- Rumpler Taube
Infobox Aircraft
name = Rumpler Taube
type = Fighter, Bomber, Surveillance, and Trainer
manufacturer = Various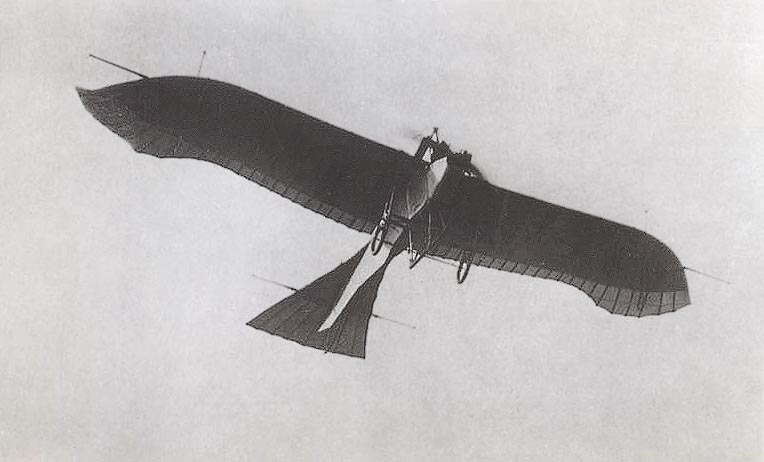
caption =
designer =Igo Etrich
first flight = 1910
introduced =
retired =
status =
primary user = "Luftstreitkräfte "
more users =
produced =
number built =
unit cost =
variants with their own articles = The Rumpler Taube (German, dove) is a pre-World War I monoplane aircraft, and the first mass produced military plane inGermany . Being the Germans' first practical military plane, it was used for all common military aircraft applications, including as a fighter,bomber , surveillance plane and trainer from its first flight in 1910 until the beginning ofWorld War I . Due to the rapid advancement ofaviation during the war, the design was obsolete by the end of 1914. The plane was very popular and was used by the air forces ofItaly ,Germany andAustria-Hungary .Design and development
The plane was developed by
Igo Etrich fromAustria in 1909, with the first flight in 1910, and was called the "Etrich Taube". The design was licensed for serial production by Lohner in Austria and Rumpler in Germany, and called the "Etrich-Rumpler-Taube". However, Rumpler soon changed the name to "Rumpler-Taube", and stopped paying royalties to Etrich. Etrich subsequently abandoned his patent.Despite its name, the "Taube" was not modeled after a bird, but after the Zanonia macrocarpa seeds, which glide to the ground in a slow spin induced by a single wing. Similar wing shapes have also been used by
Karl Jatho . While Etrich had tried to build a flying wing aircraft based on theZanonia wing shape, the conventional "Taube" was much more successful.Most notably, the plane did not have
aileron s in the wings. Instead, the pilot turned the plane by warping the wings (effectively providing the same functionality as ailerons) and using the elevators at the rear of the tail.Operational history
The design provided for very stable flight, suitable for observation. In addition, the translucent wings made it difficult for ground based observers to detect a "Taube" at an altitude above 400m. The French called it "the Invisible Aircraft", and it is sometimes also referred to as the "world's first stealth plane". The first hostile engagement was an Italian "Taube" in 1911 in
Libya , using pistols and 2 kg bombs. "Taube" airplanes were able to detect the advancing Russian army during theBattle of Tannenberg (1914) . The plane was also used for bombing, when the pilot dropped small bombs in theBalkans in 1911 and 3 kg bomblets andpropaganda leaflets overParis in 1914.DuringWorld War I , Imperial German units stationed atQingdao ,Shandong ,China only had one operational airplane, a Rumpler Taube piloted byLieutenant Gunther Plutschow facing the attacking Japanese who had a total of eight airplanes. OnOctober 2 ,1914 , the Rumpler Taube attacked Japanese warships with two small bombs but did not score any hits. OnNovember 7 ,1914 , shortly before the fall of Qingdao, Lieutenant Plutschow was ordered to fly top secret documents toShanghai but was forced to make an emergency landing atLianyungang where the lieutenant and his Rumpler Taube were both interned by a local Chinese force. Plutschow was rescued by local Chinese civilians under the direction of an American missionary, and successfully reached his destination at Shanghai with his top secret documents, after he gave the engine to one of the Chinese civilians who rescued him and burnt the engine-less Rumpler Taube.Poor rudder and lateral control made this plane difficult and slow to turn. Subsequently the plane was a very easy target for the faster and more mobile enemy planes at the beginning of World War I. Therefore, six months into the war, the "Taube" was removed from the front lines and instead used to train new pilots. Consequently many famous pilots learned how to fly using a "Taube".
Variants
Due to the lack of license fees, a total of no less than 14 companies built a large number of variations of the initial design, making it difficult for historians to determine the exact manufacturer based on historical photographs. An incomplete list is shown below. The most common version was the "Rumpler Taube" with two seats.
;Albatros Taube:Produced by the
Albatros Flugzeugwerke ;Albatros Doppeltaube:Biplane version produced by the Albatros Flugzeugwerke.;Aviatik Taube:Produced by the Aviatik.;DFW Stahltaube (Stahltaube):Version with a steel frame.;Etrich Taube:Produced by the inventor Igo Etrich.;Etrich-Rumpler-Taube:Initial name of the "Rumpler Taube".;Gotha Taube:Produced by theGothaer Waggonfabrik as the LE.1, LE.2 and LE.3 ("Land Eindecker" - "Land Monoplane") and designated A.I by the Idflieg;Harlan Pfeil Taube;Halberstadt Taube III:Produced by the Halberstadt.;Jeannin Taube (Jeannin Stahltaube):Version with a steel frame.;Kondor Taube:Produced by the Kondor.;Lüdemann Taube:Produced by the Lüdemann.;RFG Taube:Produced by the Reise- und Industrieflug GmbH (RFG).;Roland Taube;Rumpler-Taube:Produced by Edmund Rumpler, Luftfahrzeugbau.;Rumpler Delfin-Taube (Rumpler Kabinentaube "Delfin"):Version with a closed cabin, produced by Edmund Rumpler, Luftfahrzeugbau.Operators
;China as ROC
*Two units were ordered by Chinese revolutionaries to fight Imperial Qing China, but when the they reachedShanghai in December, 1911 with other Rumpler Taube airplanes ordered by Imperial German forces stationed in China, the Imperial Qing dynasty had already been overthrown and the airplanes did not have the opportunity to participate in the battle.;flag|Austria-Hungary
*Austro-Hungarian Imperial and Royal Aviation Troops ;flag|German Empire
*"Luftstreitkräfte ";flag|Italy|1861;flag|Norway
*Royal Norwegian Navy Air Service pecifications (Rumpler Taube)
aircraft specifications
plane or copter?=plane
jet or prop?=prop
ref=
crew=two
capacity=
payload main=
payload alt=
length main= 9.9 m
length alt= 33.5 ft
span main= 14.3 m
span alt= 45.83 ft
height main= 3.2 m
height alt= 10.5 ft
area main= 32.5 m²
area alt= 280 ft²
airfoil=
empty weight main= 650 kg
empty weight alt= 950 lb
loaded weight main=
loaded weight alt=
useful load main=
useful load alt=
max takeoff weight main= 850 kg
max takeoff weight alt= 1,200 lb
more general=
engine (prop)= 4-cylinder Argus or 6-Cylinder Mercedes Typ E4F
type of prop=
number of props=1
power main= 74 kW
power alt= 99 hp
power original=
max speed main= 100 km/h
max speed alt= 60 mph
cruise speed main=
cruise speed alt=
stall speed main=
stall speed alt=
never exceed speed main=
never exceed speed alt=
range main= 140 km
range alt= 86 miles
ceiling main= 2,000 m
ceiling alt= 10,000 ft
climb rate main=
climb rate alt=
loading main=
loading alt=
thrust/weight=
power/mass main=
power/mass alt=
more performance=
armament=
* Rifles and pistols
* Hand dropped bombs
avionics=ee also
* The Rumpler Taube has recently been selected as a main motif for an euro collectors' coin, the Austrian Aviation commemorative coin, minted in
February 28 2007 . This reverse side of the coin shows the Rumpler Taube as well as the “Zanonia ” glider and a wavingIgo Etrich sitting in the open cockpit of a plane.aircontent
related=
similar aircraft=
sequence=
lists=
see also=
*Aviation history
*Aircraft References
* [http://www.ctie.monash.edu.au/hargrave/etrich_taube.htm Erich Taube]
* [http://www.members.shaw.ca/flyingaces/archive1.htm Rosebud's Archive with many Photos]
* [http://www.ohtm.org/etrich.html Owl's Head Transportation Museum-flyable reproduction 1913 Etrich Taube]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
