- International maritime signal flags
-
The system of international maritime signal flags is one system of flag signals representing individual letters of the alphabet in signals to or from ships. It is a component of the International Code of Signals (INTERCO).[1]
Contents
Overview
There are various methods by which the flags can be used as signals:
- each flag spells an alphabetic message, letter by letter.
- individual flags have specific and standard meanings[2]; for example, diving support vessels raise the "A flag" indicating their inability to move from their current location because they have a diver underwater.
- one or more flags form a code word whose meaning can be looked up in a code book held by both parties. An example is the Popham numeric code used at the Battle of Trafalgar.
- in yacht racing and dinghy racing, flags have other meanings; for example, the P flag is used as the "preparatory" flag to indicate an imminent start, and the S flag means "shortened course" (for more details see Race Signals).
NATO uses the same flags, with a few unique to warships, alone or in short sets to communicate various unclassified messages. The NATO usage generally differs from the International meanings, and therefore warships will fly the Code/Answer flag above the signal to indicate it should be read using the International meaning.
During the allied occupations of Axis countries after World War II, use and display of those nations' national flags were banned. In order to comply with the international legal requirement that a ship identify its registry by displaying the appropriate national ensign, swallow-tailed versions of the C, D, and E signal flags were designated as, respectively, provisional German, Okinawan, and Japanese civil ensigns. Being swallowtails, they are commonly referred to as the "C-Pennant" (C-Doppelstander), "D-Pennant", and "E-Pennant".
Letter flags (with ICS meaning)
-
A (Alfa)"I have a diver down; keep well clear at slow speed."
With three numerals, azimuth or bearing. -
B (Bravo)"I am taking in, or discharging, or carrying dangerous goods." (Originally used by the Royal Navy specifically for military explosives.)
-
E (Echo)"I am altering my course to starboard."** Crew at meals
-
I (India)"I am altering my course to port."**
-
L (Lima)In harbour: "The ship is quarantined."
At sea: "You should stop your vessel instantly."
With four numerals, latitude. (The first two denote degrees and the rest minutes.) -
O (Oscar)"Man overboard."** (often attached to the man overboard pole on boats).
With a sinister hoist, the semaphore flag. -
Q (Quebec)"My vessel is 'healthy' and I request free pratique."
-
T (Tango)"Keep clear of me; I am engaged in pair trawling."
With four numerals, local time. (The first two denote hours and the rest minutes.) -
Z (Zulu)"I require a tug."
When made by fishing vessels operating in close proximity on the fishing grounds it means: "I am shooting nets."
With one or more numerals, time (UTC). (The first two denote hours and the rest minutes.)***
* ^ N and C together (No and Yes) is used as a distress signal.
** Also signallable on a ship's whistle using Morse code. See International Code of Signals.
*** The Z flag was also famously hoisted by Adm. Heihachiro Togo at the 1905 Battle of Tsushima as the Japanese fleet prepared to engage the Russian fleet. In Japanese coding at the time, the flag meant, "The Empire's fate depends on the result of this battle, let every man do his utmost duty."
Substitute
Substitute or repeater flags allow messages with duplicate characters to be signaled without the need for multiple sets of flags.
The four NATO substitute flags are as follows:

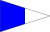


First substitute Second substitute Third substitute Fourth substitute To illustrate their use, here are some messages and the way they would be encoded:
"N" 
"O" 
"NO" 

"NON" 


"NOO" 


"NOON" 



"NONO" 



"NONON" 




"NONNN" 




See also
- Character encoding
- Day shapes
- Diver down flag
- England expects that every man will do his duty
- Flag of Germany after World War II (C-Pennant)
- Flag semaphore
- Heliograph
- International Code of Signals
- List of international common standards
- NATO phonetic alphabet
- Signal lamp
References
- ^ International Marine Signal Flags
- ^ AB Nordbok. "The Lore of Ships", page 138. New York: Crescent Books, 1975.
External links
- "How Ships Talk With Flags", October 1944, Popular Science
- John Savard's flag page. Collection of different flag systems.
- Freeware to aid memorizing the flags
- La flag-alfabeto - signal flags used for the Esperanto language - the flags for the Esperanto letters with diacritical marks have the lighter color in the normal flag replaced with light green, which is not used in any normal flag.
Telecommunications (general) History Beacons · Broadcasting · Computer networks · Drums · Electrical telegraphy · Fax · Heliography · Hydraulic telegraphs · Internet · Mass media · Mobile phones · Optical telegraphy · Photophone · Radio · Radiotelephone · Satellite communications · Telegraphy · Telephones · Telephone patent controversies · Television · Undersea telegraph lines · Videophones
Pioneers Alexander Graham Bell · Alfred Vail · Alexander Popov · Charles Wheatstone · Claude Chappe · Edwin Armstrong · Elisha Gray · Guglielmo Marconi · Jagadish Bose · Johann Philipp Reis · John Logie Baird · Lee De Forest · Nikola Tesla · Philo Farnsworth · Reginald Fessenden · Tim Berners-Lee · Vint Cerf · Vladimir ZworykinMediums Coaxial cable · Free-space optical · Landlines · Optical fiber · Radio waves · Terrestrial microwaveNetworks Advanced Research Projects Agency · BITNET · Ethernet · FidoNet · ISDN · Internet · Local area · Mobile/Cellular · NGN · Packet switched · Public Switched Telephone · Radio · Television · Telex · Wide area · World Wide Web · WirelessGeographic Telecommunications in Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Telecommunications in North America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Navassa Island
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
Telecommunications in South America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territoriesTelecommunications in Oceania Sovereign states - Australia
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Fiji
- Indonesia
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
Telecommunications in Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Telecommunications in Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territories- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Hong Kong
- Macau
Categories:- Flags
- Latin-alphabet representations
- Nonverbal communication
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

























