- Lophius piscatorius
image_width = 240px
regnum =Animal ia
phylum =Chordata
classis =Actinopterygii
ordo =Lophiiformes
familia =Lophiidae
genus = "Lophius "
species = "L. pisctorius"
binomial = "Lophius piscatorius"
binomial_authority = Linnaeus, 1758The angler, also sometimes called fishing-frog, frog-fish or sea-devil, "Lophius piscatorius", is amonkfish in the familyLophiidae . It is found in coastal waters of the northeastAtlantic , from theBarents Sea to theStrait of Gibraltar , theMediterranean and theBlack Sea .External anatomy
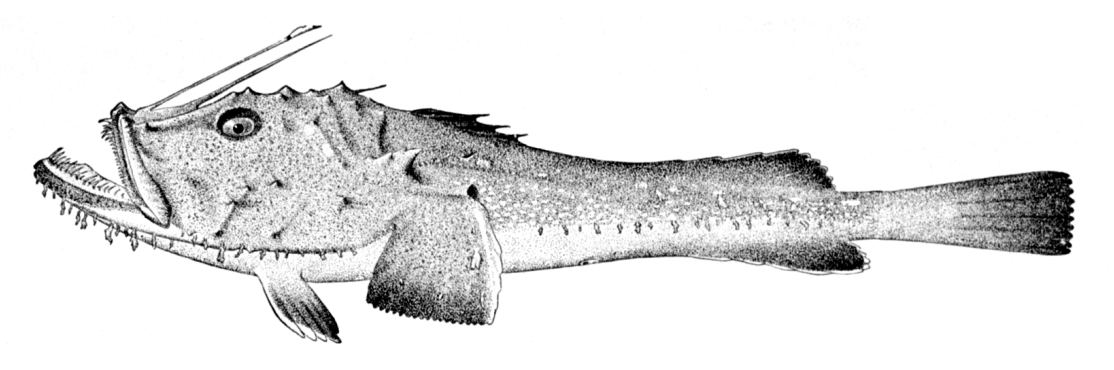
It has a very large head which is broad, flat and depressed; the rest of the body appears to be a mere appendage. The wide mouth extends all the way around the anterior circumference of the head, and both jaws are armed with bands of long pointed
teeth . These are inclined inwards, and can be closed so as to offer no impediment to an object gliding towards the stomach, but to prevent its escape from the mouth. It has only one eye.The pectoral and
pelvic fin s are so articulated as to perform the functions of feet, so that the fish is able to walk along the bottom of the sea, where it generally hides itself in thesand or amongstseaweed . All round its head and also along the body the skin bears fringed appendages resembling short fronds of seaweed, a structure which, combined with the extraordinary faculty of assimilating the colour of the body to its surroundings, assists this fish greatly in camouflaging itself in the places which it selects on account of the abundance of prey.Female anglers grow to a length of more than 2 m.
Angling
The fish also has three long filaments along the middle of its head, which are, in fact, the detached and modified three first spines of the anterior
dorsal fin . The filament most important to the angler is the first, which is the longest, terminates in alappet , and is movable in every direction. The angler is believed to attract other fishes by means of its lure, and then to seize them with its enormous jaws. It is probable enough that smaller fish are attracted in this way, but experiments have shown that the action of the jaws is automatic and depends on contact of the prey with the tentacle. Its stomach is expandable and it is not unknown for these fish to swallow prey of its own size.Lifecycle
The spawn of the angler is very remarkable. It consists of a thin sheet of transparent gelatinous material 2 or 3 feet broad (60–90 cm) and 25 to 30 feet (8 or 9 metres) in length. The eggs in this sheet are in a single layer, each in its own little cavity. The spawn is free in the sea. The
larva e are free-swimming and have thepelvic fin s elongated into filaments.References
*
*
*
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.