absent.
It was superseded by the Aurignacian industry around 29,000 BP. Controversy exists as to how far archaeologically it is associated with Neanderthal people.[2][3] The Châtelperronian industry may relate to the origins of the very similar Gravettian culture. French archaeologists have traditionally classified both cultures together under the name Périgordian, Early Perigordian being equivalent to Châtelperronian and all the other phases corresponding to Gravettian,[4][5][6] though this scheme is not often used by Anglophone authors.
Contents
Lithic production and associations
Large thick flakes/small blocks were used for cores, and were prepared with a crest over a long smooth surface. Using one or two striking points, long thin blades were detached. Direct percussion with a soft hammer was likely used for accuracy. Thicker blades made in this process were often converted into side scrapers, burins were often created in the same manner from debitage as well.
The quality of tools produced is uncharacteristic of the earlier Mousterian industries that are associated with Neanderthals, this industry is more "modern" than other industries in the Middle Paleolithic. However, the manner of production is a solid continuation of the Mousterian, the ivory adornments found in association seem to be a more clear connection to Aurignacian peoples,[1] who are often argued to be the earliest introduction of H. sapiens sapiens into Europe. The technological refinement of the Châtelperronian and neighboring Uluzzian in Central-Southern Italy is often argued to be the product of cultural influence from H. sapiens sapiens that lived nearby, but these predate both the Aurignacian and the earliest presence of H. sapiens sapiens in Europe.
Dispute over disruption of the site
João Zilhão and colleagues argue that the findings are complicated by disturbance of the site in the 19th century, and conclude that the apparent pattern of Aurignacian/Châtelperronian inter-stratification is an artifact of disturbance.[7][8] Paul Mellars and colleagues have criticized Zilhão et al.'s analysis, and argue that the original excavation by Delporte was not affected by disturbance.[9] Paul Mellars, however, now has concludeed on the basis of new radiocarbon dating on the cave of Grotte du Renne [2] "that there was strong possibility—if not probability— that they were stratigraphically intrusive into the Châtelperronian deposits from .. overlying Proto-Aurignacian levels" and that "The central and inescapable implication of the new dating results from the Grotte du Renne is that the single most impressive and hitherto widely cited pillar of evidence for the presence of complex “symbolic” behavior among the late Neanderthal populations in Europe has now effectively collapsed."[3]
In popular culture
Author Jared Diamond argues in his 1991 non-fiction book, The Third Chimpanzee, that Châtelperron may represent a community of Neanderthals who had to some extent adopted the culture of the modern Homo sapiens that had established themselves in the surrounding area, which would account for the signs of a hybrid culture found at the site. Diamond compares these hypothetical Neanderthal hold-outs to more recent Native Americans in North and South America who adopted European technologies such as firearms or domestication of horses in order to survive in an environment dominated by technologically more-advanced competitors.[10]
The fifth book of Jean Auel's Earth's Children series, The Shelters of Stone, 2002, is set in this region of modern day France, during this period.
See also
Preceded by
MousterianChâtelperronian
35,000–29,000 BPSucceeded by
AurignacianReferences
- ^ a b d'Errico, F.D., Zilhao, J., Julien, M., Baffier, D. and Pelerin, J. 1998. Neanderthal Acculturation in Western Europe? A Critical Review of the Evidence and it's Interpretation. Current Anthropology Supplement to 39: S1-S44
- ^ a b Higham T, Jacobi R, Julien M, David F, Basell L, Wood R, Davies W, Ramsey CB.C (2010). Chronology of the Grotte du Renne (France) and implications for the context of ornaments and human remains within the Chatelperronian. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. doi:10.1073/pnas.1007963107 PMID 20956292
- ^ a b Mellars P. (2010). Neanderthal symbolism and ornament manufacture: The bursting of a bubble? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014588107
- ^ F. Jordá Cerdá et al., Historia de España 1. Prehistoria. Gredos ed. 1986. ISBN 84-249-1015-X
- ^ X. Peñalver, Euskal Herria en la Prehistoria. Orain ed. 1996. ISBN 84-89077-58-4
- ^ M.H. Alimen and M.J. Steve, Prehistoria. Siglo XXI ed. 1970. ISBN 84-323-0118-3
- ^ Zilhão, João; Francesco d’Errico, Jean-Guillaume Bordes, Arnaud Lenoble, Jean-Pierre Texier, and Jean-Philippe Rigaud (2006). "Analysis of Aurignacian interstratification at the Châtelperronian-type site and implications for the behavioral modernity of Neandertals". PNAS 103 (33): 12643–12648. Bibcode 2006PNAS..10312643Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605128103. PMC 1567932. PMID 16894152. http://www.pnas.org/content/103/33/12643.full.
- ^ Zilhão, João; et al. (2008). "Like Hobbes’ Chimney Birds". PaleoAnthropology: 65−67. http://paleoanthro.org/journal/content/PA20080065.pdf.
- ^ Mellars, Paul; Brad Gravina, and Christopher Bronk Ramsey (2007). "Confirmation of Neanderthal/modern human interstratification at the Chatelperronian type-site". PNAS 104 (9): 3657–3662. Bibcode 2007PNAS..104.3657M. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608053104. PMC 1805566. PMID 17360698. http://www.pnas.org/content/104/9/3657.full.
- ^ F. Jared Diamond, The Third Chimpanzee: The Evolution and Future of the Human Animal Harper Perennial. 2006. ISBN 978-0060845506
External links
- Picture Gallery of the Paleolithic (reconstructional palaeoethnology), Libor Balák at the Czech Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Archaeology in Brno, The Center for Paleolithic and Paleoethnological Research
Categories:- Archaeological cultures
- European archaeology
- Stone Age Europe
- Upper Paleolithic
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.