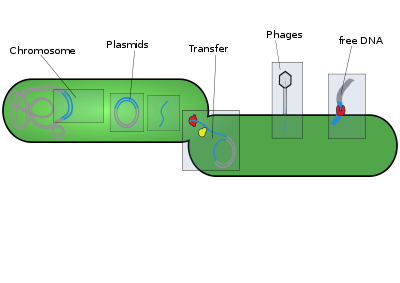
- Mobile genetic elements
-
Mobile genetic elements (MGE) are a type of DNA that can move around within the genome. They include:
- Transposons (also called transposable elements)
- Retrotransposons
- DNA transposons
- Insertion sequences
- Plasmids
- Bacteriophage elements, like Mu, which integrates randomly into the genome
- Group II introns
The total of all mobile genetic elements in a genome may be referred to as the mobilome.
Barbara McClintock was awarded the 1983 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for her discovery of mobile genetic elements".[1]
See also
References
- Miller, W. J.; Capy, P., eds. (2004), Mobile genetic elements : protocols and genomic applications, Humana Press, ISBN 1-58829-007-7.
- Shapiro, J.A., ed. (1983), Mobile genetic elements, Academic Press, ISBN 0-12-638680-3.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1983". nobelprize.org. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1983/. Retrieved 14 July 2010.
Genetics: homologous recombination / mobile genetic elements Primarily prokaryotic Occurs in eukaryotes B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°) Categories: - Transposons (also called transposable elements)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.